Goldschmidt classification Wikipedia
These classifications broadly follow Goldschmidt's original classifications (Goldschmidt, 1937) with the addition of organophile and fluid-mobile elements. Lithophile elements ("rock loving") are preferentially partitioned into silicate minerals. These include cations that commonly form oxides, such as Ca, Mg, Mn, Ti, Na, K, the rare.
Victor Moritz Goldschmidt • Biografias •
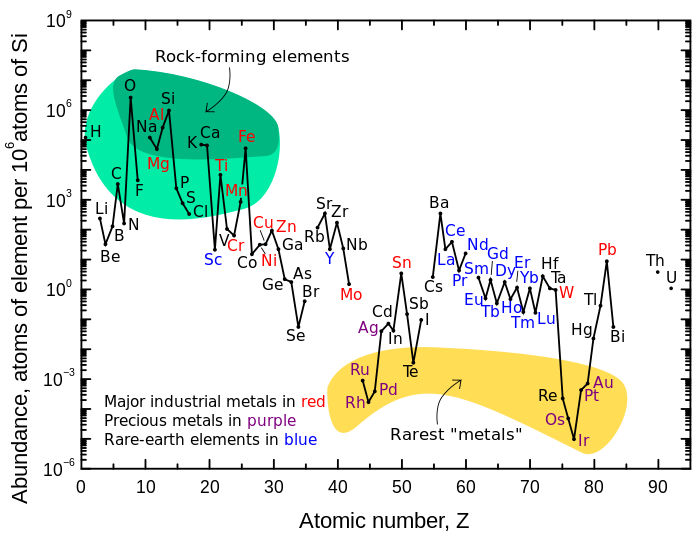
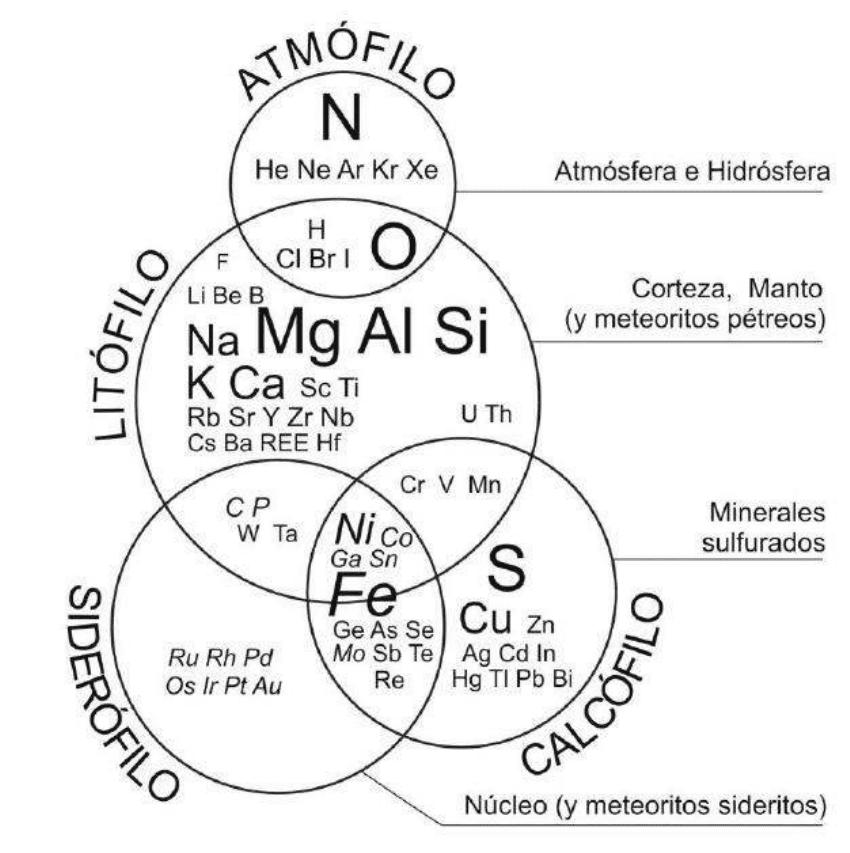
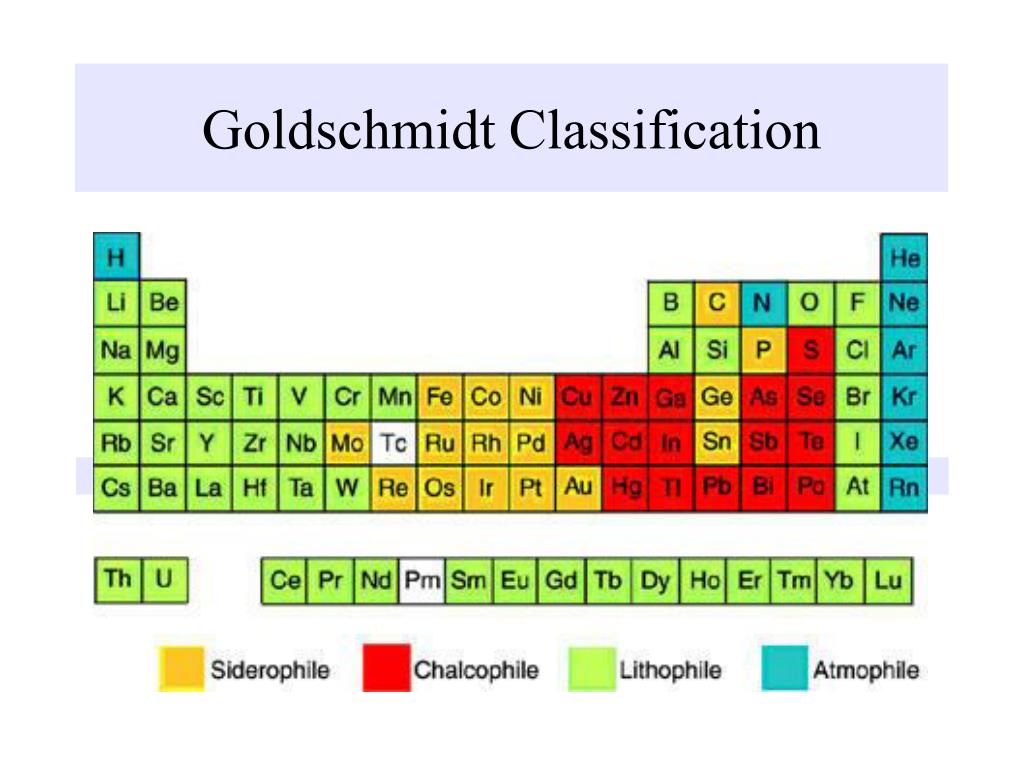
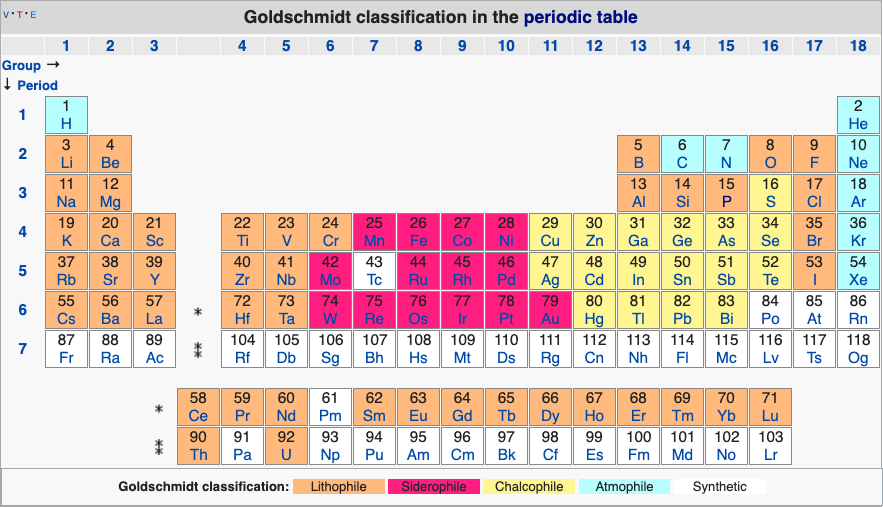
The Goldschmidt geochemical classification of elements groups the chemical elements according to their preferred host phases within the Earth into lithophile (rock-loving), siderophile (iron-loving), chalcophile (sulfur-loving), and atmophile (gas-loving).
PPT Introduction to Trace Element Geochemistry PowerPoint Presentation ID2001747
(January 2010) The Goldschmidt classification, developed by Victor Goldschmidt, is a geochemical classificationwhich groups the chemical elementsaccording to their preferred host phases into lithophile (rock-loving), siderophile (iron-loving), chalcophile (sulphur-loving), and atmophile (gas-loving).

