
Facts about Mast Cell Tumors Dog Owners Should Know Dog Discoveries
A mast cell tumour (MCT) is the most common malignant skin tumour in dogs. In fact, it is estimated that up to 20% of skin masses in dogs are actually MCTs. They are normally found in the body and are most often found on your dog's skin either on the surface or underneath.

What Does A Mast Cell Tumor Look Like On A Dog
Clinical Signs of Mast Cell Tumor in Dogs. Mast cell tumors in dogs can vary in appearance, but they're usually in the form of a lump. These lumps can occur on the skin, muzzle, mouth, genitals or even inside the body on the organs. When you're petting or examining your dog, you may notice a firm lump tightly adhered to the skin or a squishy.
Mast Cell Tumors vs Histiocytomas in Dogs [10 pictures]
Articles Dog Mast Cell Tumors in Dogs Mast Cell Tumors in Dogs Estimated Reading Time: 5 minutes Mast cell tumors are a common cancer in dogs and cats. Most are located on the skin or in the tissue layer below the skin, called the subcutaneous tissue. Mast cell tumors are considered a Great Mimicker and can have a wide range of appearances.
What Causes Mast Cell Tumors In Dogs
What are mast cell tumors? Mast cell tumors develop from specific cells of the immune system called "mast cells," which normally treat inflammation and allergic reactions in a dog's body. The cause of these tumors is currently unknown, and the tumors can develop anywhere on your dog's body.

Mast Cell Tumors Veterian Key
Overview Mast cell tumors are the most common type of skin tumor found in dogs and the second most common skin tumor in cats. These represent 14-21% of all skin tumors diagnosed in dogs. They are usually noticed in middle aged patients, but can occur in patients of any age. Boxers and Boston terriers make up ~ 50% of all cases.

