
Parts of a tree CLIL Science Pinterest
The given anatomy of a tree will walk you through the details of each part to let you get some education: 1. Crown. The canopy or crown stands on the peak of a tree, where leaves, branches, fruits, and flowers reside. From here, every tree is prone to release oxygen, absorb Co2, create nutrients, and conduct photosynthesis.
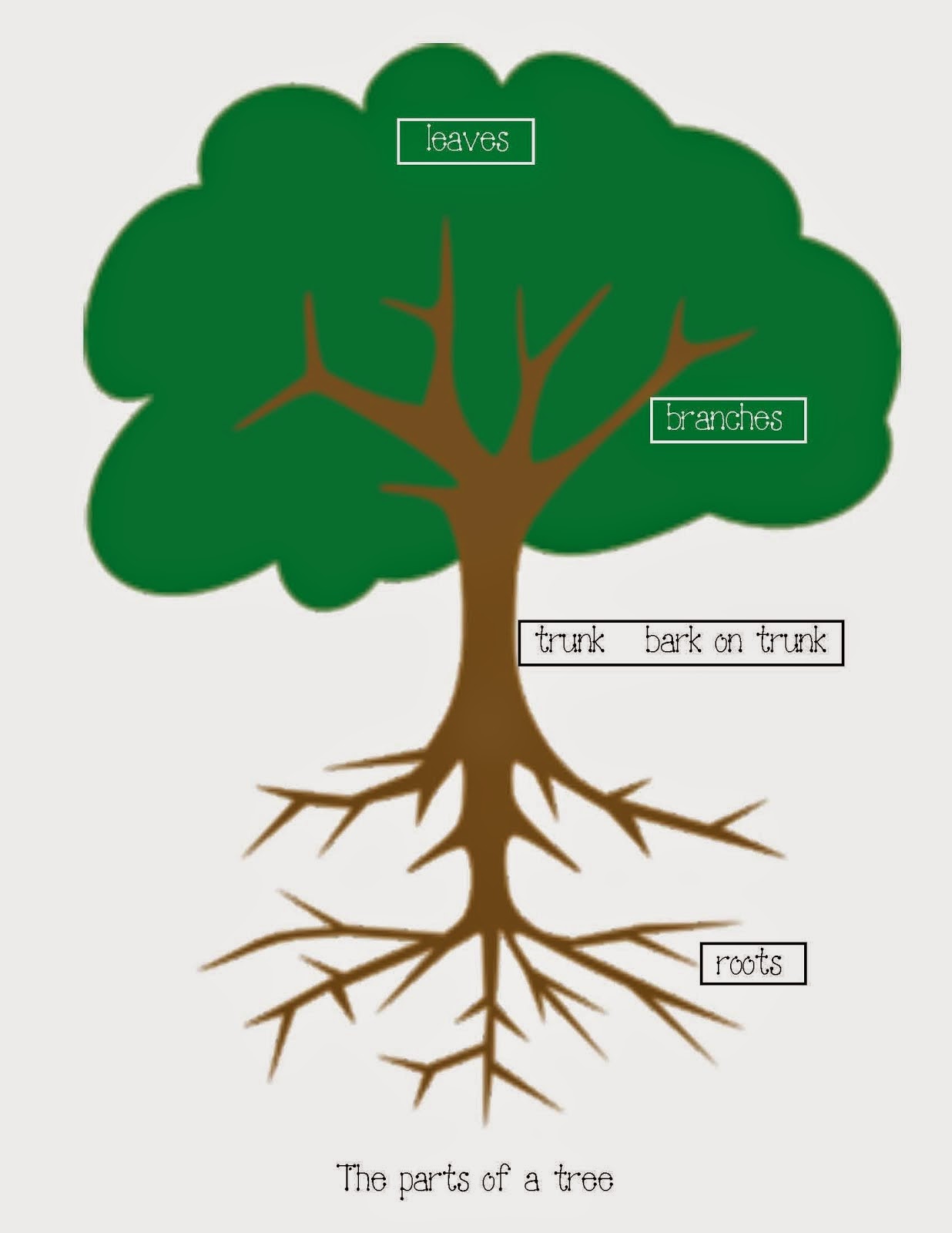
ESL and Close Reading, A Work in Progress! Parts of a Tree
Trees have limbs, trunks and roots. Think of the limbs like our arms, the trunks like our bodies and the roots as our feet. NPS Image / Kelly Savannah How you ever noticed how similar we are to trees? Trees are living organisms just like us who need nutrients, air, water and sunlight to survive.
