
skeletal rabbit anatomy
Natural history. While the European rabbit is the best-known species, it is probably also the least typical, as there is considerable variability in the natural history of rabbits. Many rabbits dig burrows, but cottontails and hispid hares do not.The European rabbit constructs the most extensive burrow systems, called warrens. Nonburrowing rabbits make surface nests called forms, generally.

Rabbit skeletal structures Diagram Quizlet
Like other species, rabbits are composed of eyes, noses, ears, lips, and other body systems. All parts of their body work as one to help your pet function effectively. According to the American Association of Anatomy, the word " anatomy " is the study of the body structure in humans, animals, and plants.
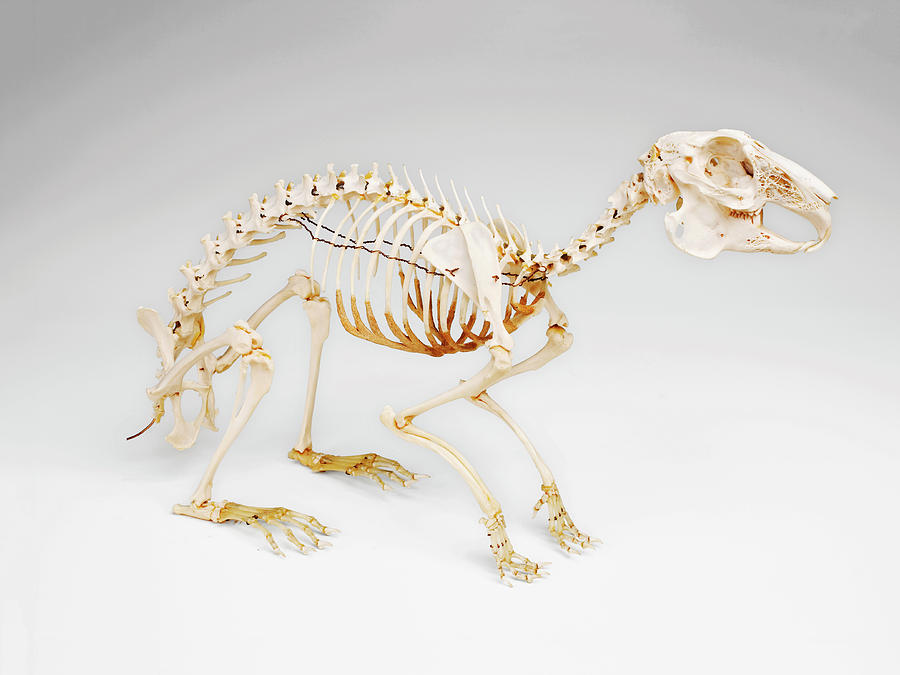

Rabbit Skeleton Photograph by Ucl, Grant Museum Of Zoology Pixels
Parts of the Rabbit skeleton It is important to learn the skeletal anatomy of a rabbit to understand where the bones are in relation to the external anatomy. You also should know the skeletal structure to be knowledgeable about what bones you are feeling when examining a rabbit. Knowing the skeletal anatomy can help you select better rabbits.

Anatomy Of The Rabbit Anatomical Charts & Posters
Part of LafeberVet's Rabbit Basics Teaching Module, the Rabbit Anatomy Basics slideshow is a 22-minute recording designed to impart a basic understanding of rabbit anatomy for the veterinary technician and veterinary nurse.

Full Color Art Paper Laminated Skeleton Of Rabbit For Zoology Chart
CLASS SET Rabbit Anatomy - Rabbit Body Systems Rabbit Anatomy - Body Areas Rabbit Anatomy - Systems Rabbit Skeletal System Rabbit Muscular System Rabbit Digestive System Rabbit Respiratory System Rabbit Cardiovascular System Rabbit Urogenital System Urinary System Reproductive System Rabbit Dental System Rabbit Sense System Eyes Nose Ears

4.12 shows the rabbit skeleton. The bones used in this study were the
Rabbits' skeletal structure consists of a short spine, powerful hind legs, and long ears. Their hind legs are strong and muscular, allowing them to leap up to three feet in the air. The ears, meanwhile, are long and mobile, allowing them to detect predators from far away.

