
Body Cavities Chest Cavity Anatomy and Body Cavities Anatomy
A body cavity is a space created in an organism which houses organs. It is lined with a layer of cells and is filled with fluid, to protect the organs from damage as the organism moves around. Body cavities form during development, as solid masses of tissue fold inward on themselves, creating pockets in which the organs develop.
PPT Body Planes, Directions, and Cavities PowerPoint Presentation
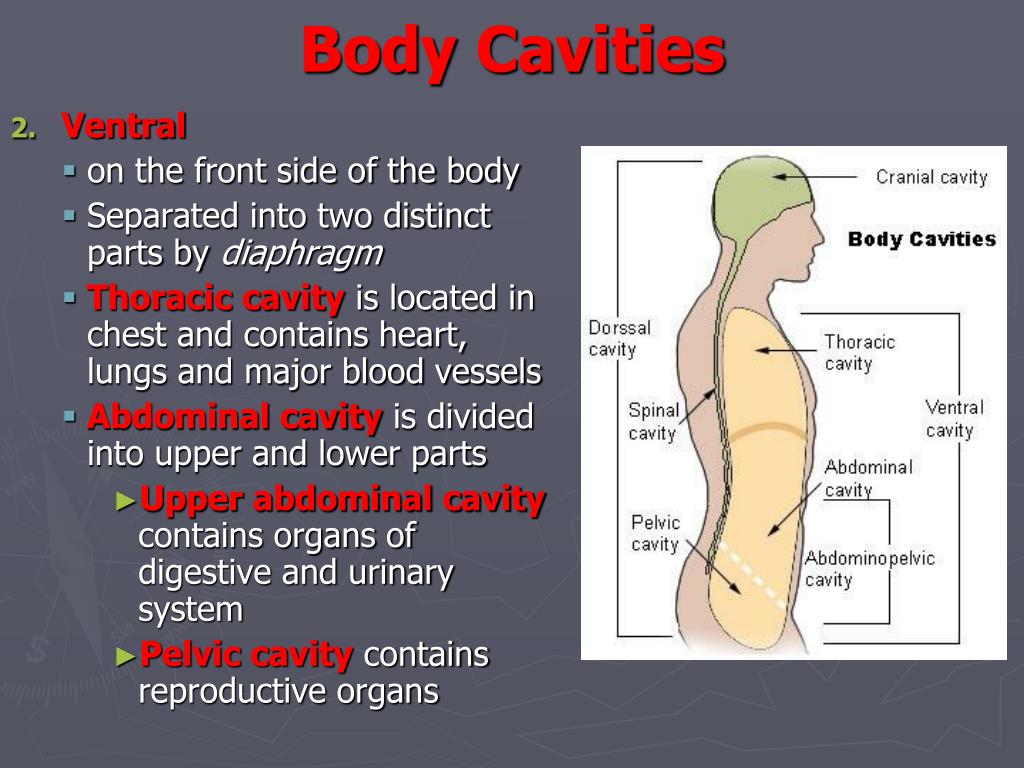
In the body itself, it is a hollow place usually filled with organs, nerves, vessels, and muscles. Here are the body's cavities: The cranial cavity. Image from Visible Body Suite . The thoracic cavity. Image from Visible Body Suite. The abdominal cavity. Image from Visible Body Suite. The pelvic cavity. Image from Visible Body Suite.

Human Anatomy Labeling Body Cavities Human Anatomy
Figure 1.4.3 - Planes of the Body: The three planes most commonly used in anatomical and medical imaging are the sagittal, frontal (or coronal), and transverse planes. Body Cavities . The body maintains its internal organization by means of membranes, sheaths, and other structures that separate compartments.
