
Frog Anatomy, Illustration Stock Image F031/8303 Science Photo
In order to correctly make a diagram of frog anatomy you could look at a biology book and find pictures of the inside of a frog, or you could do a frog dissection. Frog dissection sounds really gross, but once you get the frog opened it is really very cool. Inside the frog you will be able to see all of the frog anatomy for your diagram.
Frog Dissection Diagram and Labeling
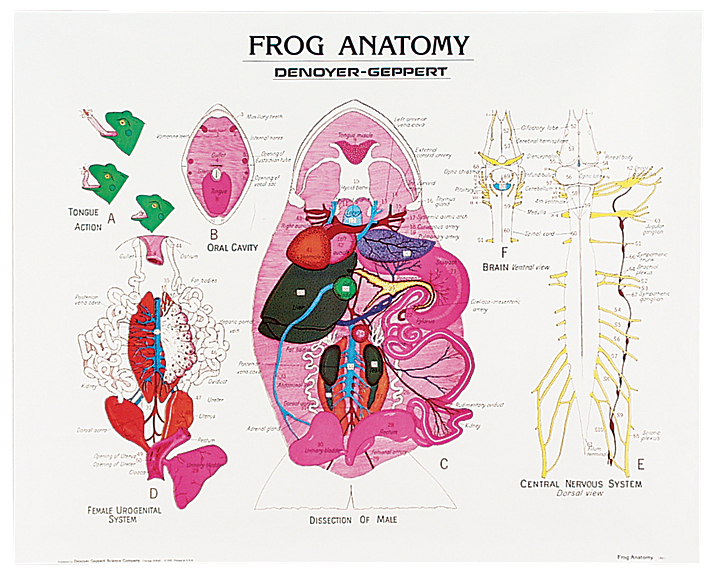
The Urogenital System Kidneys (D): Filter Blood Ureters (G): Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Testes (C): Make sperm Oviducts (B): eggs travel through these Ovary: makes eggs (A) - ovary is often too small to see, but eggs are visible Urinary Bladder (F): Stores Urine Cloaca (E): Where sperm, eggs, urine, and feces exit. © Biologycorner.com
Frog Anatomy Overview 1 Carlson Stock Art
biology Do Frogs Have Internal Organs? © Don Farrall—DigitalVision/Getty Images Like humans, frogs are vertebrates, or animals with backbones. The frog body may be divided into a head, a trunk, and limbs. The flat head contains the brain, mouth, eyes, ears, and nose. A short, almost rigid neck permits only limited head movement.
Frog Anatomy Chart Flinn Scientific
Below is an easy and well labelled diagram of frog ( Rana tigrina) for your better understanding. Anatomy The body plan of frogs consists of well-developed structures which help them in their physiological activities.
Frog Anatomy HD Wallpapers Plus
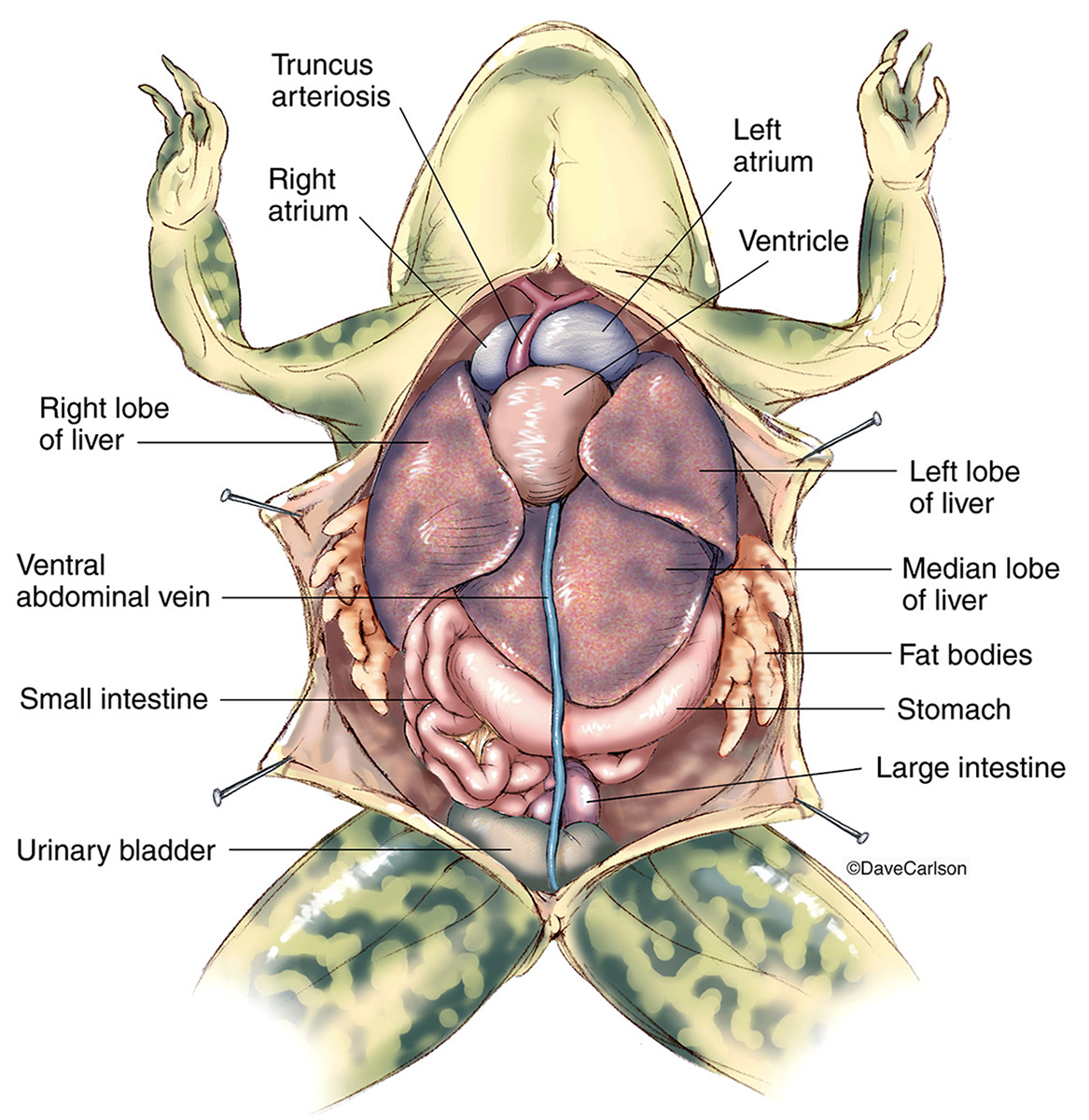
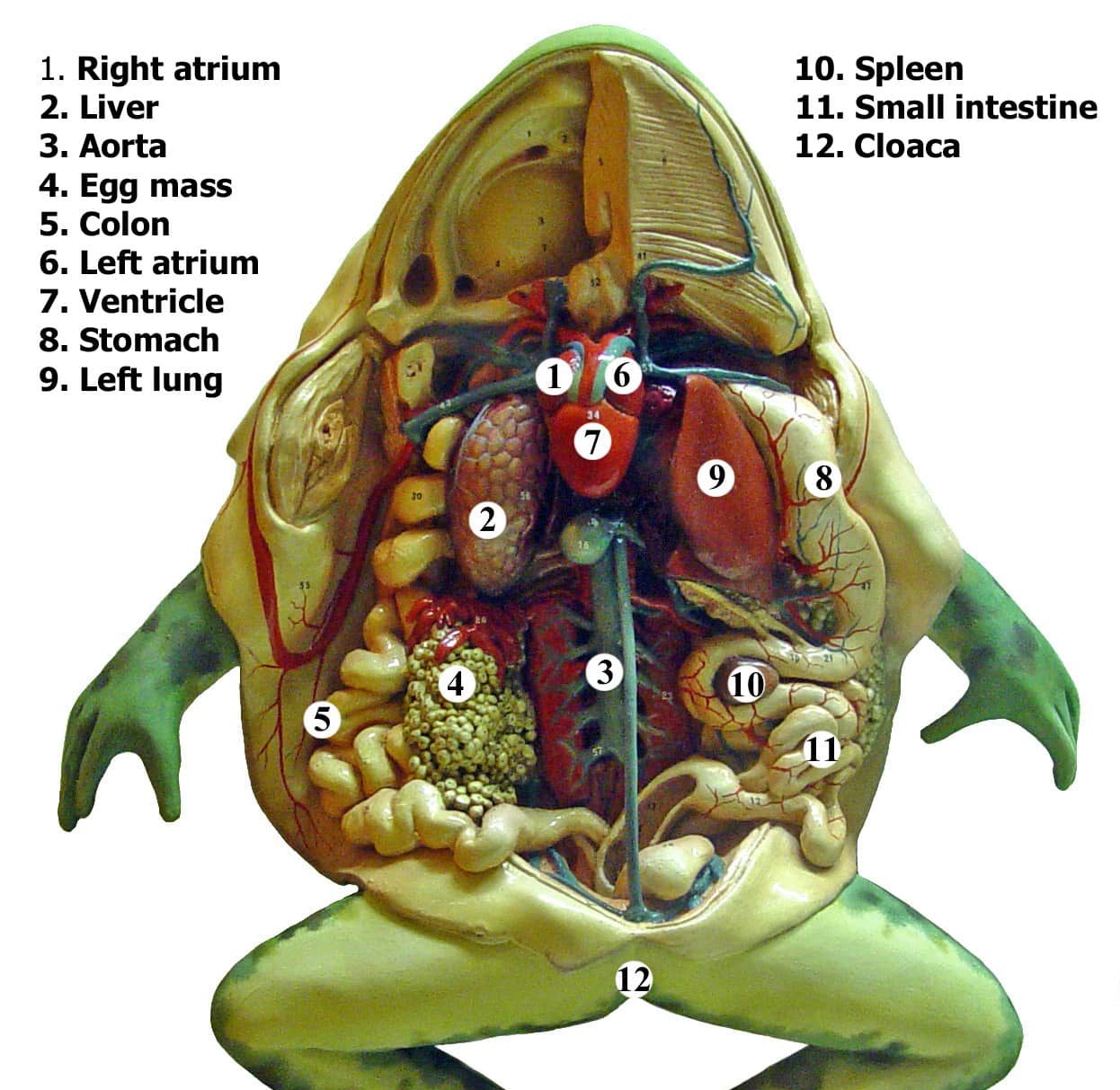
Ribbit ribbit. GIF made using Tours in Visible Biology . Circulatory System The frog's heart is made of three chambers: the left atrium, the right atrium, and the ventricle. The skin and lungs provide oxygenated blood to the left atrium, and veins supply deoxygenated blood to the right atrium.