4.12 shows the rabbit skeleton. The bones used in this study were the
AnatomyStuff 330 subscribers 4 698 views 11 months ago Learn the names and placements of a rabbit's internal organs with our new video. Discover more with our free resources section on our.

Rabbit Skeletal Structure Diagram Quizlet
The rabbit's skeleton is delicate in relation to its size. The skeleton makes up approximately 8% of their body weight in comparison to a cat, whose skeleton repre-sents 12-13% of its body weight (Cruise and Brewer, 1994). Strong epaxial muscles in the presence of a rela-tively weak lumbar spine predisposes rabbits to frac-

Parts of the Rabbit skeleton
Rabbits have two pairs of incisors in the maxilla, and one pair in the mandible which has enabled zoologists to clearly distinguish between rabbits (and lagomorphs in general), and rodents that only have one pair in the maxilla and one pair in the mandible.

Rabbit Skeletal System On White Background Stock Vector (Royalty Free
Husbandry Etymology The mammalian order Lagomorpha consists of two living families: Leporidae (rabbits and hares) and Ochotonidae (pikas) (Fig. 12-1). The scientific name for the Old World or European rabbit from which all domestic breeds originate is Oryctolagus cuniculus.
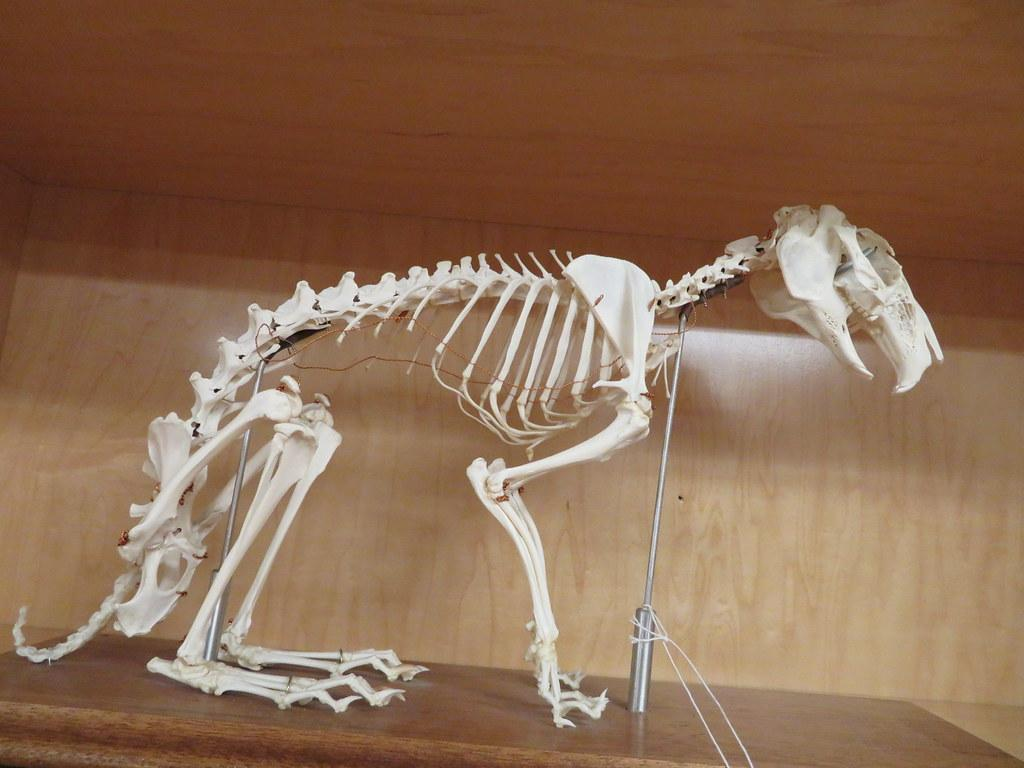

Total number of bones in appendicular skeleton of rabbit is(A) 128(B
In rabbits, the skeleton is very light weighted and brittle which contributes only 7-8% to total body weight . But the bones have a higher content of calcium, whereas the muscle mass accounts for half of the body weight. The skeletal system consists of the axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton . The axial skeleton of the rabbit is composed.