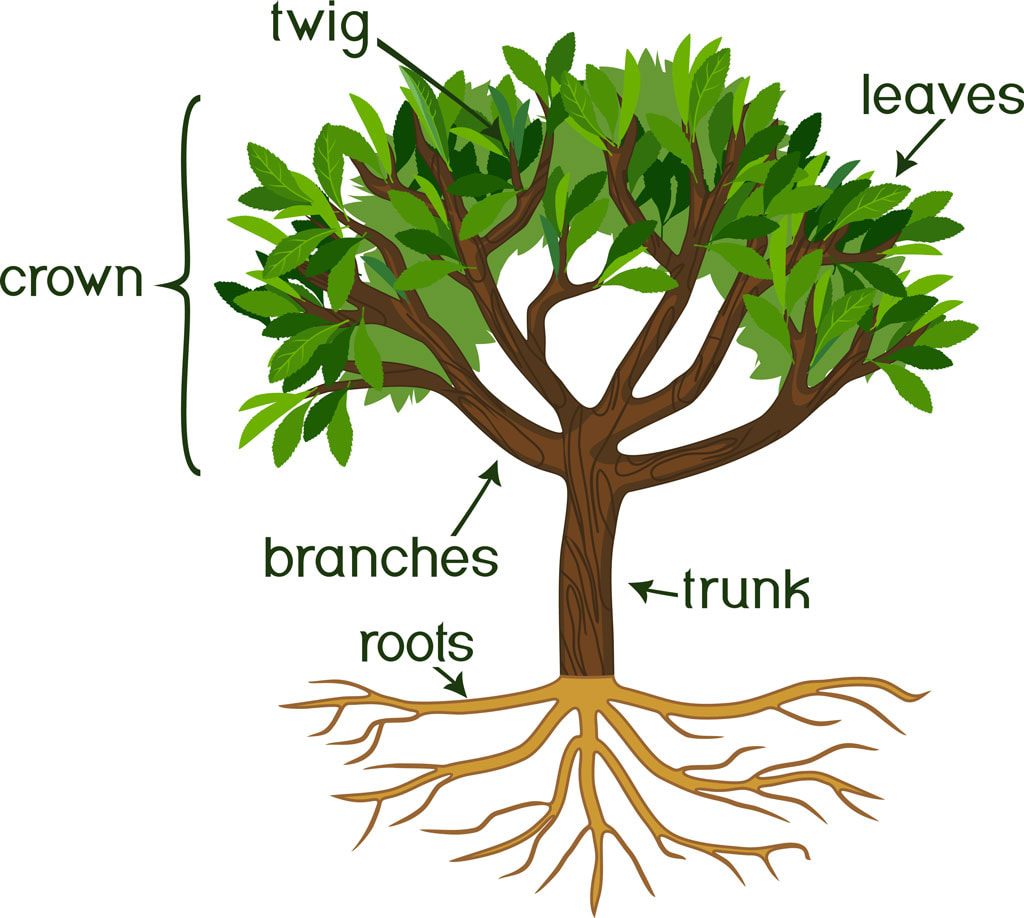
Basic Tree Anatomy The parts of a tree, and their function Snohomish
The three key parts of a tree and their functions are: The roots anchor the trunk and crown of the tree and make them stable. They also take up water and nutrients from the soil and serve as a store for carbohydrates. The trunk, branches and stems of the tree give the tree height so the leaves can capture as much light energy as possible.
