Draw the graph of sin^2x and sinx and show the continuity and
Interactive online graphing calculator - graph functions, conics, and inequalities free of charge

Trigonometric Graph How to draw y = 3 sin (2x)+1 YouTube
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. For math, science, nutrition, history.

Solve the ecuation sinx+sin2x=2? Socratic
Free graphing calculator instantly graphs your math problems.
Trig Curve Sine Function Crystal Clear Mathematics
Trigonometry Graph y=sin (x)+sin (2x) y = sin(x) + sin(2x) y = sin ( x) + sin ( 2 x) Graph. y = sin(x)+sin(2x) y = sin ( x) + sin ( 2 x) Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor.
Graphing Sine And Cosine Worksheets
Interactive, free online graphing calculator from GeoGebra: graph functions, plot data, drag sliders, and much more!
Six Trigonometric Functions Graph Examples
2.1: Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions - Mathematics LibreTexts 2π 3 1 2 π 2 2 y = 0 |A| = 1 2 P = 2π |B| = 6π C B = π f(x) = sin(x) + 2 y = 4 sin(π 5x − π 5) + 4 y = −4 sin(π 5x + 4π 5) + 4 2.1.20 y = 0 |A| = 0.8 P = 2π |B| = π C B = 0 2.1.22 y = 0 |A| = 2 P = 2π |B| = 6 C B = −1 2 2.1.25 y = 3 cos(x) − 4 2.1.29 menu search Search

📈This graph represents the function f(x)=sin(2x)
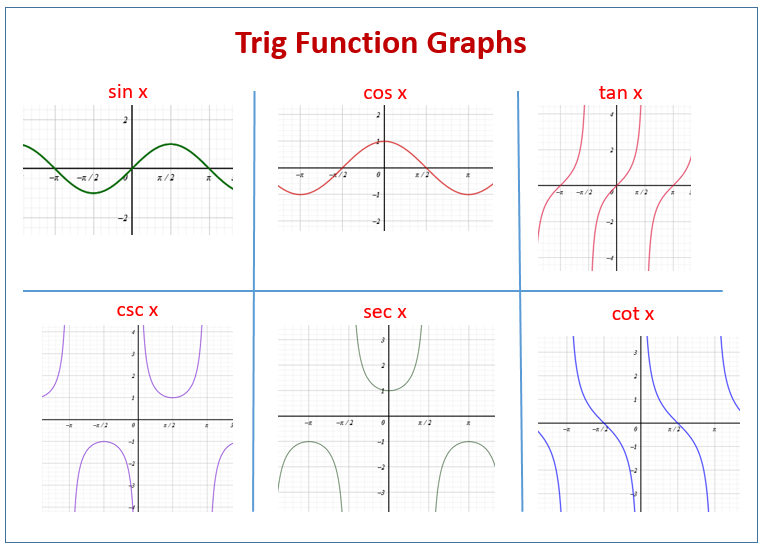
It uses functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent to describe the ratios of the sides of a right triangle based on its angles. What are the 3 types of trigonometry functions? The three basic trigonometric functions are: Sine (sin), Cosine (cos), and Tangent (tan).

