
Normal ankle joint, Xray Stock Photo Alamy
The true anteroposterior view of the ankle is often performed in the setting of ankle trauma and suspected ankle fractures in addition to the lateral and mortise views of the ankle. Other indications include: assessment of fragment position and implants in postoperative follow up. evaluation of fracture healing.

Ankle xrays Don't the Bubbles
The ankle AP mortise (mortice is equally correct) view is part of a three view series of the distal tibia, distal fibula, talus and proximal 5 th metatarsal. On this page:. the x-ray beam can be angled 15-20° medially to achieve the view although this will result in some artifactual elongation of structures.
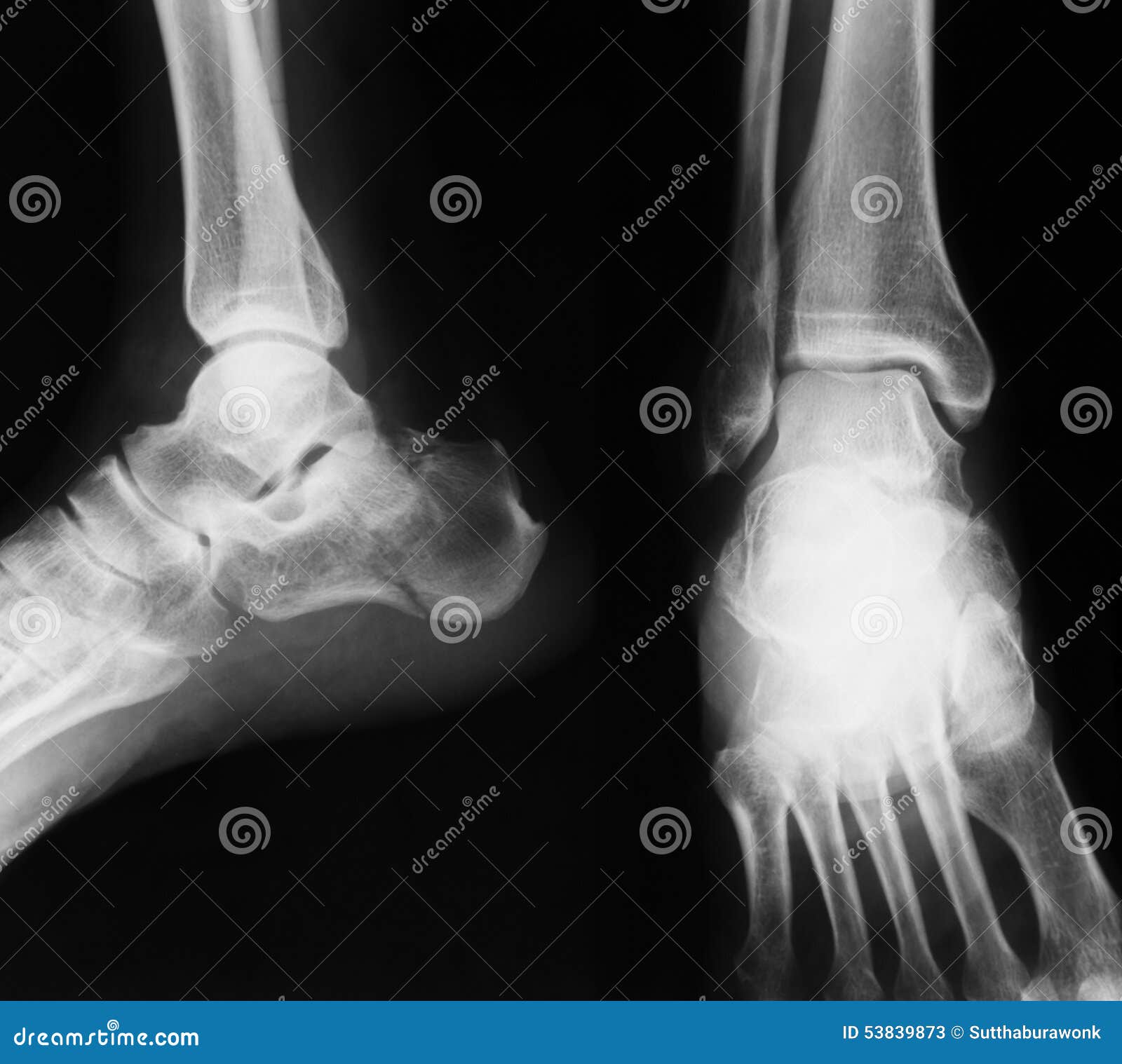
Xray Image of Ankle, AP and Lateral View. Stock Image Image of joint, metatarsal 53839873
A structured approach to ankle X-ray interpretation to identify fractures and other abnormalities. The guide includes X-ray examples of key pathology.. Mortise view: this is a modified anteroposterior (AP) view of the ankle in 10-20° internal rotation so that the medial and lateral malleoli are in the same horizontal plane and joint.