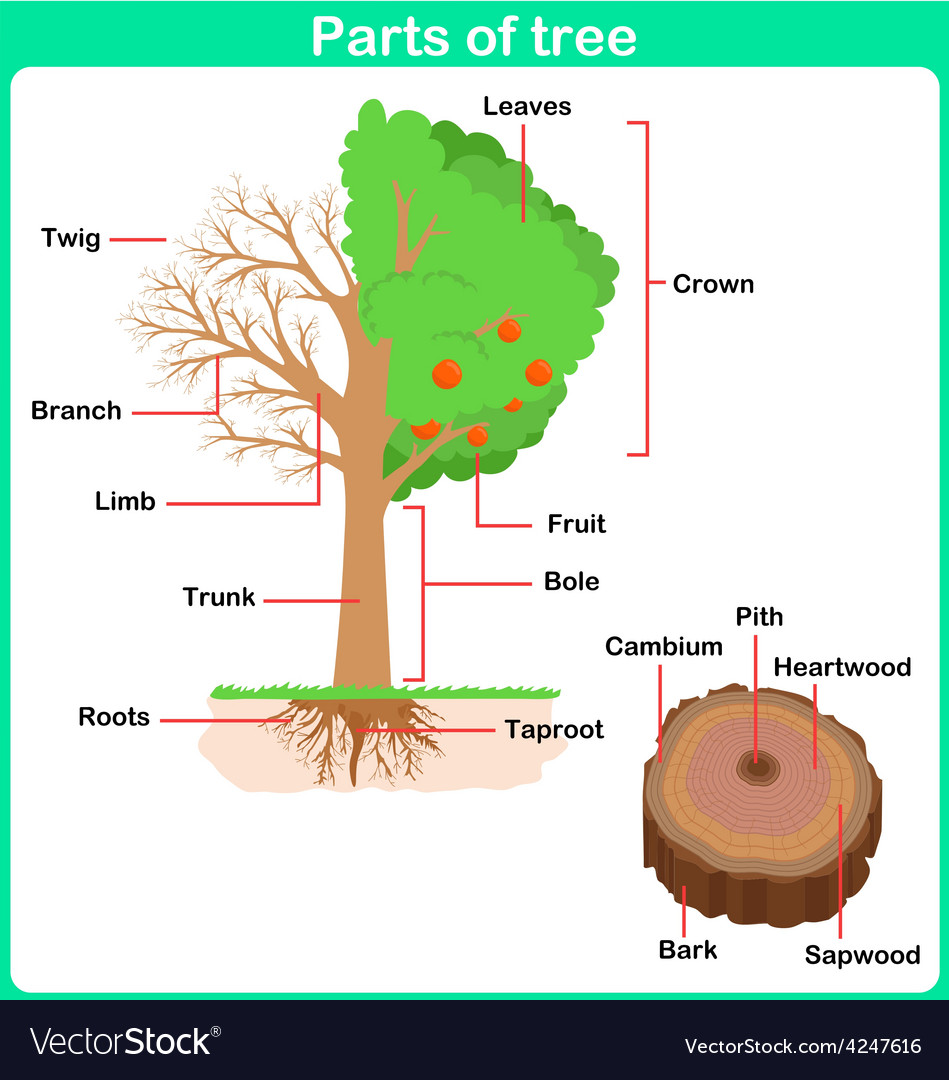
Parts Of A Tree Worksheet
Basic grade school education explains that the trunk, roots and leaves are the most commonly identified parts of a a tree, but there are some additional cool things about the trunk anatomy and cambium layers that you may not know.
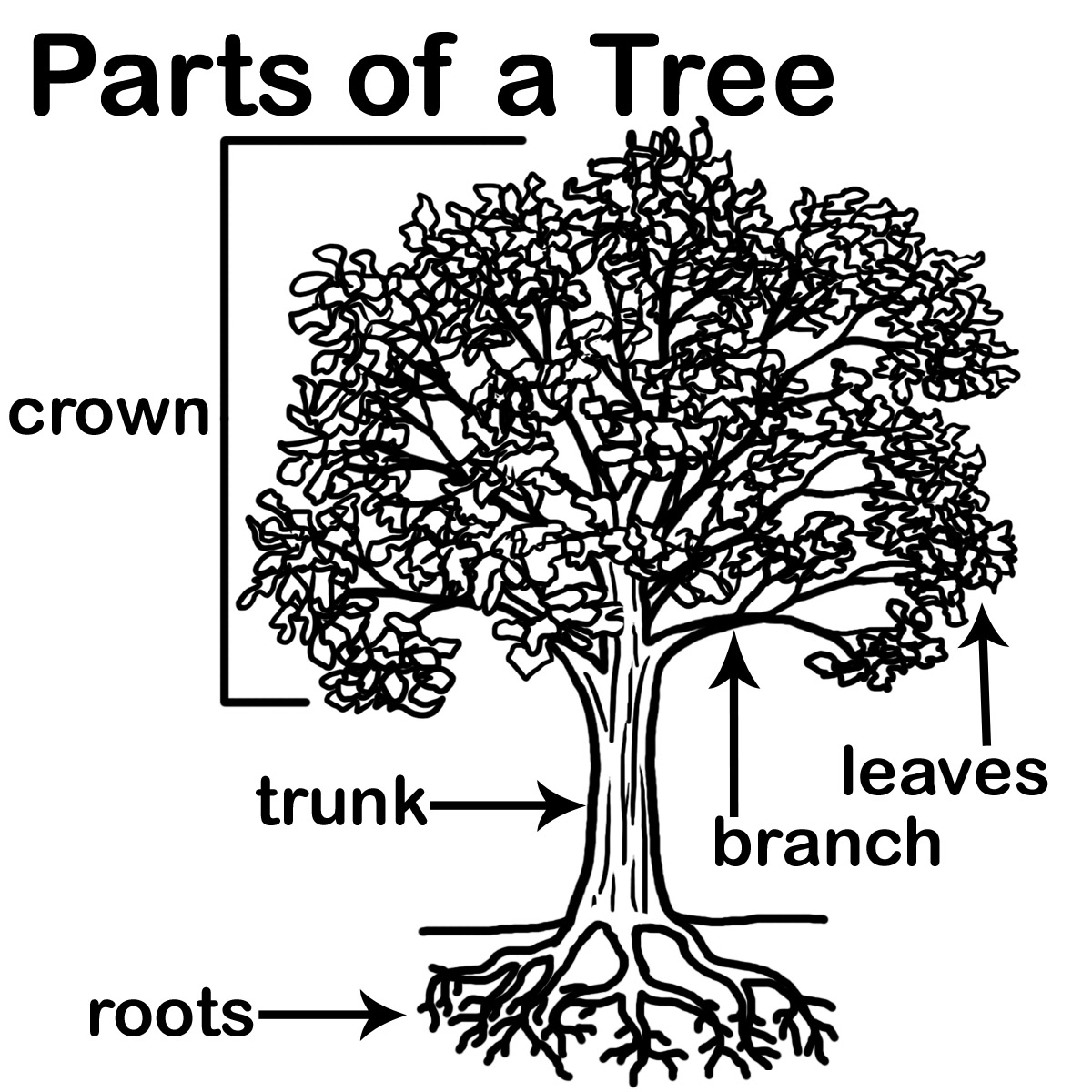
9 Label The Parts Of A Tree Worksheets Kindergarten /
Leaves. First, they are the food factories of the tree, using the sun's energy to convert the carbon dioxide in the air into sugar and oxygen. The green material in leaves is called chlorophyll and is essential in photosynthesis. The sugar provides food for the tree, allowing it to grow. Leaves release water and oxygen into the atmosphere.