functions Sin^2(x) Boundaries (Very Basic Question) Mathematics
Explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more.
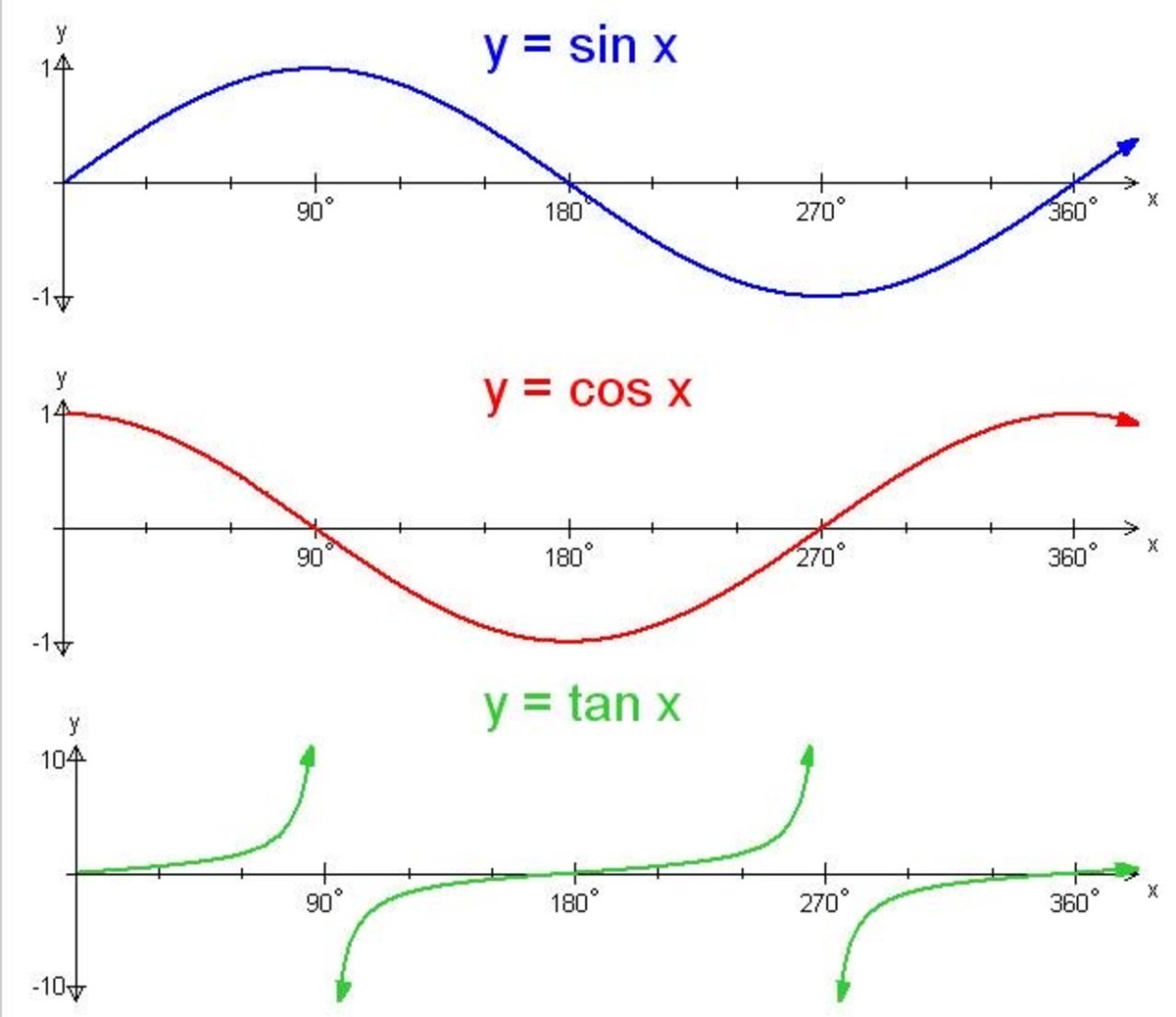
Trigonometry Graphing the Sine, Cosine and Tangent Functions Owlcation
In this section, we will interpret and create graphs of sine and cosine functions. Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Recall that the sine and cosine functions relate real number values to the x - and y -coordinates of a point on the unit circle. So what do they look like on a graph on a coordinate plane? Let's start with the sine function.