Anatomy of the Frog Ms. McGee's Science Class
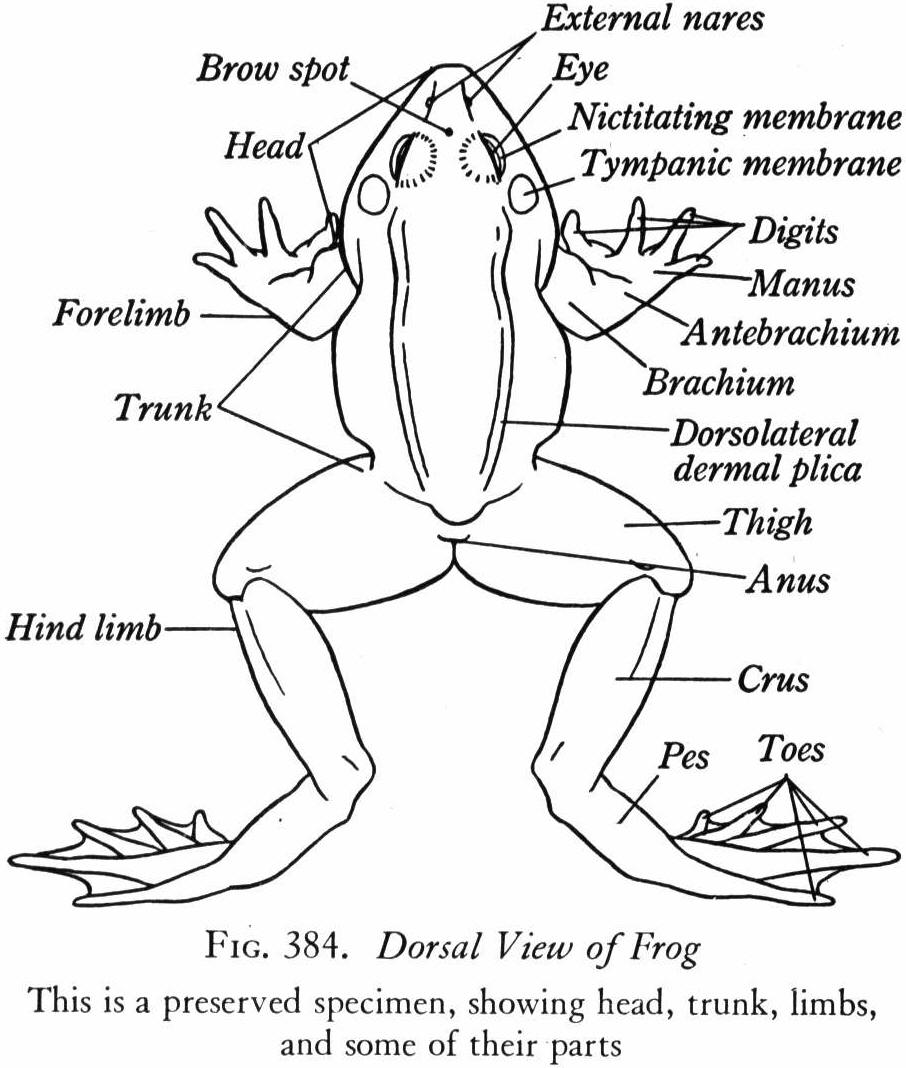
In this article we will discuss about the external anatomy of a frog, explained with the help of suitable diagrams. The body is divisible into two parts—the posterior, short and stout trunk and the anterior, broad, depressed head: There is no neck between the head and the trunk. Tail is absent (Fig. 36.1). Two pairs of limbs, one at the anterior and another at the posterior end of the trunk.
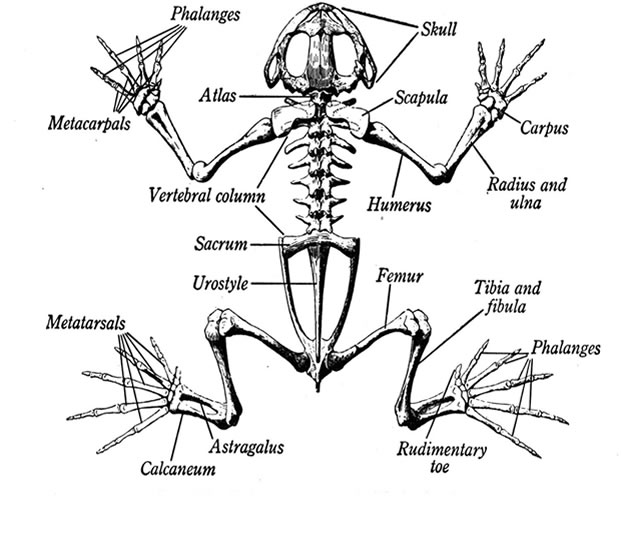
Skeletal Anatomy of a Frog Bones Within A Frog
A diagram showing the external anatomy of a frog. Look at how each limb of the frog contributes to it's everyday movement in life.