Body Cavities Labeled Organs, Membranes, Definitions, Diagram, and
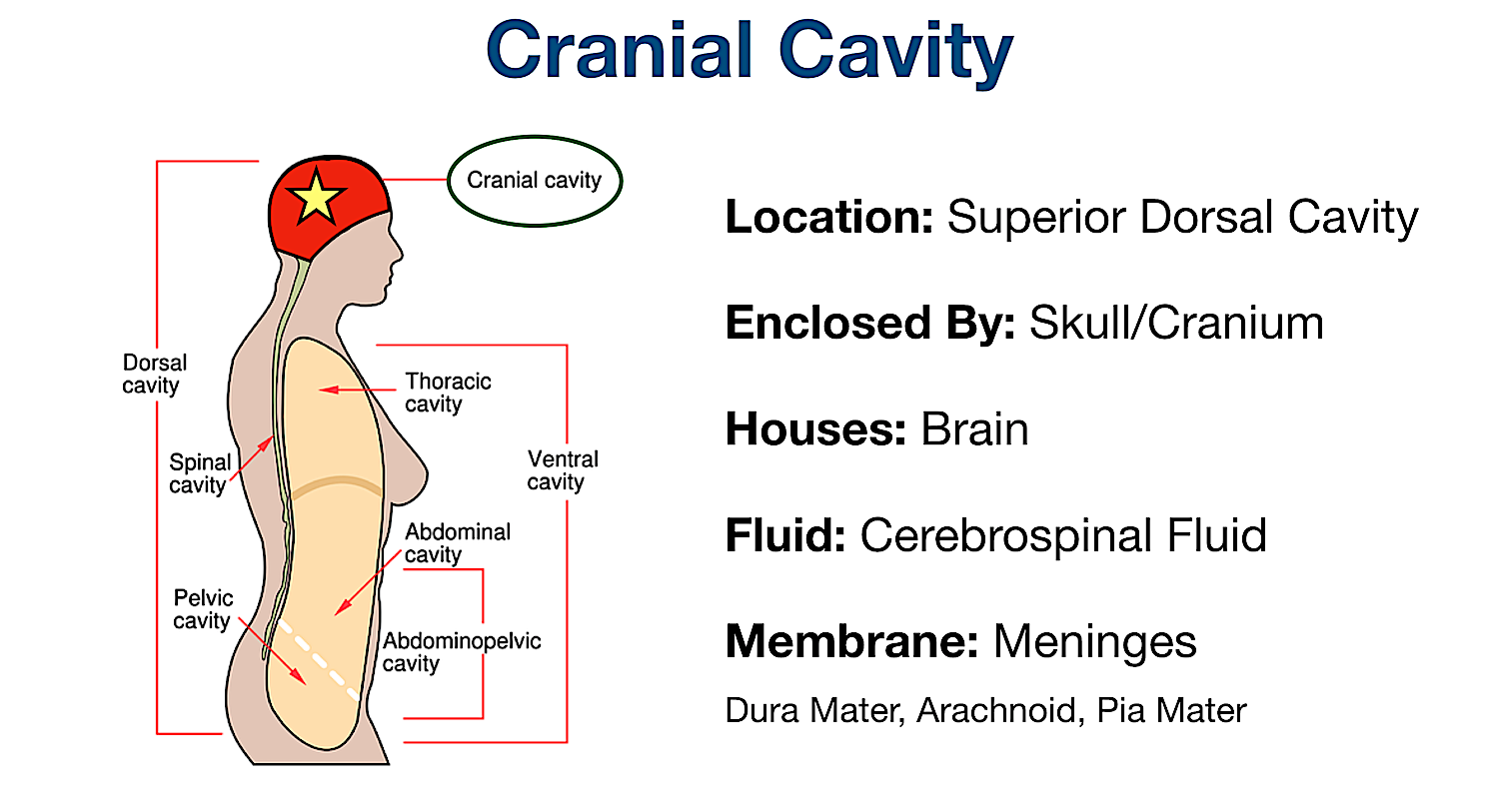
Body Membranes. The body cavities are lined with thin sheets of tissue called membranes, which cover and protect the various organs. The dorsal body cavity is lined with three layers of protective membranes (the dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater), which are called the "meninges.". In 2014, I remember reading a news story about a nursing.