Describe the Graph of a Sine Function XiomarahasChen
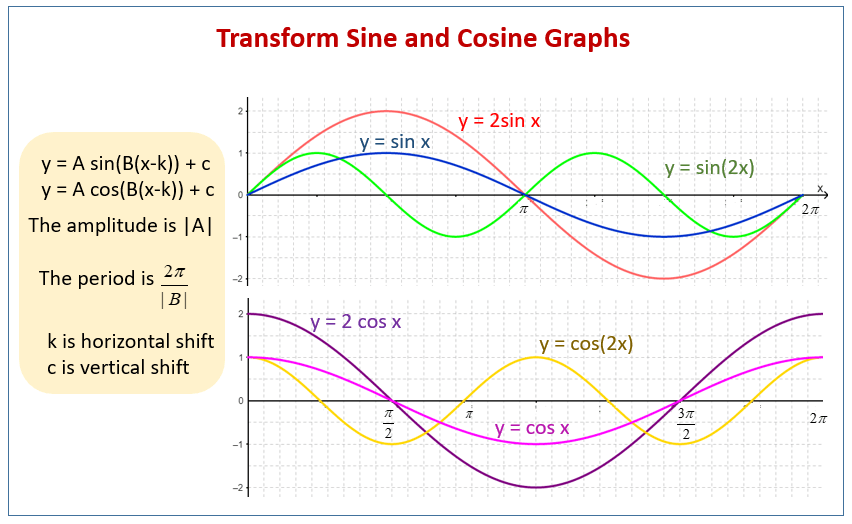
The graph of y = sin ax. Since the graph of y = sin x has period 2 π, then the constant a in. y = sin ax. indicates the number of periods in an interval of length 2 π. (In y = sin x, a = 1.) For example, if a = 2 --y = sin 2x-- that means there are 2 periods in an interval of length 2 π. If a = 3 --y = sin 3x-- there are 3 periods in that.
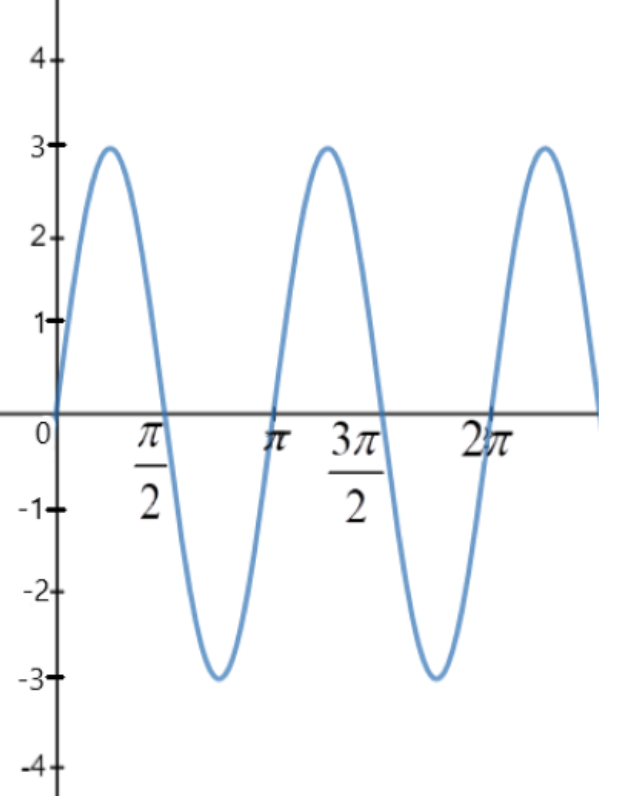
How do you graph y = 3\\sin 2x
Example 2. Graph one full period of the function y = 5cos2 3x. The amplitude of the function is 5 because A = 5, so the maximum y-value will be 5 and the minimum y -value will be − 5. The period of the graph will be 2π B which in this case is 2π 7 = 2π ∗ 3 2 = 3π. So the period is 3 π.

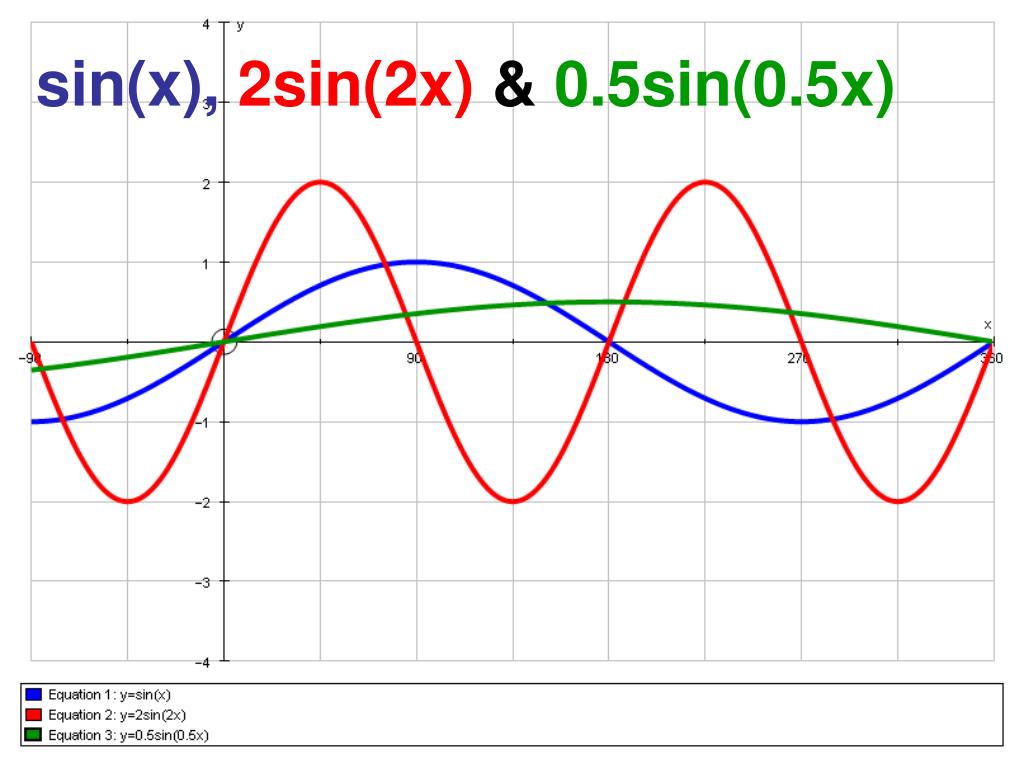
To plot the graph of sinx, sin2x, 2sinx and sinx/2 on the same
Loosely stated, the argument of a trigonometric function is the expression `inside' the function.\index {argument ! of a trigonometric function} Example 1.5.1: Cosines Sine Graphing. Graph one cycle of the following functions. State the period of each. \item f(x) = 3cos(πx − π 2) + 1. \item g(x) = 1 2sin(π − 2x) + 3 2. Solution.

