
Visceral Pleura Definition Anatomy
These lines of pleural reflection delineate the extent of the pleural cavities. The blood supply of the parietal pleura is similar to that of the thoracic wall in that it is derived from the intercostal arteries. The parietal pleura receives innervation the phrenic nerve (C3-C5) and the intercostal nerves (T1-11). This is through from somatic.

Pleura Anatomy 2 (Pleural reflections & Pleural Recess) YouTube
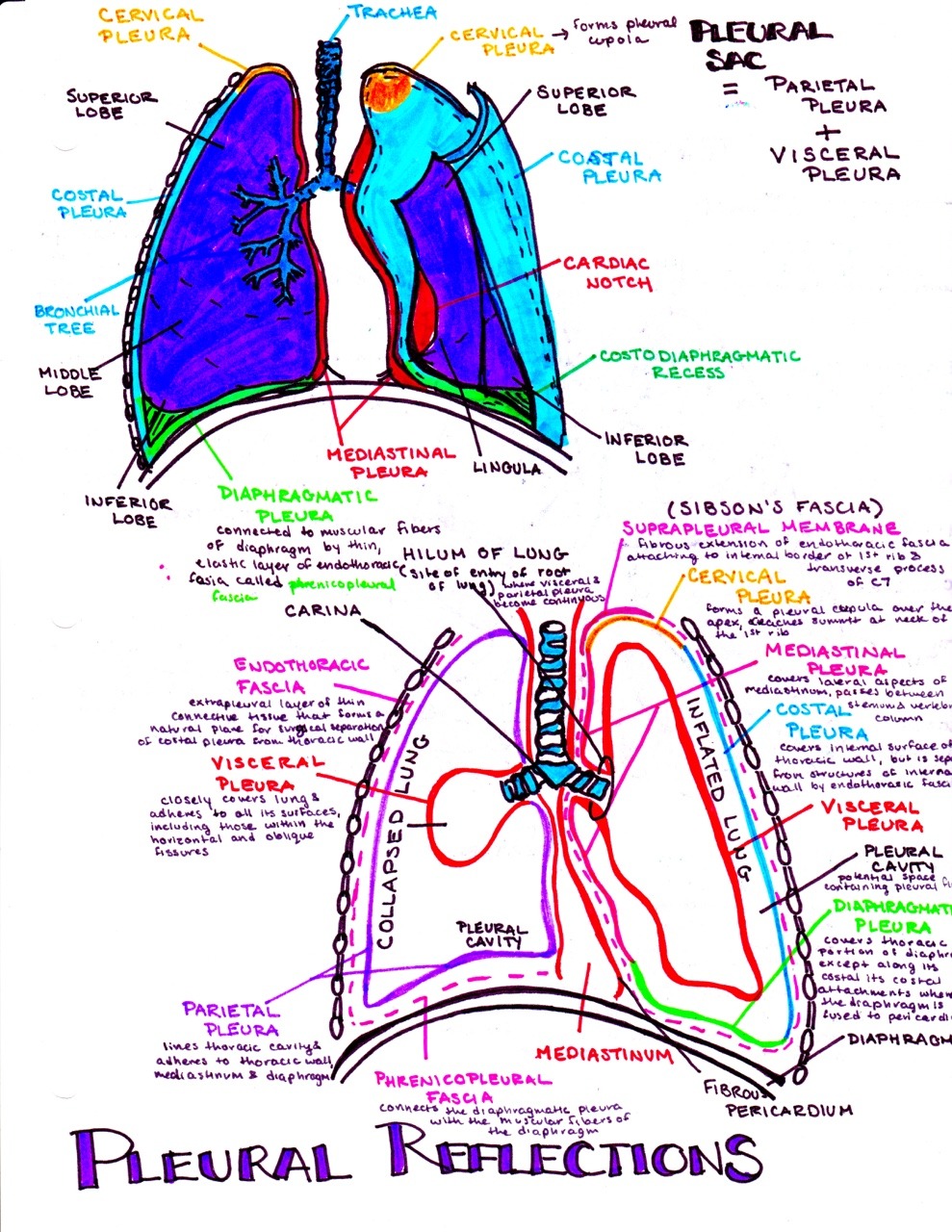
The pleura is a double-layered serous membrane that covers each lung and lines the thoracic cage. The outer layer ( parietal pleura) attaches to the chest wall. The inner layer (visceral pleura) covers the lungs, neurovascular structures of the mediastinum and the bronchi.
PPT Trachea and lungs PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4779845
The pleura is a monolayer of mesothelial cells covering the lung and inner surface of the chest cavity, creating the pleural space. The mesothelial cells rest on a matrix of collagen, elastic fibers, blood vessels, and lymphatics, which allow the lung and chest to expand and contract, protected from friction by the pleural fluid and properties of the mesothelial cells. With a rich blood supply.