Goldschmidt Classification of the Elements
A752 Goldschmidt 2004, Copenhagen 6.2.P02 The new geochemical classification of the elements and a complex model of the Earth's geochemical evolution. Dangic's geochemical classification of the elements. 1 3Anions of extremly a.s.1 N -, P3-, C4-, S-4, Pb4-2 Anions of strongly a.s.
PPT Formation de la Terre PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4501079
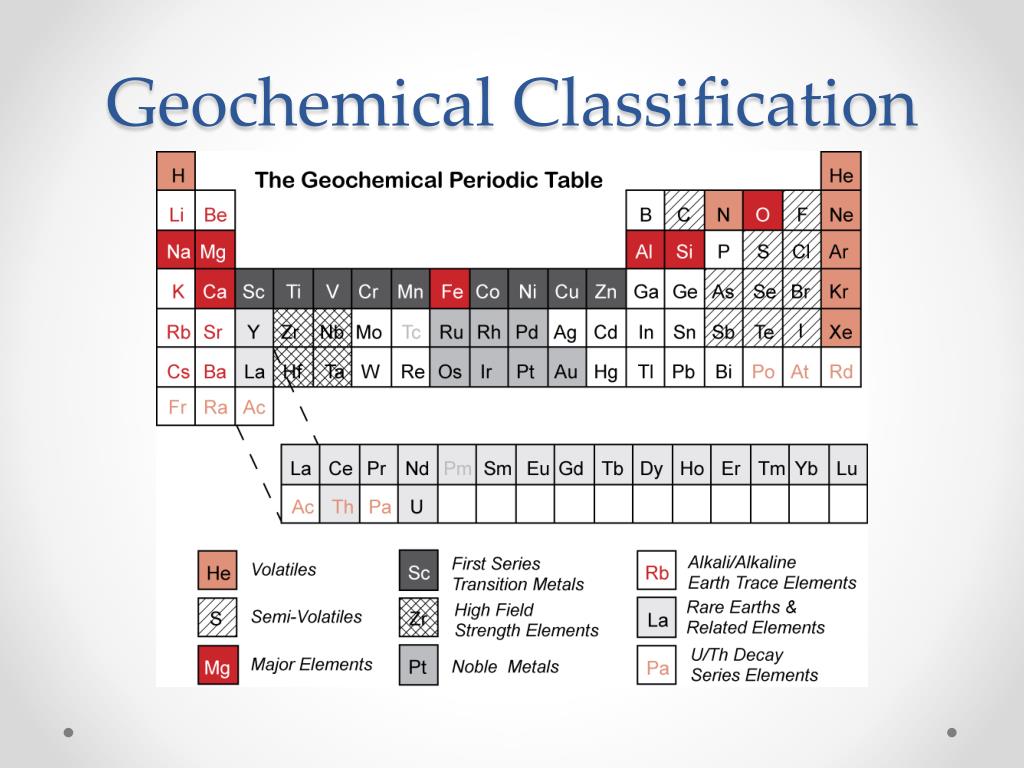
Definition Geochemists classify elements in various ways based on their abundance, behavior, and distribution in the Earth. Introduction Elements can be qualitatively classified into major (>0.4 wt%), minor (0.1-0.4 wt%), and trace elements (<0.1 wt%).