PPT The Human Body Anatomical Regions, Directions, and Body Cavities
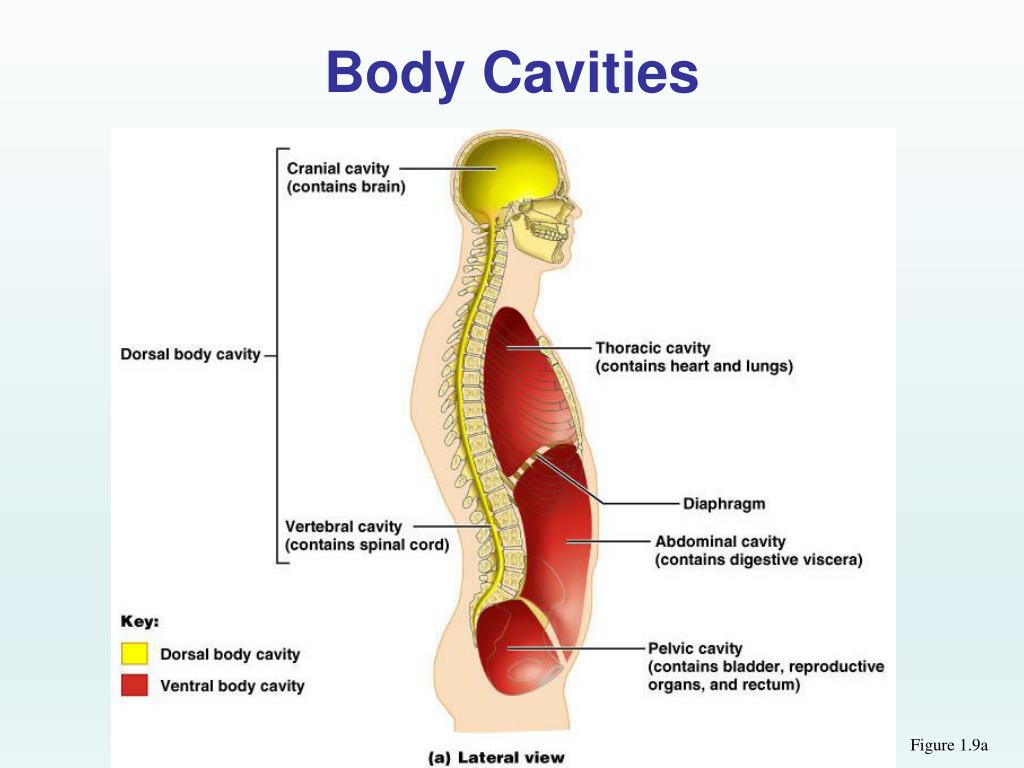
Body Cavities and Serous Membranes. The body maintains its internal organization by means of membranes, sheaths, and other structures that separate compartments. The dorsal (posterior) cavity and the ventral (anterior) cavity are the largest body compartments (Figure 1.15). These cavities contain and protect delicate internal organs, and the.

Illustration of Anterior Body Cavities Stock Image C017/2710
The thoracic cavity is the anterior ventral body cavity found within the rib cage in the torso. It houses the primary organs of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, such as the heart and lungs, but also includes organs from other systems, such as the esophagus and the thymus gland. The thoracic cavity is lined by two types of mesothelium.