Anatomy of the Pleura Thoracic Surgery Clinics
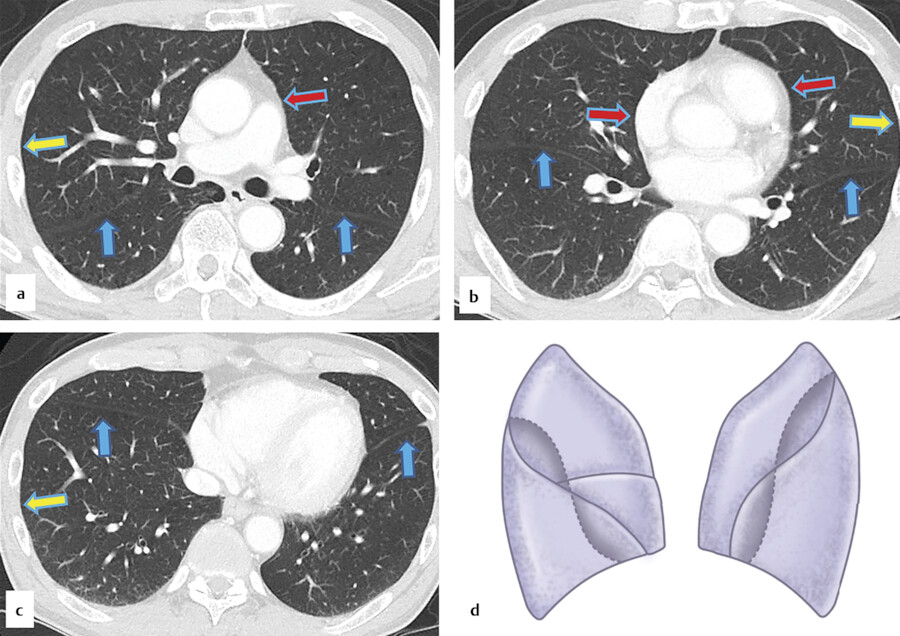
The pleural reflections may be seen to extend over the surface of the diaphragm. FIG. 26.7. The inferior pulmonary ligaments and pleural reflections over the phrenic nerves. A: HRCT on the right shows the inferior pulmonary ligament as a thin triangular opacity ( large arrow) arising in the region of the esophagus.

Anatomy of the pleura Osmosis
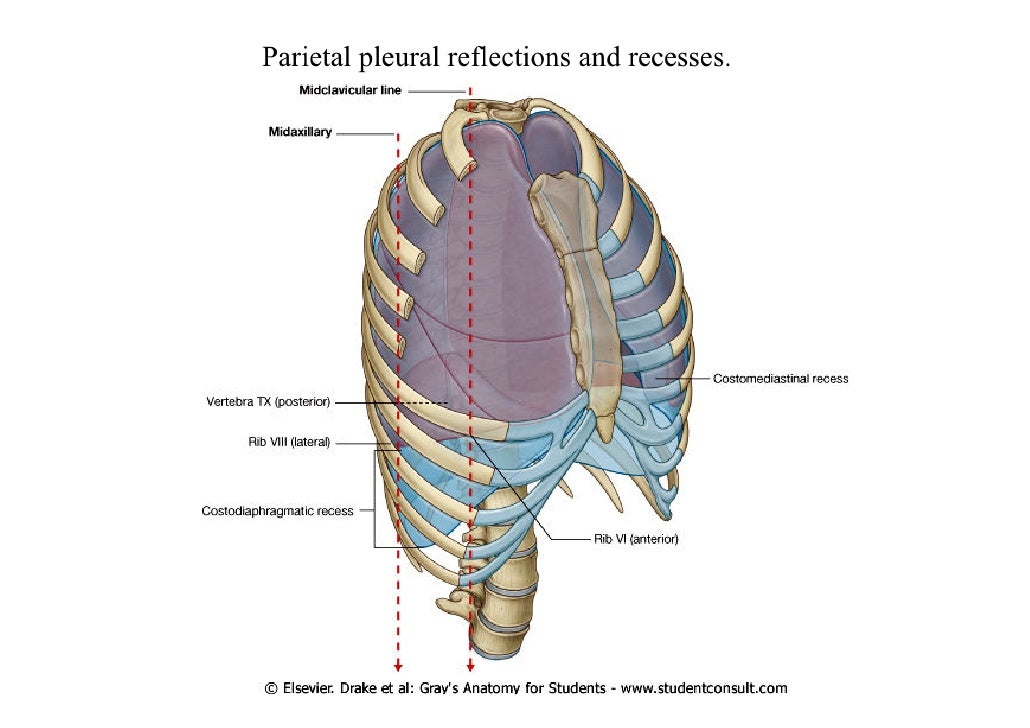
Abstract. Knowledge of the anatomy of the lines of pleural reflection, triangular ligaments, and pleural recesses is important to thoracic surgeons because their anatomic areas are used daily for.