Scientific Illustration Rabbit skeleton, Skeleton anatomy, Rabbit anatomy
There are 23 types of bones that make up a rabbit's skeleton: Cranium, scapula, spine, fibula, tibia, femur, ilium, sacrum, caudal vertebrae, calcaneus, tarsus, metatarsus, phalanges, ulna, ribs, radius, carpus, metacarpus, sternum, cervical vertebrae, atlas, mandible and maxilla. Composition

Rabbit Description, Species, & Facts Britannica
Figure 1. Body planes and directions. Safety Wear safety glasses or goggles, gloves, and a lab apron when dissecting the specimen. Perform the dissection only on the dissection tray. Follow proper hygiene practices before, during, and after the lab. External Anatomy Lay your specimen on its ventral surface. Examine its exterior carefully.
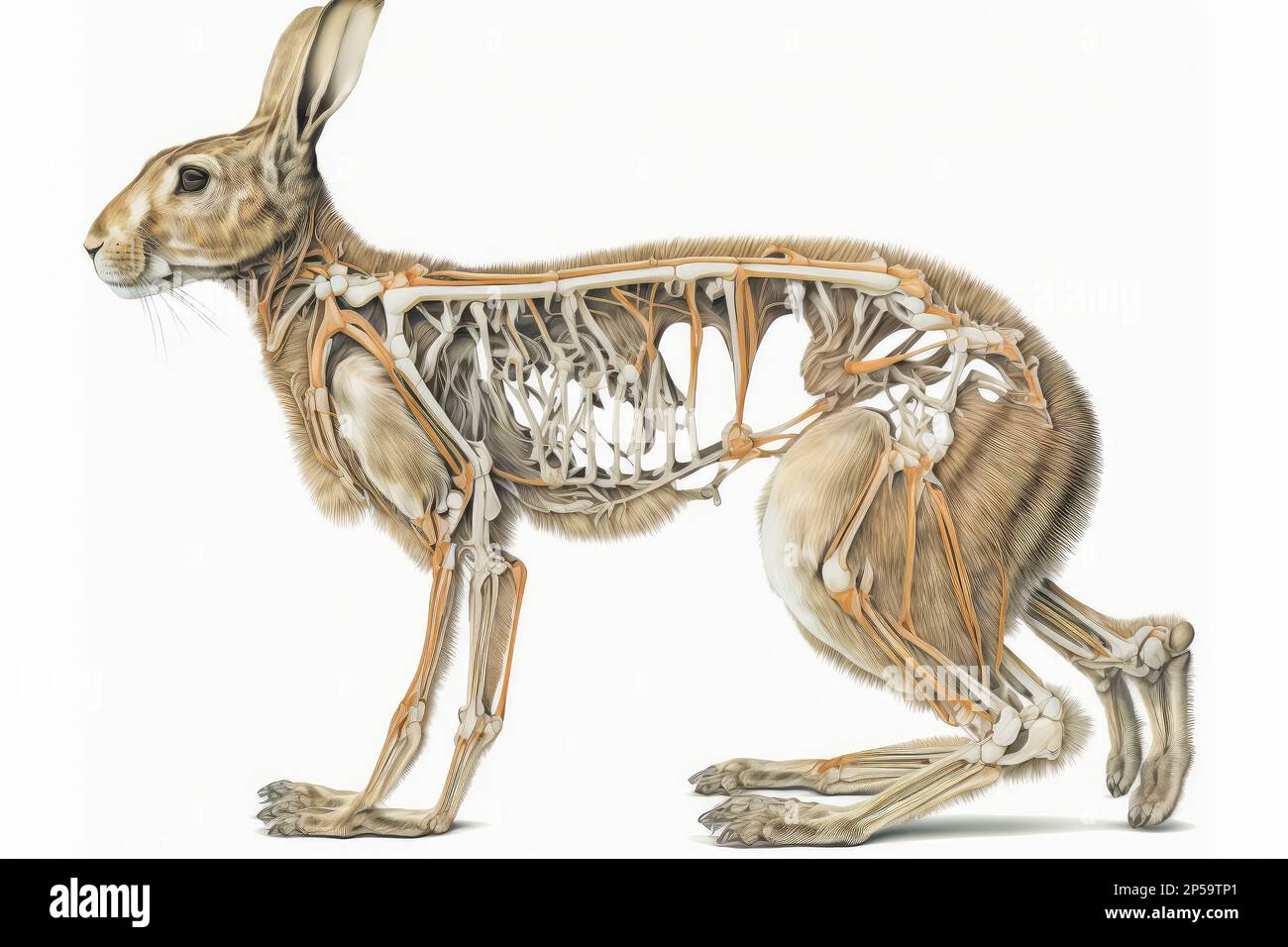
Rabbit Skeleton anatomy 3D rendering Stock Photo Alamy
Domestic rabbits, Oryctolagus cuniculus, belong to the order Lagomorpha, and their ancestors are from Western Europe and northwestern Africa. 1, 2 Unlike rodents, lagomorphs have a second set of maxillary incisors directly caudal to the first set.
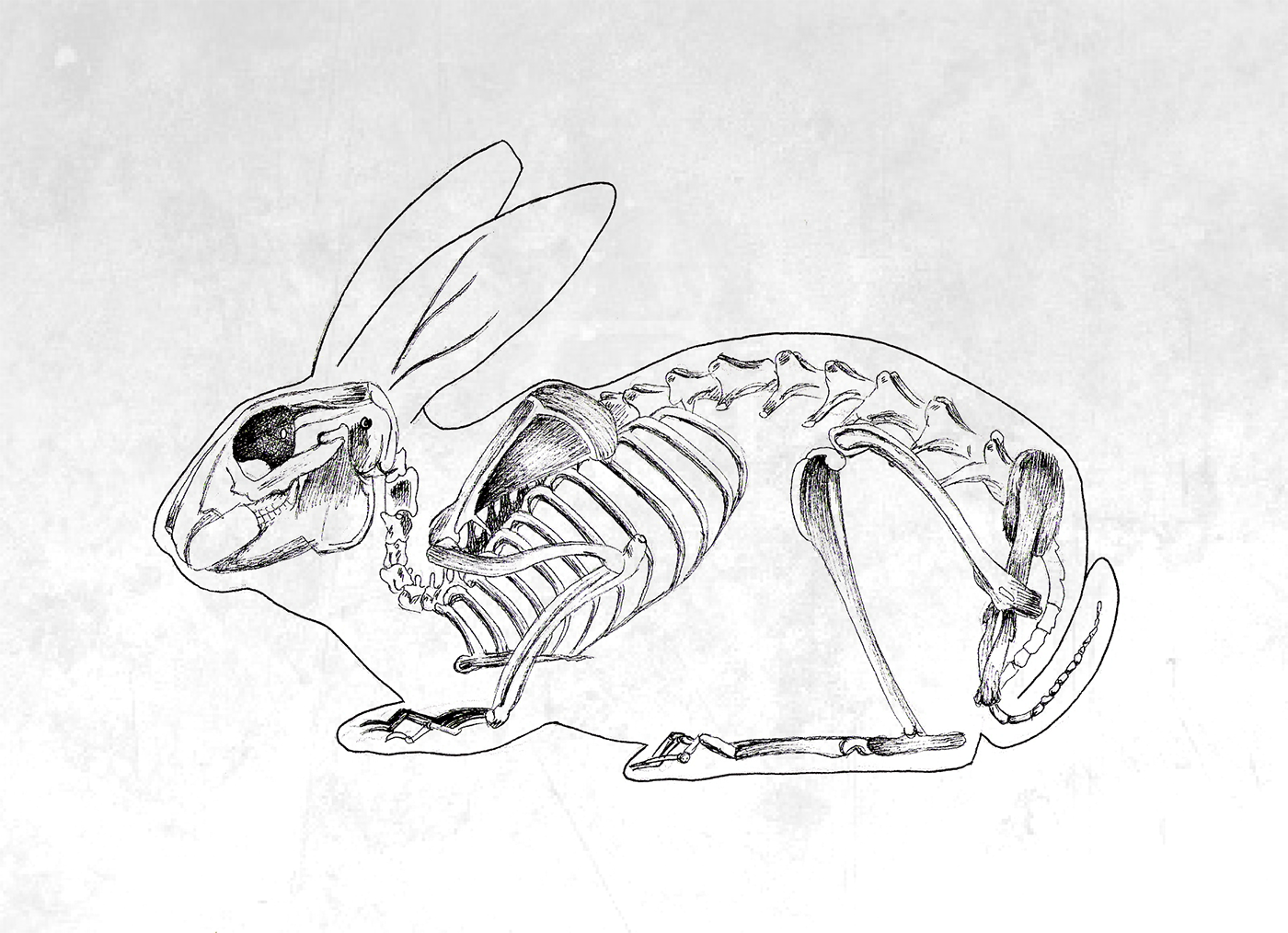
Rabbit skeleton on Behance
The skeletal system of a rabbit, providing structural integrity. Rabbits possess an array of fascinating external body