Body cavities and membranes Anatomy & Physiology
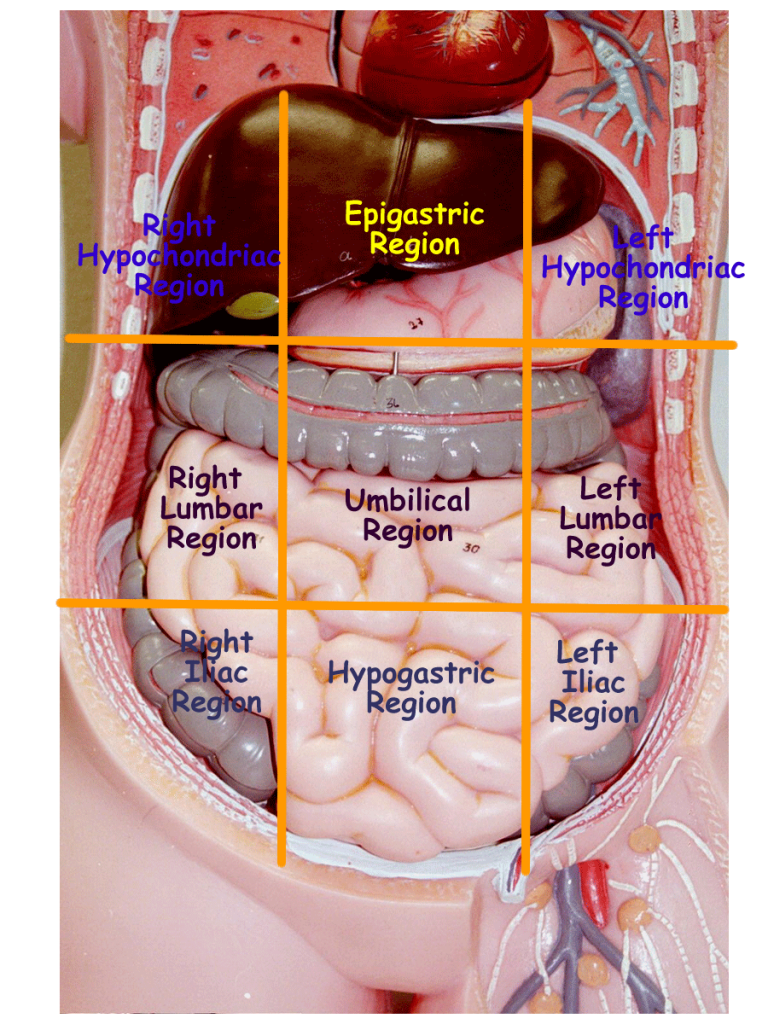
These body cavities are the fluid-fill spaces or compartments that hold and protect the animal's internal organs. Here, in this article, I will discuss the boundary of different body cavities and organs from the animal. You will also find the body cavities and organs labeled diagram so that you may identify them so quickly from the actual sample.
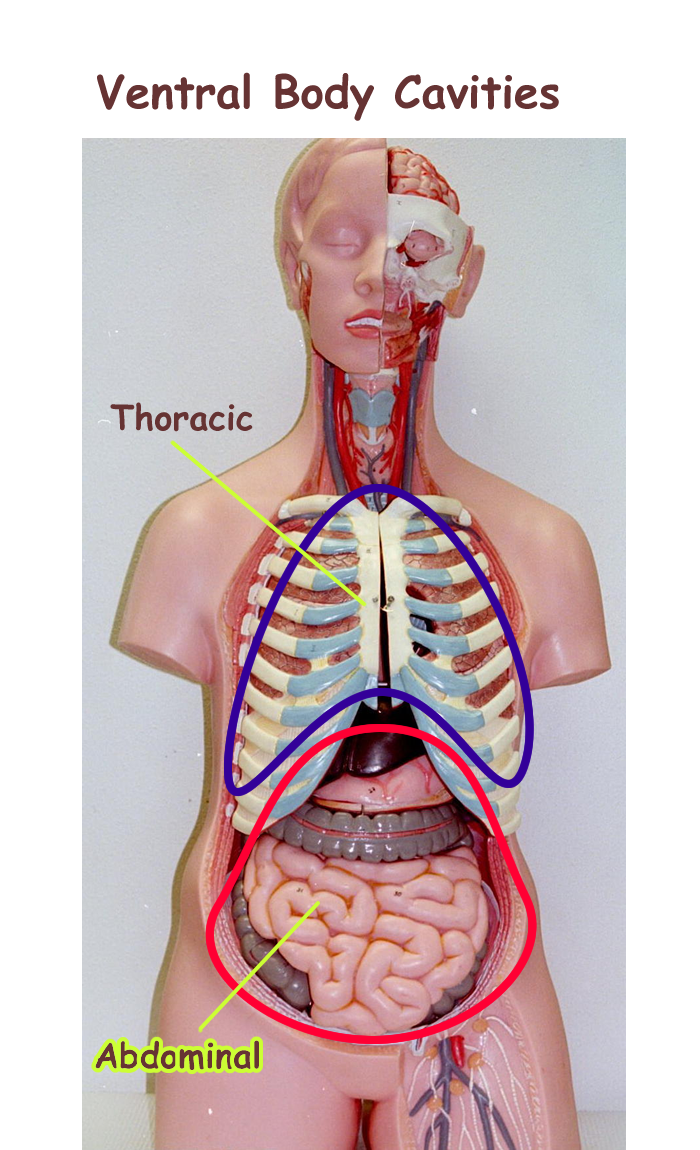
Human Anatomy Labeling Body Cavities Human Anatomy
Information. The major cavities of the human body are the spaces left over when internal organs are removed. There are additional body cavities which we will only discuss in lecture. These are the cavities created by serous membranes-the pleural cavities, the pericardial cavity, and the peritoneal cavity-and the mediastinum.