Archive Of Unremarkable Radiological Studies Knee XRay Stepwards
- on AP view differnece in width of superior clear space between medial and lateral side of the joint should be < 2 mm; - these are static measurements of the talar position; - in normal ankle, talus may tilt up to 5 deg w/ inversion stress; - measurements of talar tilt using stress x-rays are used to evaluate lateral ligament stability.

Ankle X Ray Anatomy
The AP stress view of the ankle is a highly specialized view used to assess the integrity of the syndesmosis and deltoid ligament. It can be performed one of two ways, with gravity or via manual external rotation.. In intermediate ankle injuries that have no syndesmotic widening on x-ray — yet a high suspicion of injury — will warrant a.
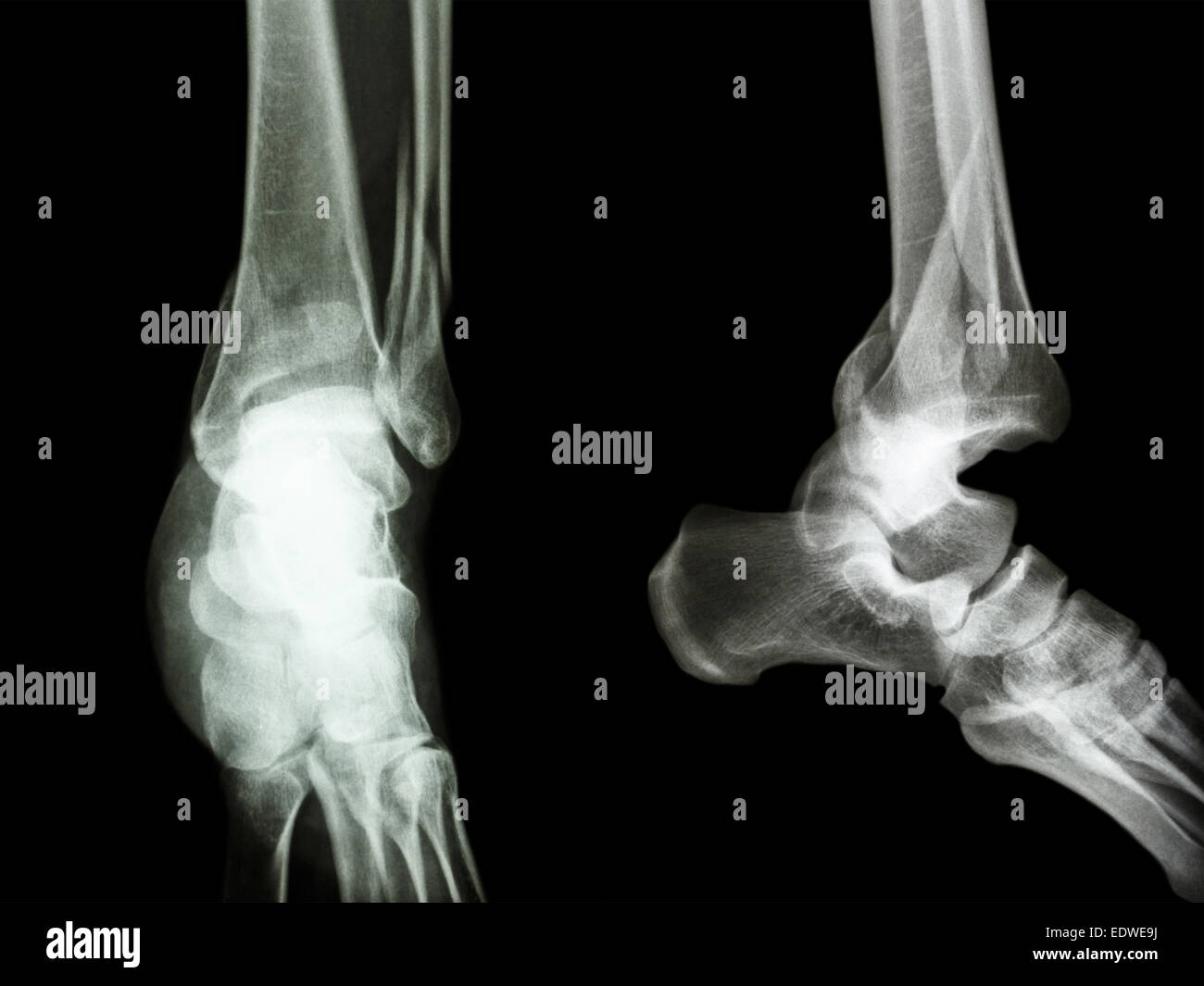
film xray ankle AP/Lateral show fracture distal tibia and fibula (leg's bone) and ankle joint
same horizontal plane as the medial malleolus and both are parallel to the x-ray tabletop. The mortise view is the true AP projection of the ankle joint. Oblique projections, 1 plain radiograph tomography , computed tomography (CT), or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be required to identify minimally displaced ankle fractures.