FuN wITh EngLisH The parts of a tree
A mature tree consists of three main parts, the roots, the trunk and the crown. Catch a quick glance at the different parts of the tree. The root system Beginning with the things closer to the ground, so, let us look at the roots of a tree, first. Roots are sophisticated systems that reside underground and thus, are not apparent to the naked eye.

parts of tree English For Life
Tree structure and growth Uncover the science behind the growing width and height of a tree Learn why there are limits on a tree's height but not its width; included is a discussion of the growth ring. (more) See all videos for this article

Parts of a Tree and Their Functions Science Facts
In fact, this part of the tree is so strong that just a small piece of heartwood could support as much as 20 tons thanks to a natural glue called lignin that holds everything together. Lifecycle of a Tree. Just like animals and other plants, trees go through various stages of life which combine together to create its entire lifecycle..
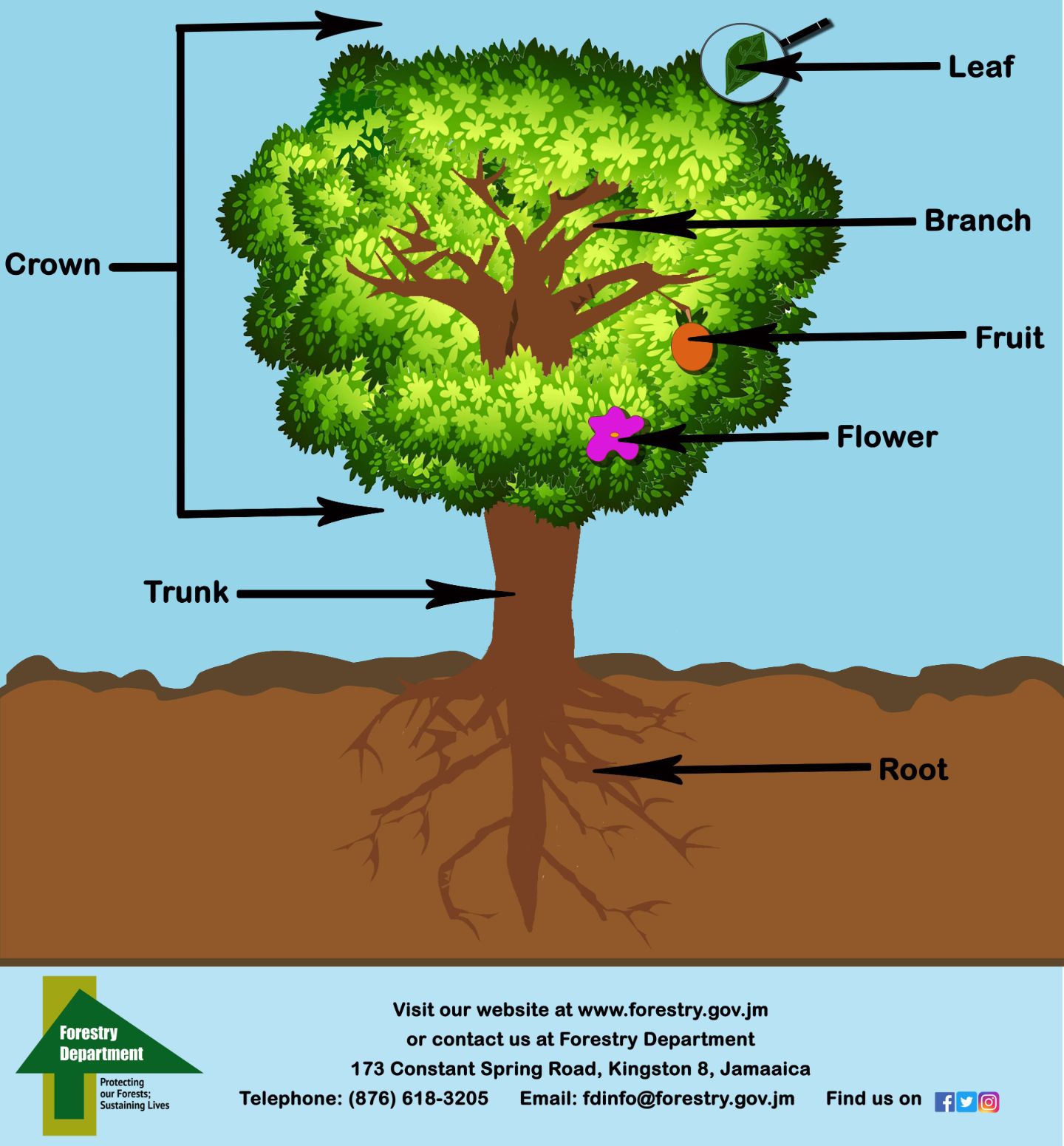
ForestryDepartment Early Childhood
A mature tree has three basic parts: 1) roots, 2) crown, and 3) trunk or bole. Although the structure of these parts may vary based on the altitude and geographical position of the tree, each of them performs distinct functions. 1) Roots Roots are the underground part of a tree.
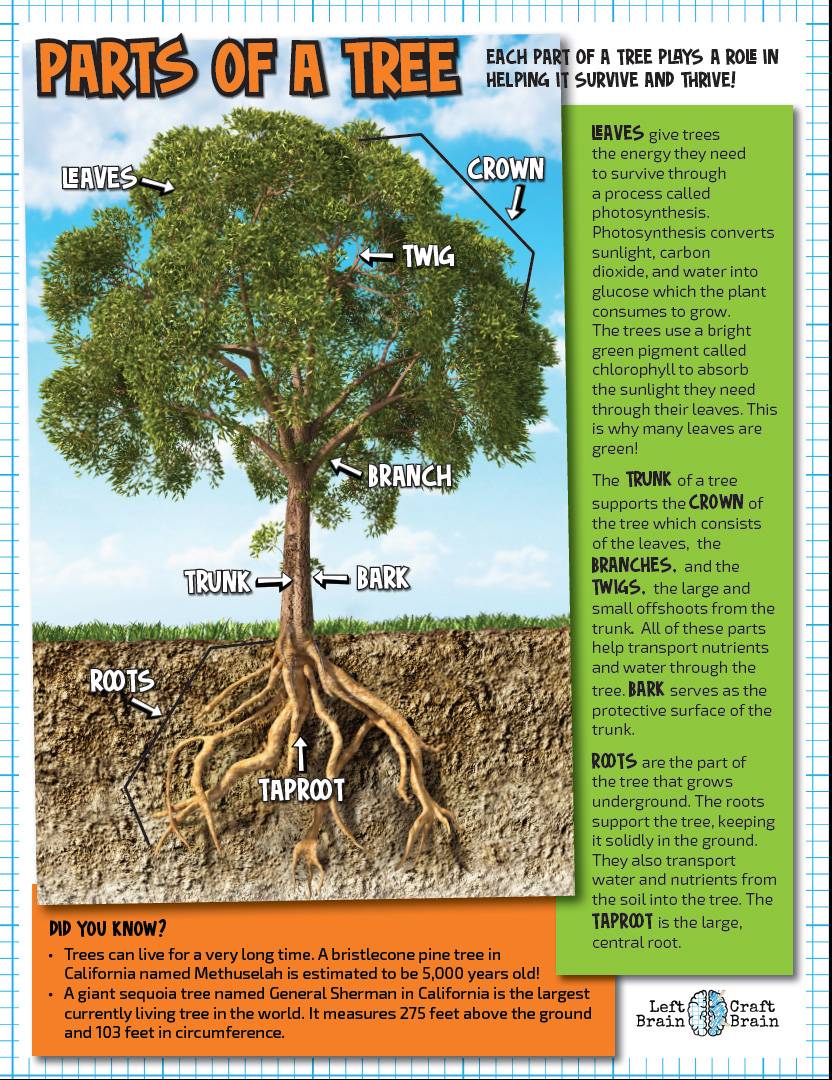