PPT Introduction to Trace Element Geochemistry PowerPoint Presentation ID2001747
Goldschmidt classification. The geochemical classification of the elements, also called the Goldschmidt classification because it is the result of work undertaken in the 1920s by the chemist Victor Goldschmidt, provides an understanding of the origin of the various proportions of chemical elements in the Earth's minerals and rocks, and more.

PPT Uncertainties… What do we mean, … mean age of the Earth? Element classification PowerPoint
Victor Moritz Goldschmidt ForMemRS (27 January 1888 - 20 March 1947) was a Norwegian mineralogist considered (together with Vladimir Vernadsky) to be the founder of modern geochemistry and crystal chemistry, developer of the Goldschmidt Classification of elements. Early life and education

Goldschmidt classification Alchetron, the free social encyclopedia
The Goldschmidt classification, [1] developed by Victor Goldschmidt (1888-1947), is a geochemical classification which groups the chemical elements within the Earth according to their preferred host phases into lithophile ( rock -loving), siderophile ( iron -loving), chalcophile ( sulfide ore -loving or chalcogen -loving), and atmophile (gas-lov.

Periodic table after V. M. Goldschmidt. Elements present in the gold... Download Scientific
According to Goldschmidt's classification (Hollabaugh 2007), Pb, As, Cu, Cd, and Zn are sulfur-loving elements with a strong affinity for sulfur; these easily polarized elements exist in.

(PDF) Lecture 31 SOEST · Goldschmidt’s Classification and the Geochemical Periodic Chart This
His name was V. M. Goldschmidt and it was his way of classifying the elements according to their affinities (philos - love) for various earth materials. Thus a siderophile element would be one with an affinity for iron metal. Before discussing this classification scheme in detail, let's learn more about its developer.

Goldschmidt classification YouTube
The Goldschmidt classification, developed by Victor Goldschmidt, is a geochemical classification which groups the chemical elements according to their preferred host phases into lithophile ( silicate loving), siderophile ( iron loving), chalcophile ( sulfur loving), and atmophile (gas loving). Some elements have affinities to more than one phase.
Goldschmidt Periodic Table Classification Photograph by Claus Lunau/science Photo Library
The Goldschmidt classification,[1]developed by Victor Goldschmidt (1888-1947), is a geochemical classificationwhich groups the chemical elementswithin the Earth according to their preferred host phases into lithophile (rock-loving), siderophile (iron-loving), chalcophile (sulfideore-loving or chalcogen-loving), and atmophile (gas-loving) or vola.
Geochemical classification diagrams for the major rock units in the... Download Scientific Diagram
The Goldschmidt classification, developed by Victor Goldschmidt (1888-1947), is a geochemical classification which groups the chemical elements within the Earth according to their preferred host phases into lithophile ( rock -loving), siderophile ( iron -loving), chalcophile ( sulfide ore -loving or chalcogen -loving), and atmophile (gas-loving).
Periodic Table Database Chemogenesis
The Goldschmidt classification of elements was introduced by Victor Moritz Goldschmidt, who is considered the father of geochemistry. The classification model is based on the preferred host phase of an element and its corresponding accumulation in either in the atmosphere, crust, mantle, or core of the Earth (Figure 1). [1]

Goldschmidt classification Meaning YouTube
Goldschmidt's original list of major biophile elements was C, H, O, N, P, S, Cl, and I. His list of minor biophile elements was B, Ca, Mg, K, Na, V, Mn, Fe, and Cu. Biophile elements are enriched in the biosphere—life, organic waste, dead remains, and naturally processed materials from the biosphere (coal, oil, natural gas, and kerogen).

Goldschmidt's geochemical classification in 2022 Classification, Periodic table
His name was V. M. Goldschmidt and it was his way of classifying the elements according to their affinities (philos - love) for various earth materials. Thus a siderophile element would be one with an affinity for iron metal. Before discussing this classification scheme in detail, let's learn more about its developer.