AP and lateral radiograph of the left ankle showing ball and socket... Download Scientific Diagram
The x-ray beam is then angled cephalad about 40 degrees to the long axis of the foot and first penetrates the sole of the foot. The dorsoplantar view is performed with the patient prone with a wedge or pillow placed under the distal calf.. In the AP ankle view with passive hindfoot varus stress 12 degrees of talar tilt or 5 degrees more than.

Xray picture of the right ankle joint in the AP view. Thick ening... Download Scientific Diagram
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. The ankle series is comprised of an anteroposterior (AP), mortise and lateral radiograph. The series is often used in emergency departments to evaluate the distal tibia, distal fibula, and the talus; forming the ankle joint. See approach to an ankle series.

EMRad Radiologic Approach to the Traumatic Ankle
Ankle views. An x-ray of the ankle will have three views - AP, mortise, and lateral. It should be noted, though, that in some countries, including the UK, only the mortise and lateral are used. See the annotated images below from WikiFoundry, and thanks also to Radiopaedia:
Assessing Heel Pain Diagnostic Ultrasound of the Foot and Ankle
AP images are obtained by directing the x-ray beam from the dorsum of the ankle to the plantar surface, with the image receptor beneath the sole of the foot. Internal oblique images are obtained by internally rotating the ankle 15-20 degrees and directing the x-ray beam in a dorsoplantar direction similar to the AP view.
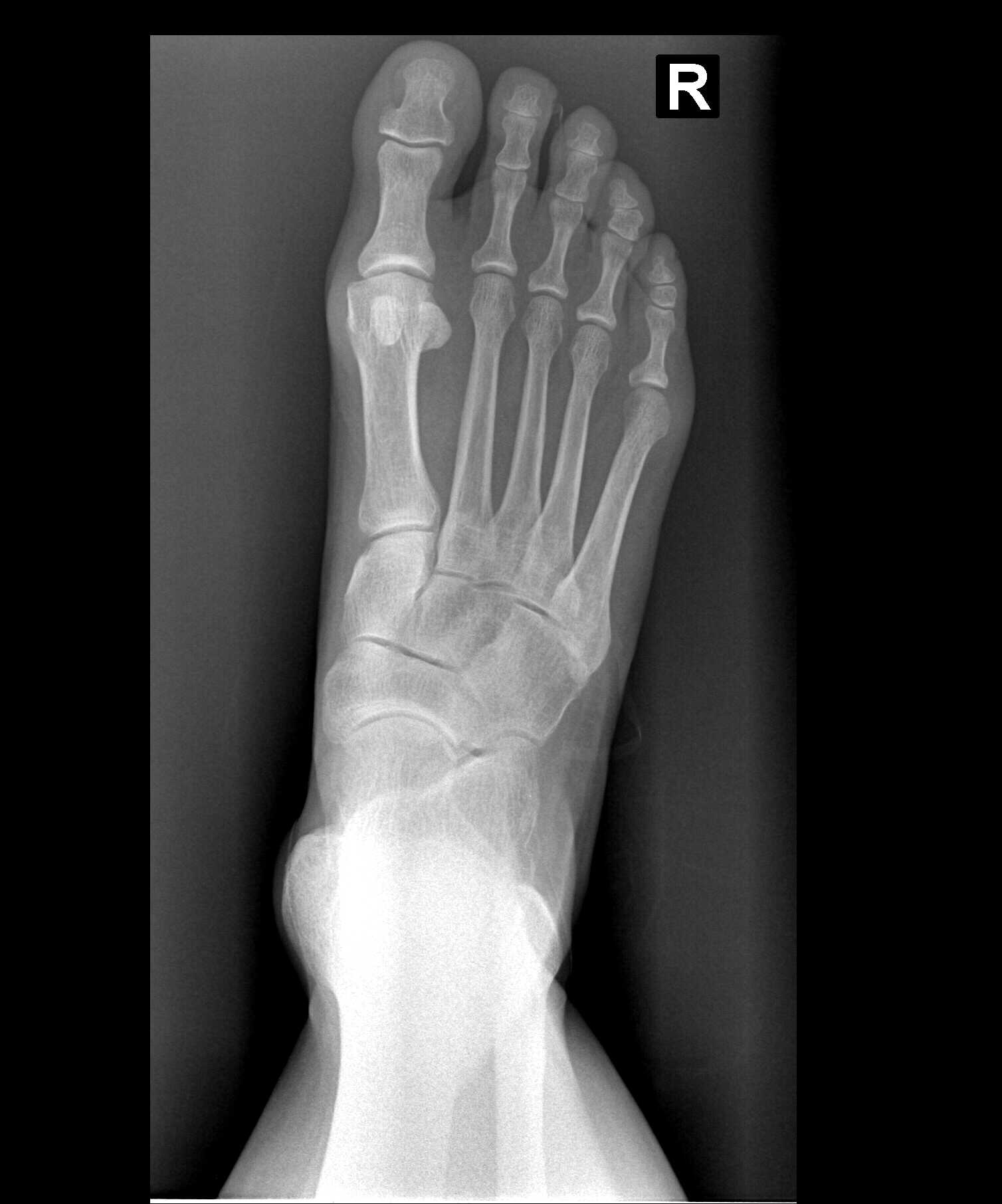
Rt AP Foot Xray 1012013
Stress view. Positioning. patient. manual stress = supine + knee extended + ankle inverted/everted. gravity stress = supine + hip ER + knee flexed + ankle placed on bump. beam. aim at tibiotalar joint. Uses. joint stability = < 5° difference between ipsilateral + contralateral ankles.
The Ankle
This projection is utilized to assess the structural integrity of the ankle joint. If the patient is able, weight-bearing views should be performed in acute and follow up settings 1 . In addition, this view can show bony diseases or lesions of the distal lower leg, talus and proximal fifth metatarsal. Ultimately the radiographer will determine.