parts that contribute to their unique appearance and remarkable abilities. Let's take a closer look at the captivating features of their heads and bodies, unraveling the secrets behind each component. A. Rabbit's Head
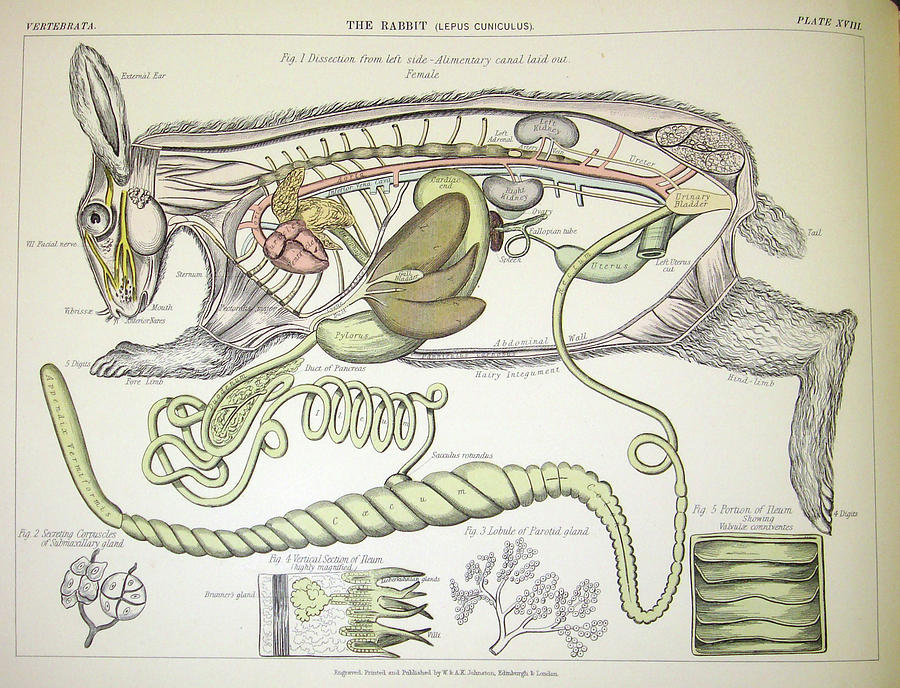
Rabbit Anatomy Photograph by Natural History Museum, London/science
Nose A r abbit's nose has sensitive whiskers. These whiskers help them to breathe easier by adjusting the exchanges of air. They also regulate the inhaled air flows and heat. Through their nasal mucosa, they can easily detect chemicals. The morphology of rabbits' noses directs how the air flows in and out of their lungs.