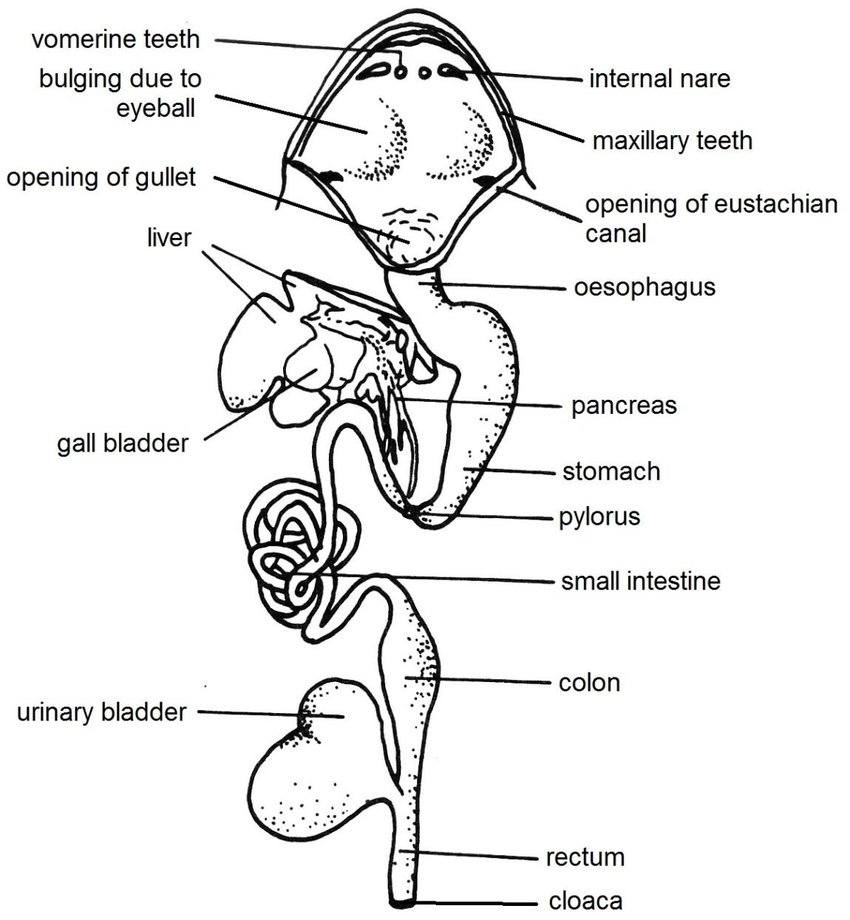
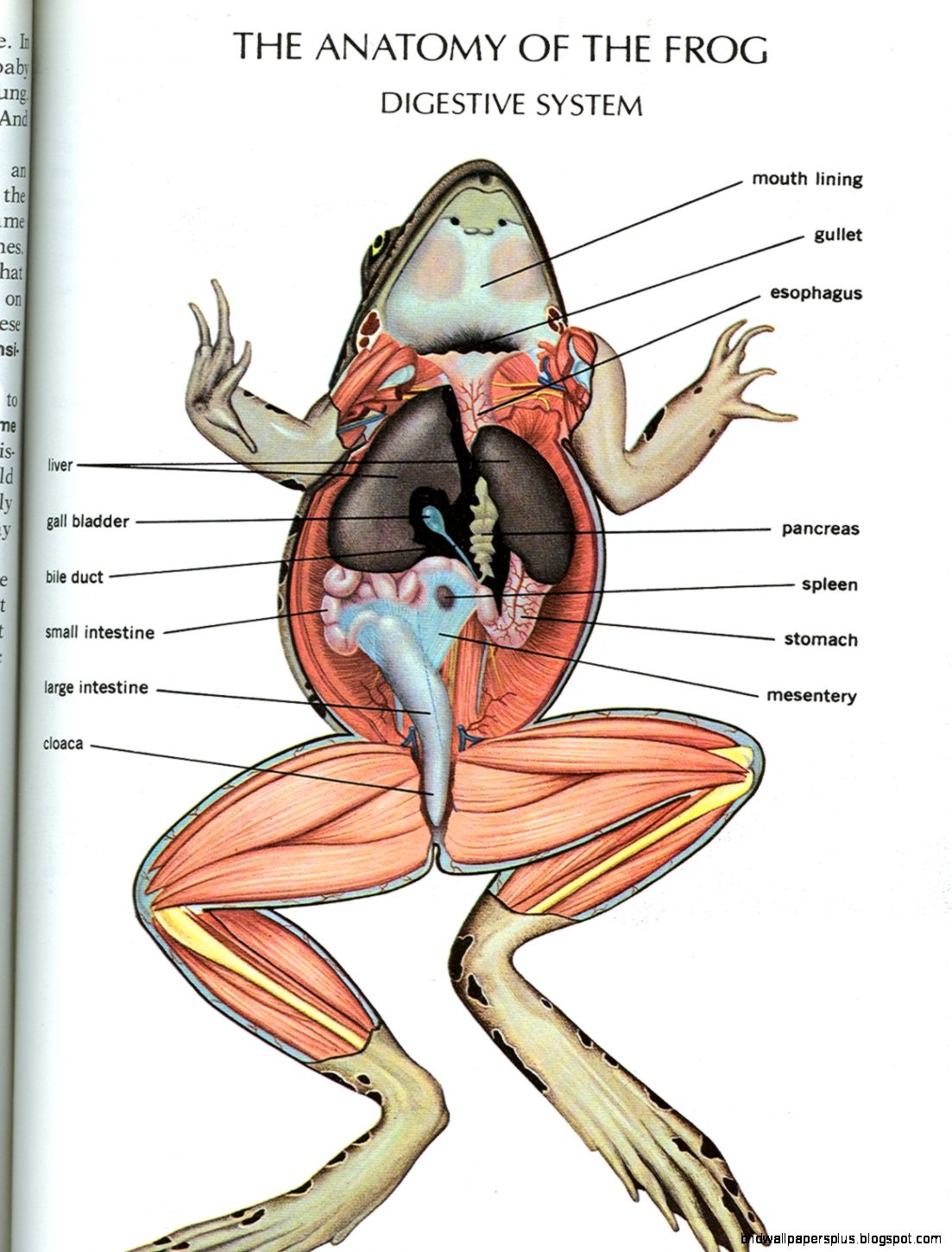
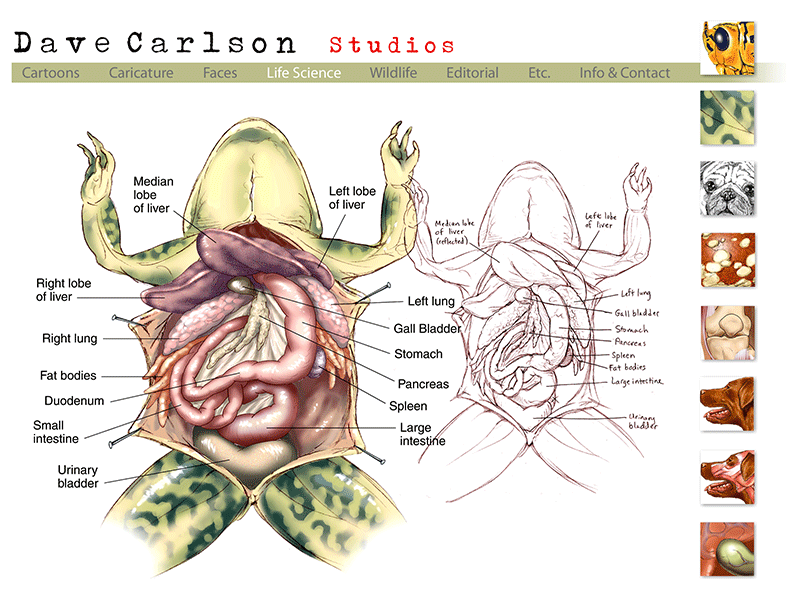
Digestive system of frog Anatomy and Physiology of digestion Online
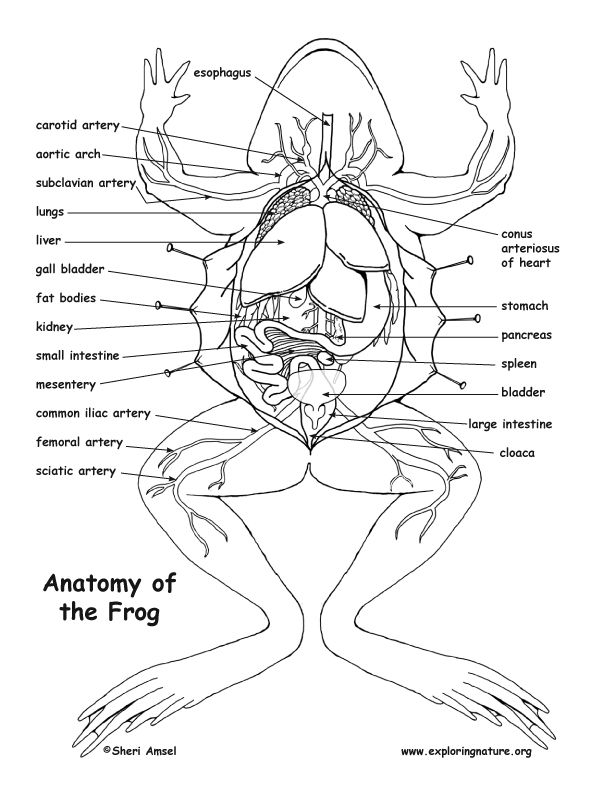
cloaca Label the Anatomy of the Frog esophagus carotid artery aortic arch subclavian artery lungs liver gall bladder fat bodies kidney small intestine mesentery conus arteriosus of heart stomach