AP, Mortise and lateral view of the right ankle in case 2. Yellow... Download Scientific Diagram
Interpret traumatic ankle x-rays using a standard approach; Identify clinical scenarios in which an additional view might improve pathology diagnosis; Why the ankle matters and the radiology rule of 2's The Ankle.. Tibiofibular clear space: On AP view, this is the distance between the medial border of the fibula and lateral border of the.

Normal values at standard Xray views (AP,Mortise and lateral)of the... Download Scientific
Central ray 10 degrees cephalad at a point 1 inch (2.5 cm) distal to the medial malleolus. LE-P-30 - Ankle AP. Purpose and Structures Shown AP projection of ankle joint, distal ends of tibia and fibula, and proximal portion of talus. Position of patient Supine position. Affected limb fully extended.

X ray right ankle joint AP and Lateral view shows irregular... Download Scientific Diagram
On a true AP-view the talus overlaps a portion of the lateral malleolus, obscuring the lateral aspect of the ankle joint.. This was the only fracture that was seen on the x-rays of the ankle and this patient turned out to have an unstable Weber-C fracture and went for surgery. The x-ray beam has to be centered on the malleoli.
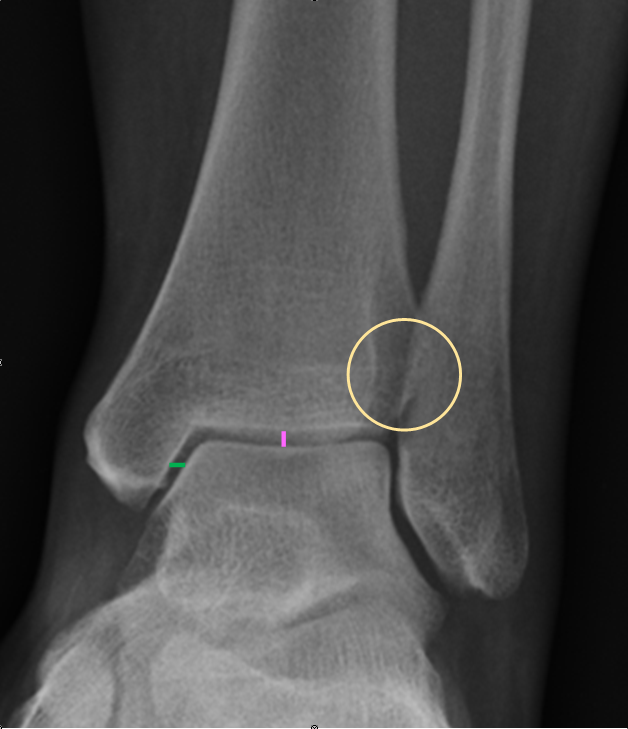
Ankle Xray Interpretation Ankle Fracture Geeky Medics
An isolated fracture of the medial malleolus, or widening of the ankle joint with no visible fracture seen on ankle X-ray, should raise the suspicion of an associated fracture of the fibula. If this is not visible in the distal fibula then further X-rays of the proximal fibula should be performed. Imaging of the proximal fibula should also be.