Printables Parts of a Tree HP® Official Site
How does a tree live, grow, and survive? Objective Students will be able to identify the basic parts of trees and understand how they help the tree to live and grow. Background This lesson plan can be found on the USFS website as part of the FireWorks Curriculum.
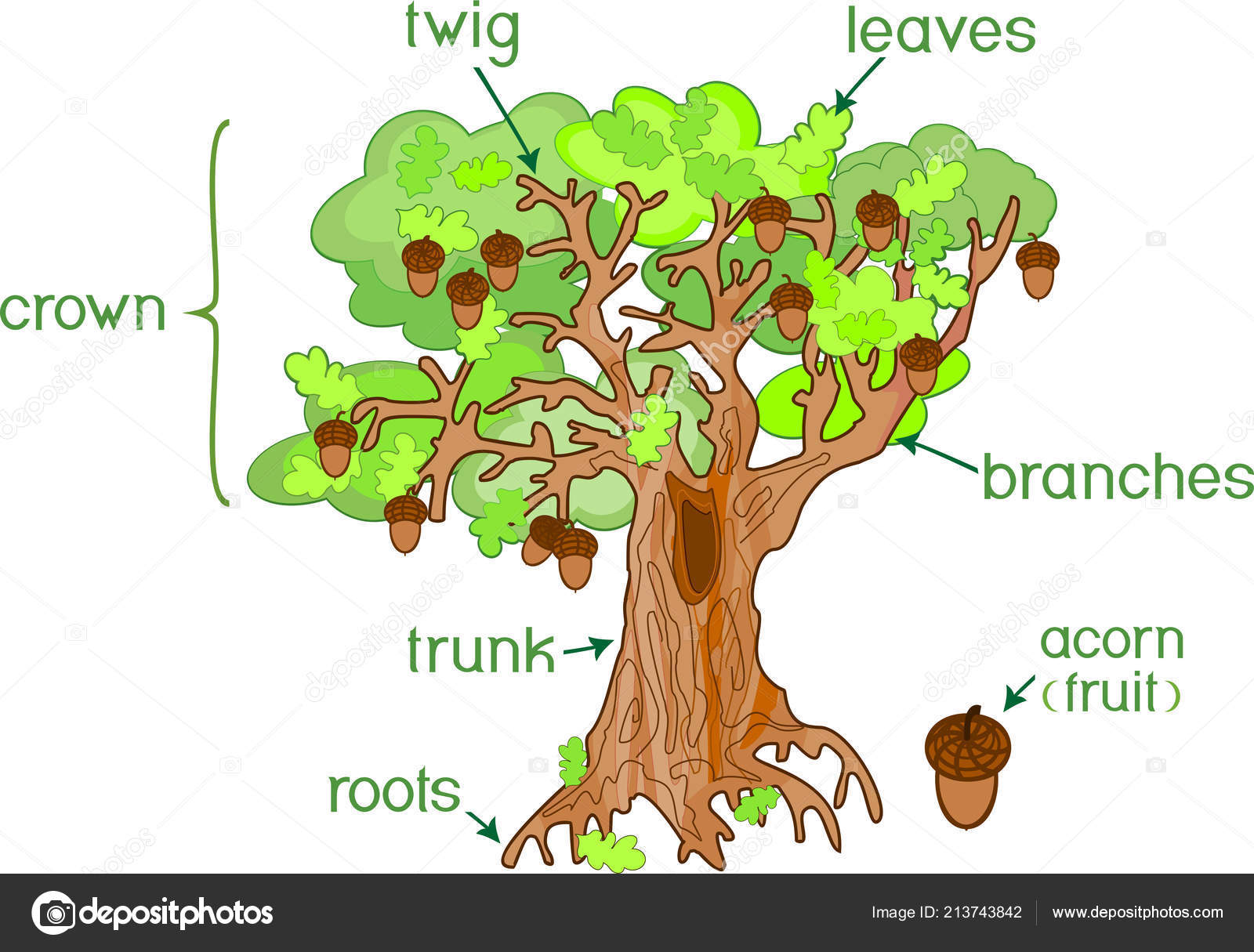
Parts Plant Morphology Oak Tree Acorns Green Leaves Root System Stock
A piece 12" long and 1" by 2" in cross section set vertically can support a weight of twenty tons! Leaves make food for the tree, and this tells us much about their shapes. For example, the narrow needles of a Douglas fir can expose as much as three acres of chlorophyll surface to the sun.