Human Body Cavity Diagram Human Body Anatomy
Figure 1.2.1 1.2. 1 : These two people are both in anatomical position. (CC-BY, Open Stax ) When referencing a structure that is on one side of the body or the other, we use the terms "anatomical right" and "anatomical left.". Anatomical right means that the structure is on the side that a person in anatomical position would consider.
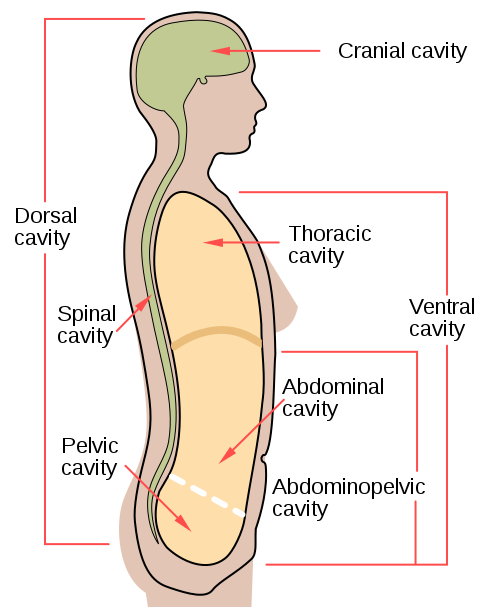
7.6 Human Body Cavities Human Biology
What Are Body Cavities? The human body, like that of many other multicellular organisms, is divided into a number of body cavities. A body cavity is a fluid-filled space inside the body that holds and protects internal organs. Human body cavities are separated by membranes and other structures.