pancreas spleen bladder common iliac artery femoral artery sciatic artery large intestine cloaca Anatomy of the Frog
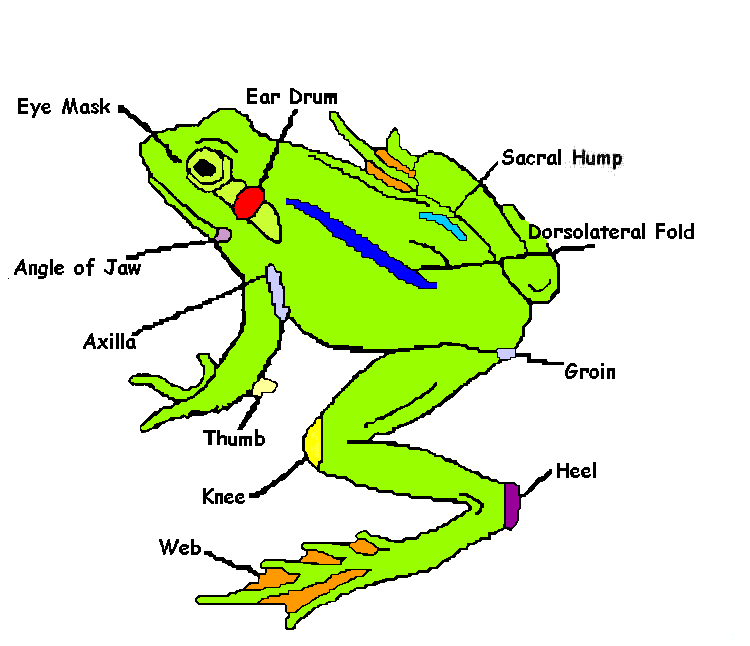
Frog Dissection External Anatomy
Frogs' teeth are not used for chewing! Instead, their special vomerine teeth (shown as 'premaxillary teeth" on the frog anatomy app) are used to hold prey in place before swallowing. The vomerine teeth are notably pointy and appear in pairs of tiny clusters at the top front of the mouth. Elisabeth Ormandy, 2020. 18
Frog Pre Lab/Lab Core 71 Science
Description. A Laboratory Guide to Frog Anatomy is a manual that provides essential information for dissecting frogs. The selection provides comprehensive directions, along with detailed illustrations. The text covers five organ systems, namely skeletal, muscular, circulatory, urogenital, and nervous system.