To plot the graph of sinx, sin2x, 2sinx and sinx/2 on the same
Amplitude: 1 1 Find the period of sin(2x) sin ( 2 x). Tap for more steps. π π Find the phase shift using the formula c b c b. Tap for more steps. Phase Shift: 0 0 List the properties of the trigonometric function. Amplitude: 1 1 Period: π π Phase Shift: None Vertical Shift: None Select a few points to graph. Tap for more steps.
PPT Translations and Transformations of Trigonometric Functions
What values of will work? Amplitude, Frequency and Phase Going from to The amplitude is halved. (the y values lie between 0 and +1, previously they were between -1 and +1). The frequency is doubled. (we have more complete cycles in the same x distance.
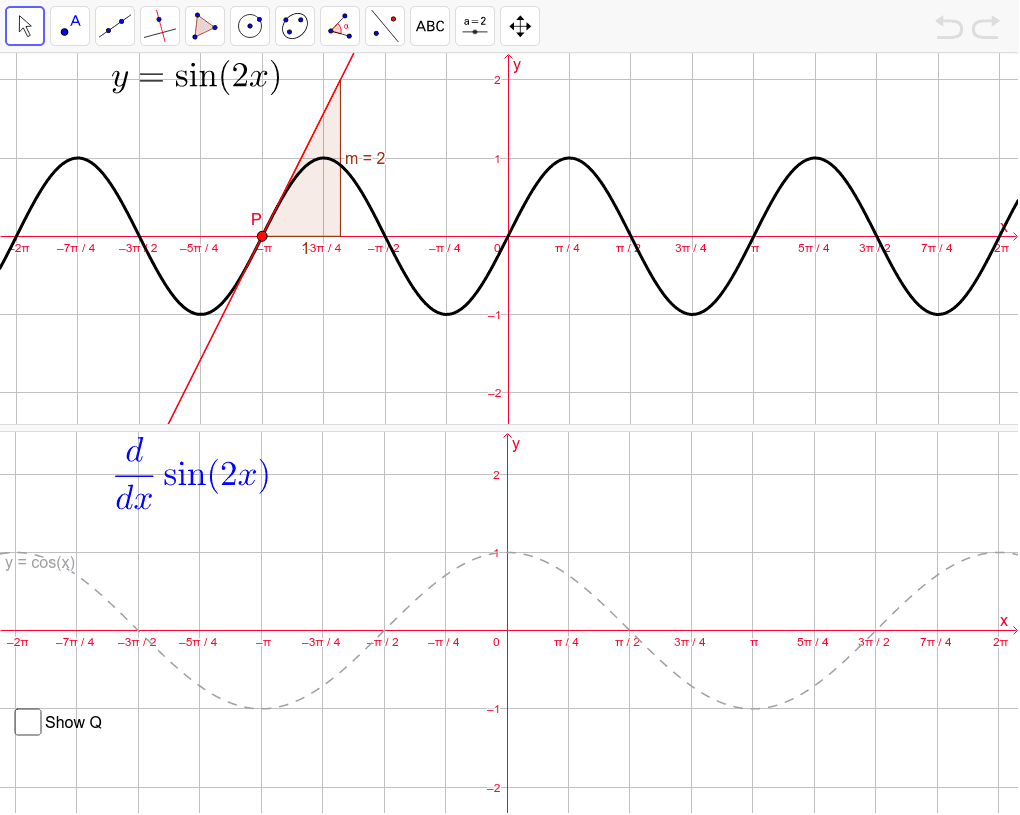
Derivative of sin(2x) GeoGebra
Here is the graph: graph { (sinx)^2 [-10, 10, -5, 5]} Recall the double-angle formula for cosine: cos(2x) = 1 − 2sin2(x) Subtract 1 from both sides: cos(2x) − 1 = − 2sin2(x) Divide both sides by −2 − 1 2cos(2x) + 1 2 You now have a standard cosine equation with Amplitude = 1 2 Period = π Vertical Shift = up by 1 2

Sin and Cos Graphs
About Transcript The graph of y=sin (x) is like a wave that forever oscillates between -1 and 1, in a shape that repeats itself every 2π units. Specifically, this means that the domain of sin (x) is all real numbers, and the range is [-1,1]. See how we find the graph of y=sin (x) using the unit-circle definition of sin (x).