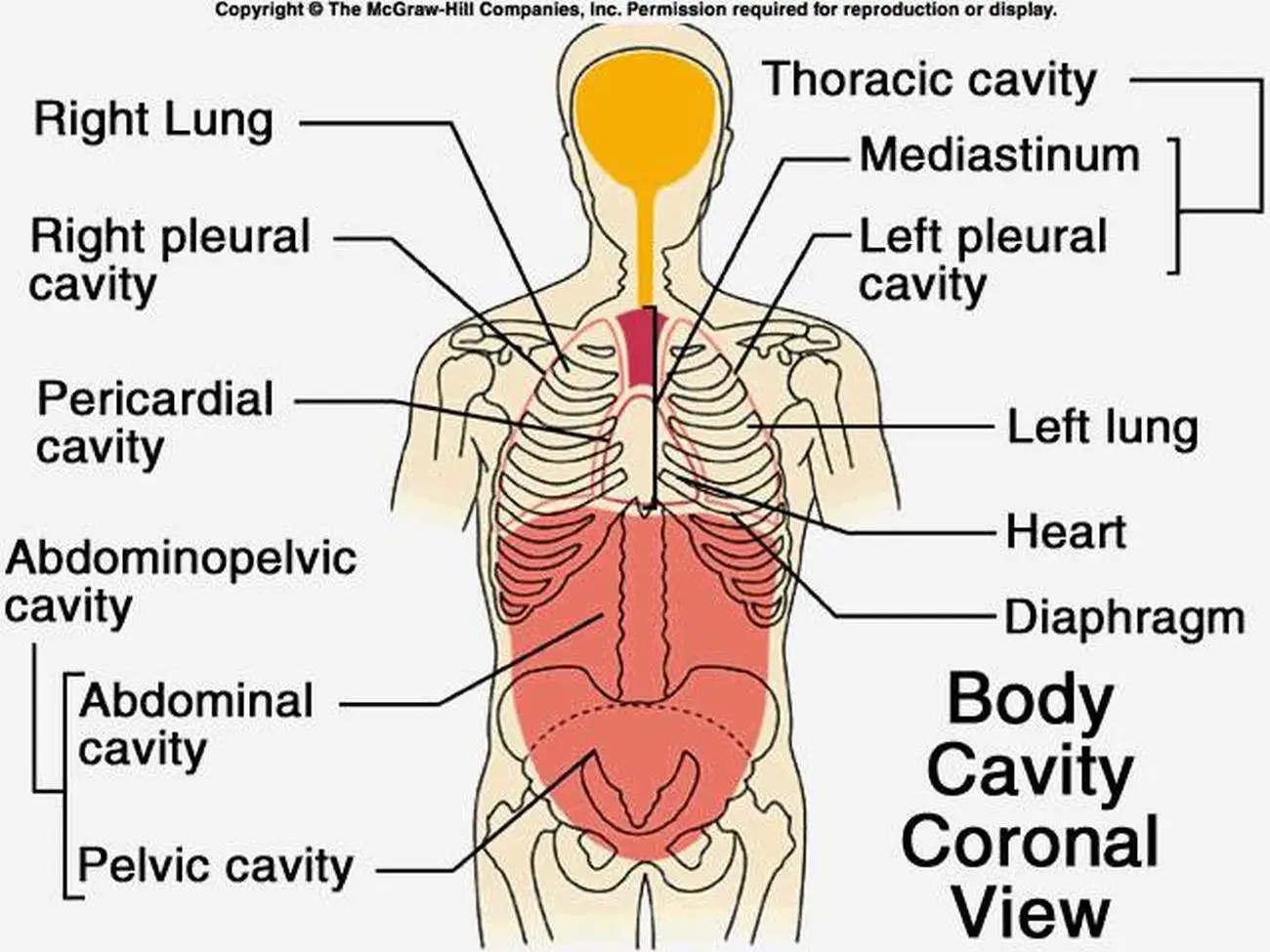
Pictures Of Cavity, Anatomical
Start studying Body Cavities. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.. The cavity located between the upper portion of the lungs + 1 more side. Term. Pleural Cavity. Definition. Contains the lungs + 1 more side. Term. Pericardial Cavity.

Dorsal and other body cavities cross section, outline illustration
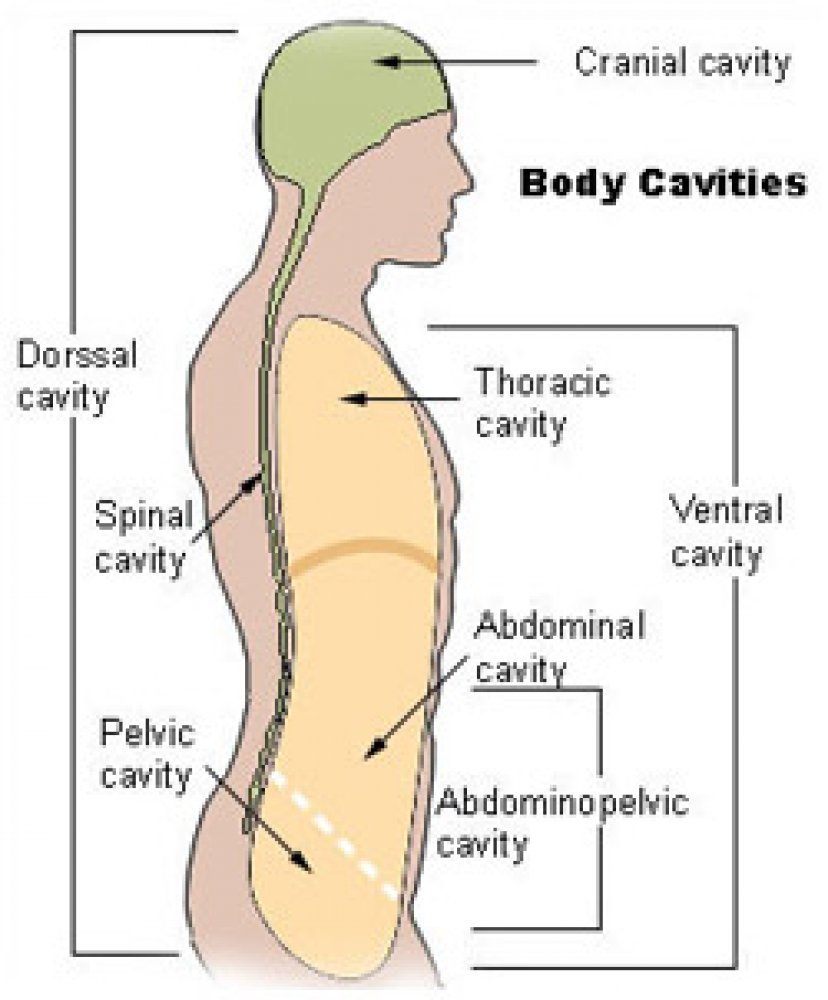
Label the Body Cavities Answers: Front View: 1. Cranial Cavity 2. Vertebral Canal 3. Mediastinum 4. Pleural Cavity 5. Pericardial Cavity 6. Diaphragm 7. Abdominal Cavity 8. Pelvic Cavity 9. Abdominopelvic Cavity 10. Ventral Cavity Side View: 1. Cranial Cavity 2. Dorsal Cavity 3. Vertebral Canal 4. Thoracic Cavity 5. Diaphragm 6. Abdominal Cavity 7.