Morphology and Anatomy of Frogs Internal Systems and FAQs
FROG ANATOMY DIAGRAMS. CLICK ON THE DESCRIPTIONS BELOW TO VIEW PICTURES OF THE FROG DISSECTION. tympanum & nictitating membranes: anatomy of the mouth: liver & lungs: circulatory system structures: gall bladder: intestines : male frog anatomy: female frog anatomy.

Arterial System of Frog Diagram Quizlet
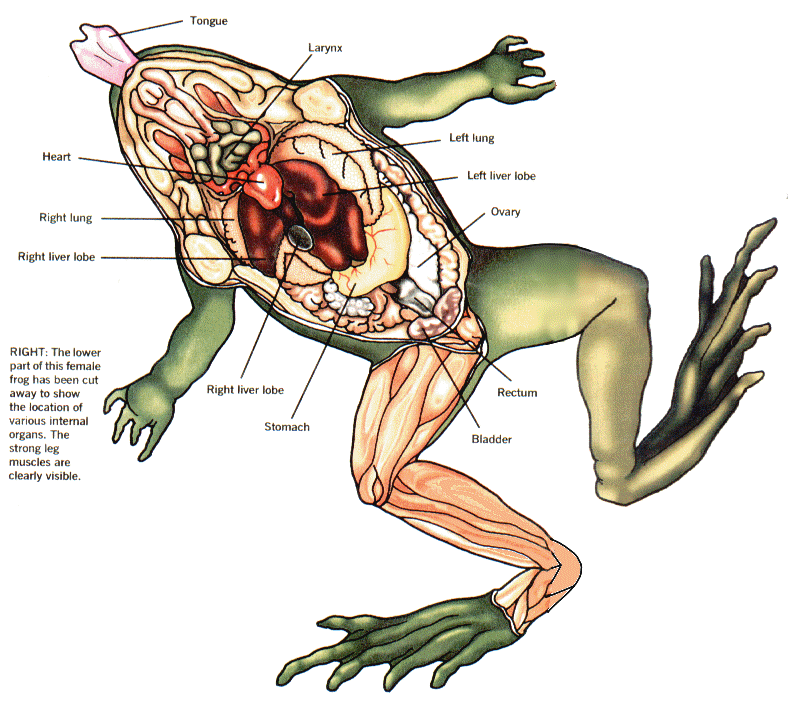
In the abdominal cavity, you can see the liver, stomach, intestines, kidneys, pancreas, fat bodies, testes (male), or ovaries (female). What is the external anatomy of a frog? The external.
All about frogs and toads Wildlife
Structural Organisation in Animals Frogs Probably the best example of an amphibian that you remember right from your childhood is the frog. Did you know just like the butterfly, a frog also undergoes complete metamorphosis.

Anatomy of a Female Common Frog Old Book Illustrations
Very few species on Earth have this ability. Frogs have been found as far back as 250M years ago. As of today, there are over 7,200 identified frog species worldwide. Most of them have similar internal anatomy, regardless of their size. I know you probably have an adult frog on the dissection table so we will get to that in a few seconds.
Anatomy Of A Frog
19 - Anatomy of the Frog. In this lab exercise, you were introduced to vertebrate anatomy through a frog dissection. Consult your lab manual for the organs that you will need to recognize on the frog dissection and model and know their functions. You will be expected to be able to identify the muscles of the hind limb and know their actions. In.

a frog with its mouth open and tongue out
Internal Anatomy Of A Frog The body cavity of a frog accommodates different organ systems such as circulatory, digestive, excretory, respiratory, nervous, and reproductive. Each organ system has well-developed structures and designated functions. A detailed study of the internal organs of a frog is what anatomy is all about.