My dog had a small grade 1 mast cell tumor removed about 4 months ago. It was on her shoulder
A mast cell tumor (MCT) is a type of malignant (cancerous) tumor consisting of mast cells. Mast cell tumors typically form nodules or masses in the skin but they can also affect other areas of the body, including the spleen, liver, intestine, and bone marrow. MCTs are the most common skin tumor in dogs.
12 Pictures of Mast Cell Tumors in Dogs [With Vet Comments]
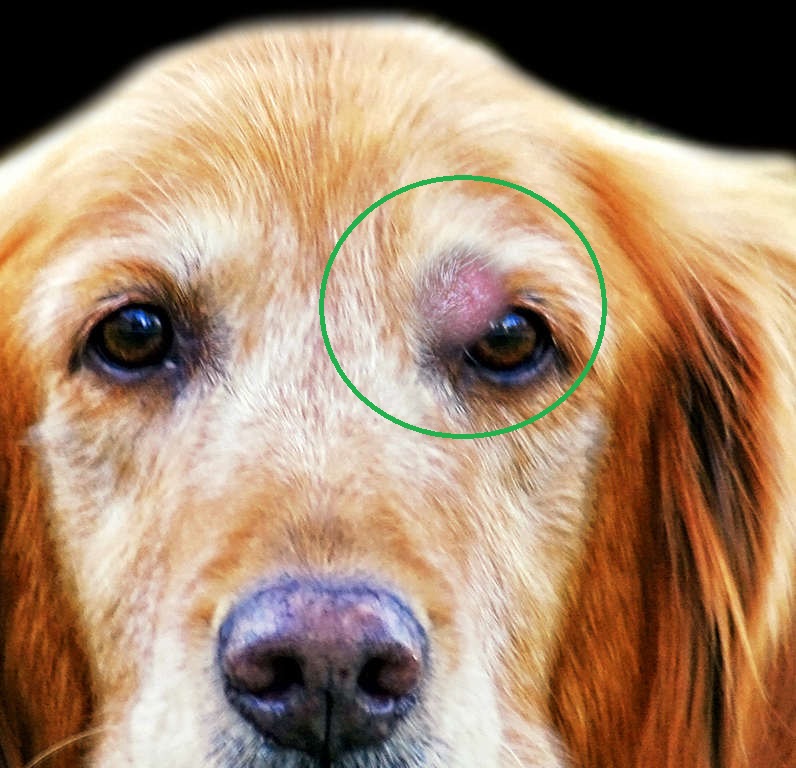
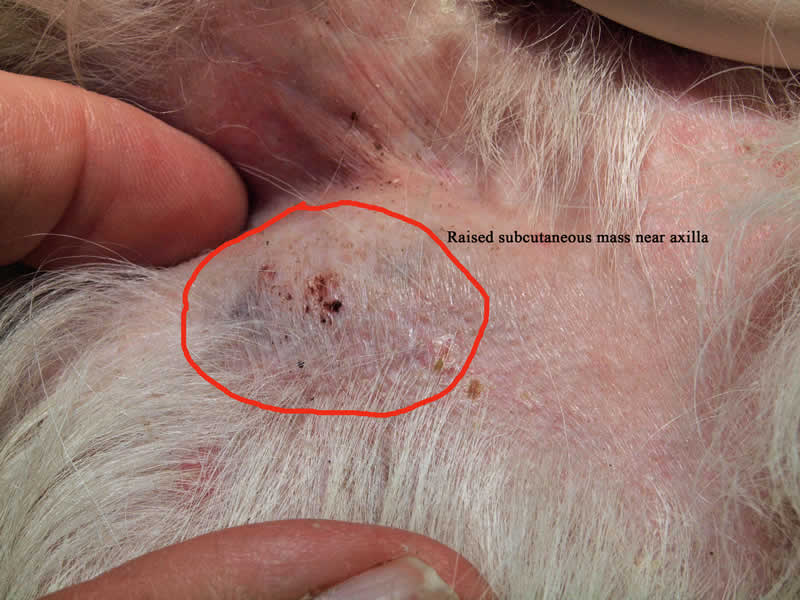
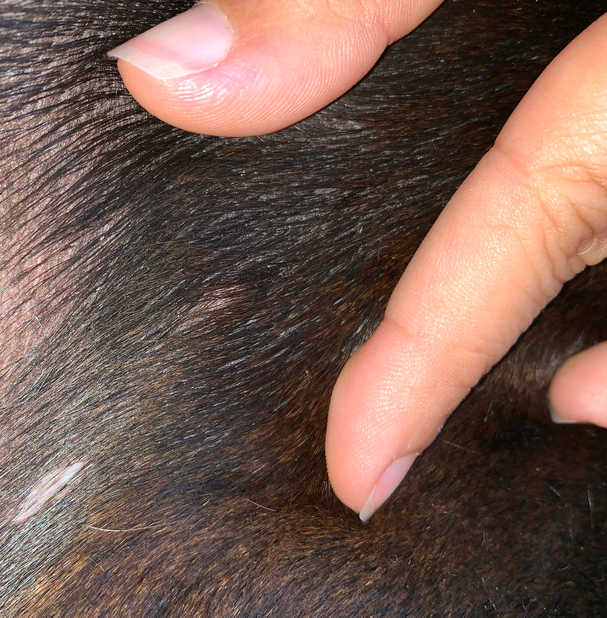
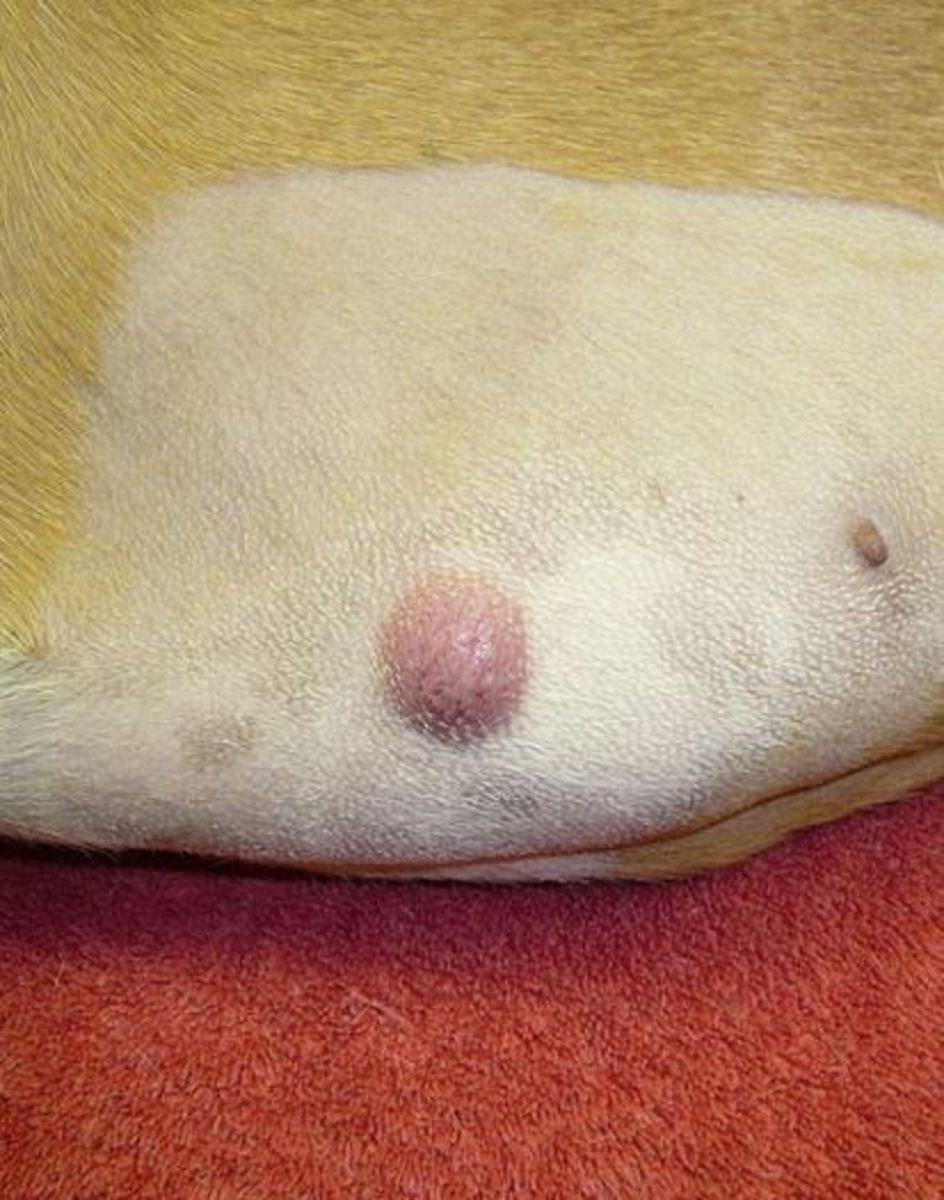
Big or small Firm or squishy Raised above the skin or located under the skin Smooth or ulcerated (i.e. having an open surface or looking like the mast cell tumor burst) Pink or tan Hairless or haired The pictures of mast cell tumors in dogs below show two of the many, many different presentations.