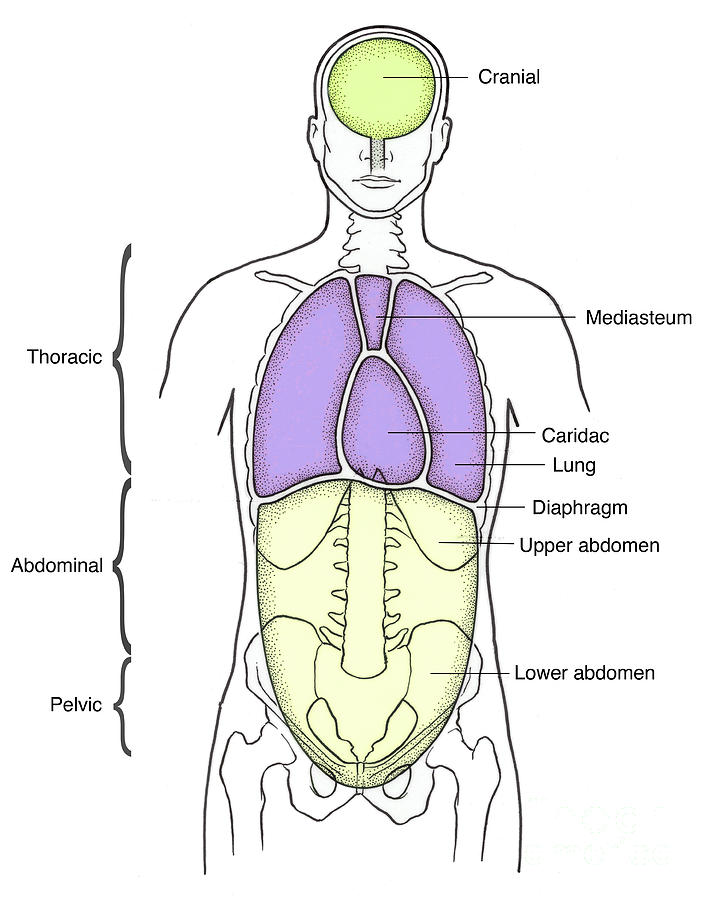
Illustration Of Anterior Body Cavities Photograph by Science Source
A body cavity can be defined as the space that remains after the organs inside it are removed, but this definition does not do justice to the variety and. Schematic diagrams of the bodies of animals with coeloms, with pseudocoeloms, or without body cavities. functions of body cavities. Humans have four body cavities: (1) the dorsal body.

Body Cavities Diagram Quizlet
The walls of the ventral body cavity and outer covering of its organs contain a thin covering called the serosa (also called serous membrane). It is a double-layered membrane made up of two parts called the " parietal serosa " (lines the cavity walls) and " visceral serosa " (covers organs in the cavity). The serous membranes are.

Body Cavities and Organs Biology Dictionary
Anatomy and Physiology Levels of organization of the Human Body Characteristics and Maintenance of Life Homeostasis and Feedback Body Cavities, Membranes, and the 11 Body / Organ Systems Diagnostic Imaging techniques and the different types of microscopes and devices for studying the body WEEK 2
Anatomical Terminology Learnful
Body Cavities and Serous Membranes The body maintains its internal organization by means of membranes, sheaths, and other structures that separate compartments. The dorsal (posterior) cavity and the ventral (anterior) cavity are the largest body compartments (Figure 3.5).