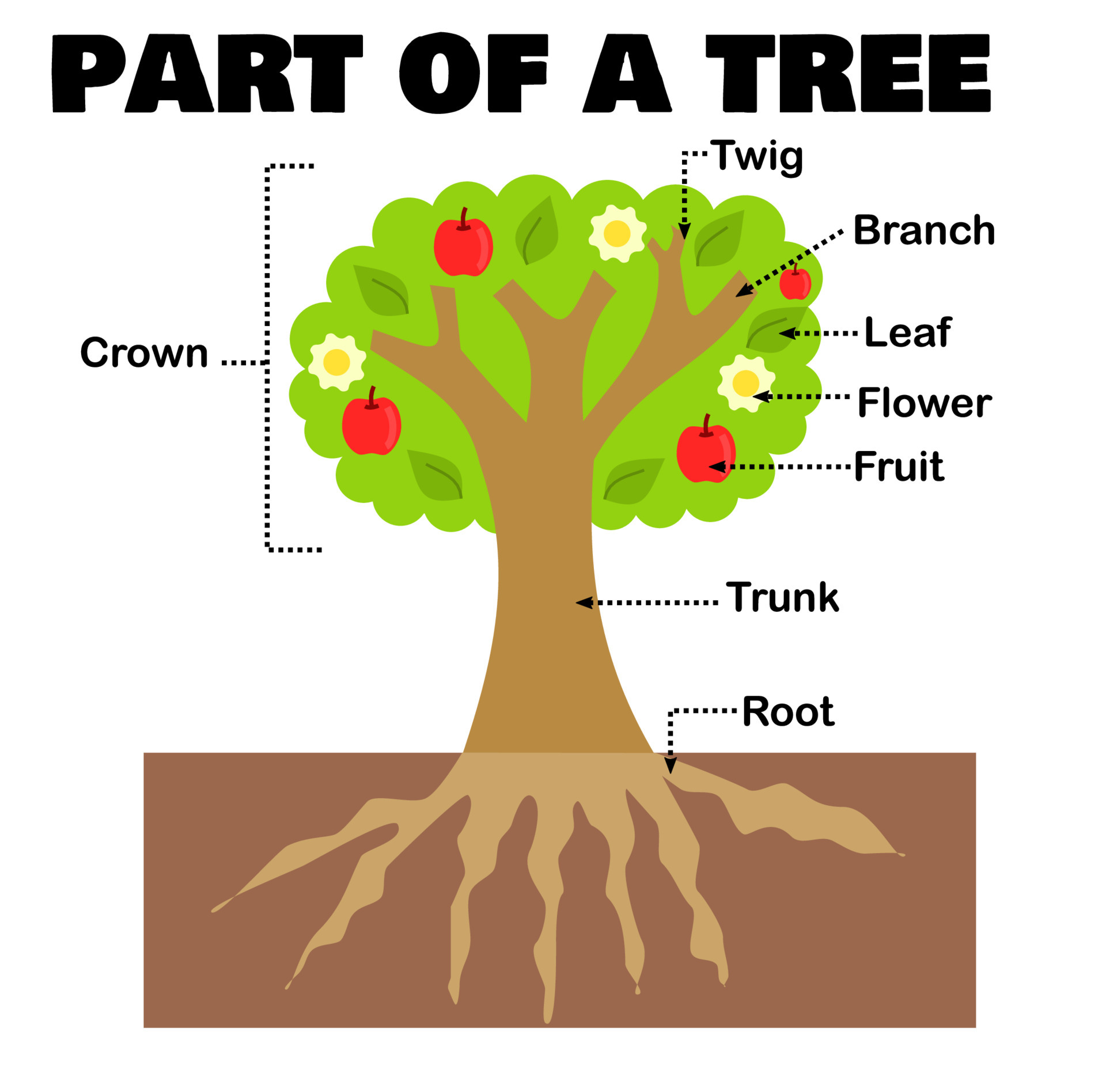
Part of a tree or plant for science and education.Worksheet for kids
What Is a Tree? A tree is any woody plant that can reach a height of 15 feet or more at maturity and that usually is single-stemmed and has a crown, or branched-out area at the top. That distinguishes trees from shrubs, which are woody but short and multi-stemmed, and from vines, which may be long and woody but lack a crown. Minnesota's Own
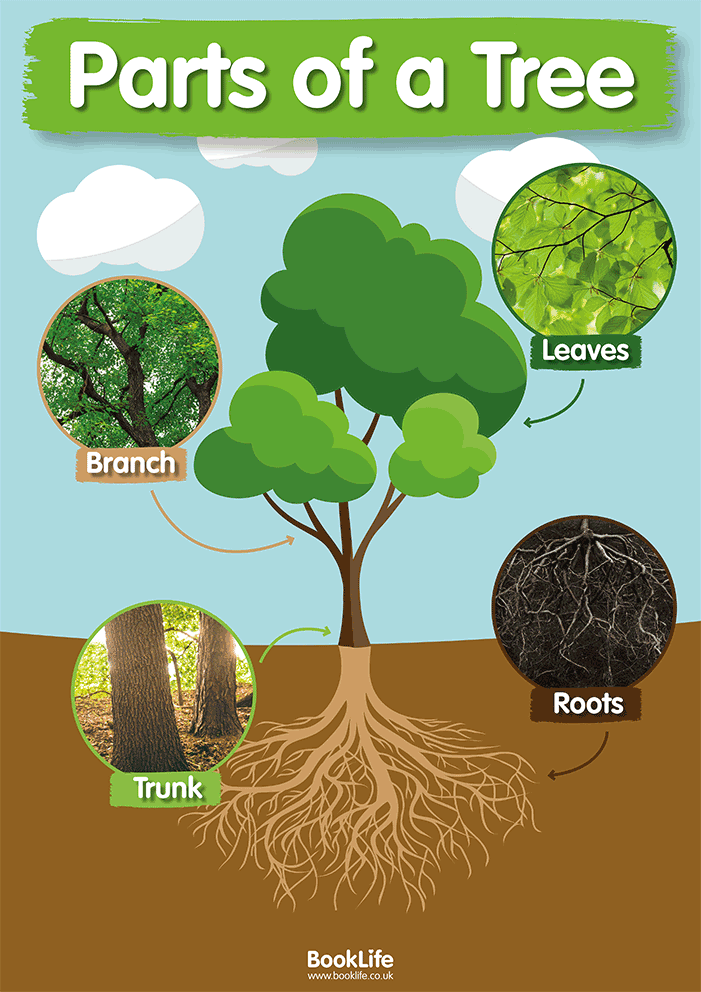
Parts of a Tree Poster BookLife
Updated November 14, 2018 By Jocelyn Kerr All trees share these three basic parts, no matter what type of tree you're examining. From palm trees with their expansive, shallow fibrous root system to giant redwoods hundreds of feet tall, every tree has the same three elements: the root system, a trunk and a crown.

A Flock of Pixels Trees in diagrams
Center The trunk is riddled with tiny tubes that run between the roots and the crown of the tree, pumping nutrients and water up into the leaves. The very center core of the trunk is called the heartwood and is the densest part of the tree. It must have a strong central structure to support the sapwood around it and the branches above it.

parts of a tree branch Yong Knowlton
The main parts of a tree and their purposes are: Roots Tree roots comprise an entire system which is almost completely underground in the case of most tree species. While the roots typically do not extend any further than 12 to 18 inches below the surface of the ground, they can spread outwards to be double the size of the tree canopy.

CIUDAD DE CÓRDOBA 3º SCIENCE BLOG PARTS OF A TREE
The 9 Parts of a Tree (With Pictures) December 23, 2022 by Anna Lad Trees are habitats for thousands of species. Birds hot between their branches, lichens grow quietly on the bark of their trunks, and fungi connect worlds of rootlets underground. Have you ever wondered about the parts of the tree?