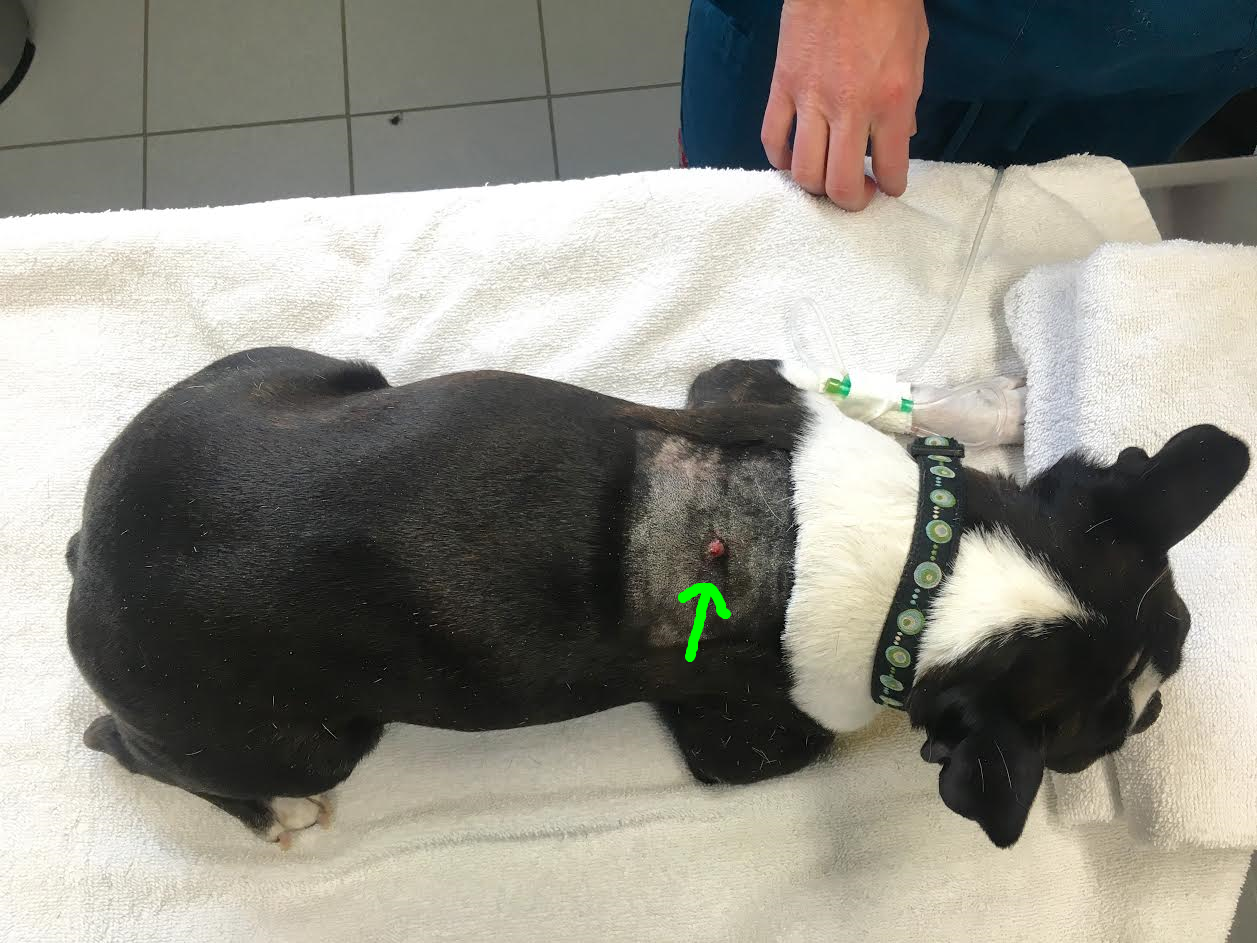
Charlie's Mast Cell Tumour — Alpine Veterinary Medical Centre
For most dogs, mast cell tumors are not a painful cancer. In fact, mast cell tumors are typically diagnosed after a pet owner takes their dog to the veterinarian because they've felt a lump in or under the skin. If other organs are also affected, you may see these signs: Decreased appetite Increased respiratory rate Vomiting Diarrhea
A Dog's Journey thru Mast Cell Tumor Treatment October 2012
Mast cell tumor (MCT) represents a cancer of a type of blood cell normally involved in the body's response to allergens and inflammation. MCT is the most common skin tumor in dogs; it can also affect other areas of the body, including the spleen, liver, gastrointestinal tract, and bone marrow. Certain dogs are predisposed to MCT, including.
Mast Cell Tumor In Dogs Mastocytoma Signs & Treatment
When dogs develop tumors of these cells in their skin, they are called cutaneous mast cell tumors. Some dogs develop only one mast cell tumor during their life. Some develop many tumors over months or years. Others develop several tumors simultaneously. When this happens, the dog is diagnosed with "multiple cutaneous mast cell tumors.".

to the menagerie My Boston terrier has a mast cell tumor; here's the plan
There is no way to tell if your dog has a mast cell tumor by its appearance alone: in fact, in veterinary medicine, these tumors are known for their unpredictable appearance. They can look like something harmless, even in their most life-threatening forms. Let's look at a few different types of mast cell tumors: 1. Small mast cell tumor
Veterinary Key Points Complete Surgical Excision of Mast Cell Tumor in Dogs and Cats
Mast cell tumors are the most common cutaneous cancer in dogs and originate from the skin or subcutaneous tissues. The cause of mast cell tumors in dogs is largely unknown, but it is believed that they may be caused by a genetic mutation that causes mast cells to grow uncontrollably. Mast cell tumors are most common in older dogs (average age.

Mast Cell Tumors Veterian Key
A mast cell tumor is a tumor consisting of mast cells. They are common in dogs, accounting for approximately 20% of all skin tumors. In addition to forming in nodules or masses in or on the skin, they can also affect regional lymph nodes, the spleen, liver, intestine, bone marrow, and other areas of the body.
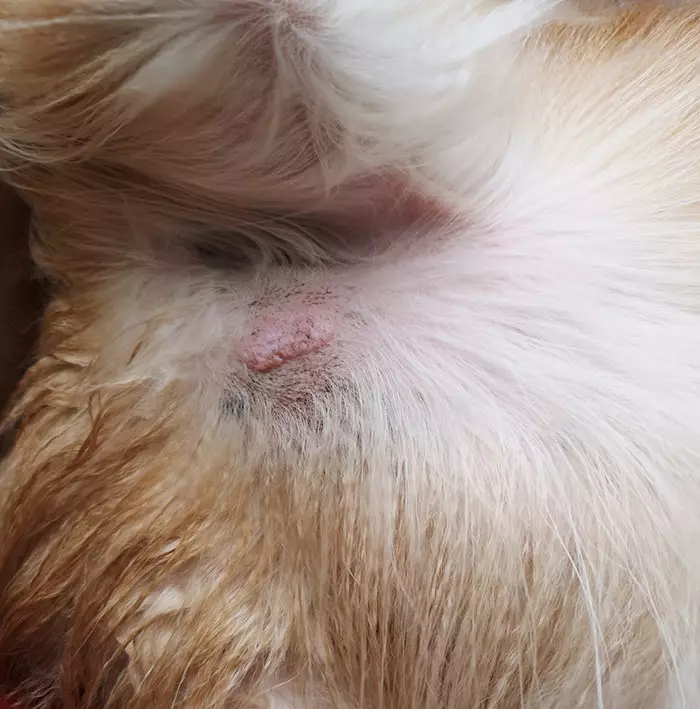
Facts about Mast Cell Tumors Dog Owners Should Know Dog Discoveries
A mast cell tumor (MCT), also known as mastocytoma, is a specific type of skin cancer that stems from mast cells. Mast cells are white blood cells that can be found in several tissues and play a major role in allergic reactions. As a skin cancer, the mast cell tumor dog causes lumps and bumps that can imitate literally any skin lesion.
12 Pictures of Mast Cell Tumors in Dogs [With Vet Comments]
Chemistry panel Urinalysis Abdominal ultrasound Lymph node Liver and spleen aspirate The grade is determined by biopsy (histopathology) and refers to the appearance of the tumor under the microscope. The pathologist will describe the features of the mast cells and report if the tumor was completely removed during surgery.

A Natural Approach To Mast Cell Tumors Mast cell tumor dogs, Tumor, Dog cancer
Pugs What does a mast cell tumor look like on a dog? Washington State University Veterinary Teaching Hospital states that mast cell tumors most commonly appear as a lump or mass on or under the skin. Dog mast cell tumors can have varying appearances. They can be mistaken for lipomas which are benign, soft-fatty lumps.