Anatomy of the Pleura Reflection Lines and Recesses Thoracic Surgery Clinics
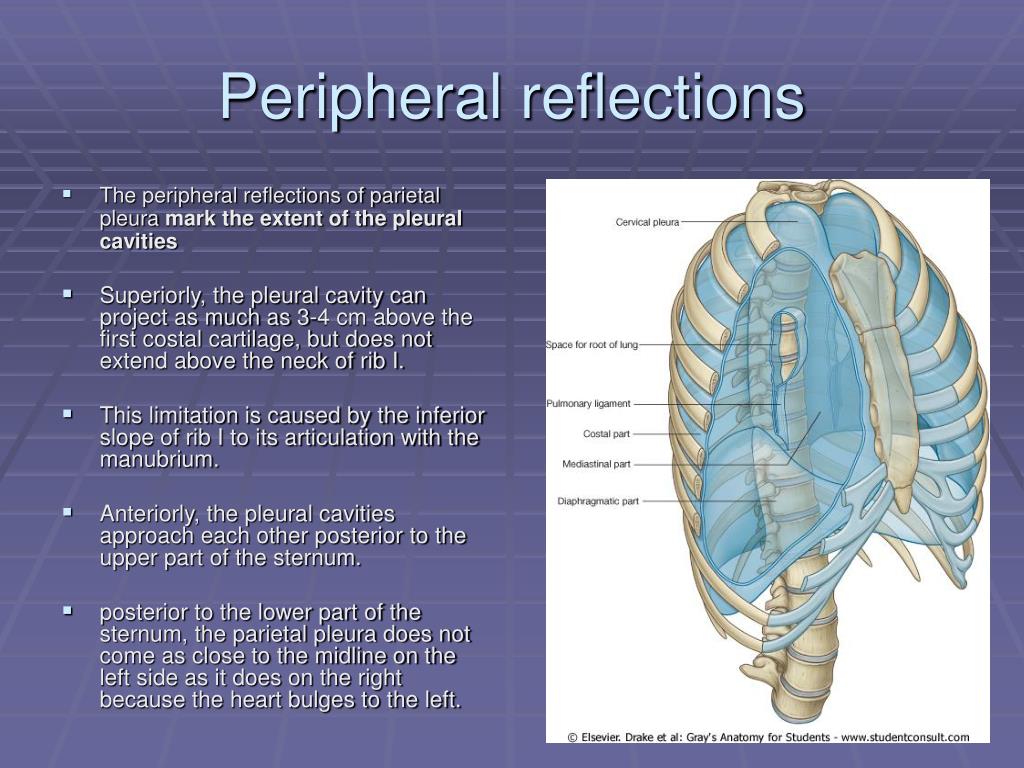
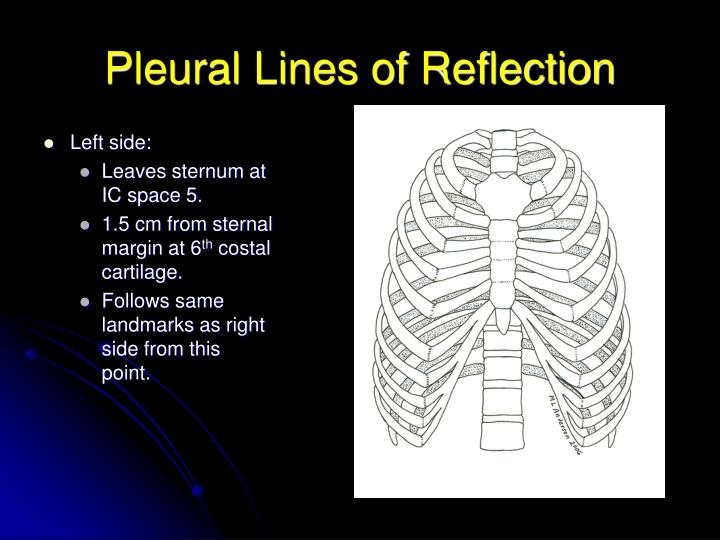
The lines of pleural reflection are formed by the parietal pleura as it changes direction (reflects) from one wall of the pleural cavity to another. The sternal lines of reflection are where the costal parietal pleura becomes continuous with the mediastinal pleura.

Pleura Learn Surgery Online
At the inferior aspect of the root, the reflection of the mediastinal pleura over the visceral pleura continues as a bilayered sheet of both visceral and parietal pleura (total of four layers) in the front and back of the hilar plane to form the inferior pulmonary ligament (also known as the triangular ligament), that is carried downward and mor.

Figure 1 from Anatomy of the pleura reflection lines and recesses. Semantic Scholar
Function Related Conditions Frequently Asked Questions The pleura is a vital part of the respiratory tract. Its role is to cushion the lung and reduce any friction that may develop between the lung, rib cage, and chest cavity. Each pleura (there are two) consists of a two-layered membrane that covers each lung.

Anatomy of the pleura Osmosis
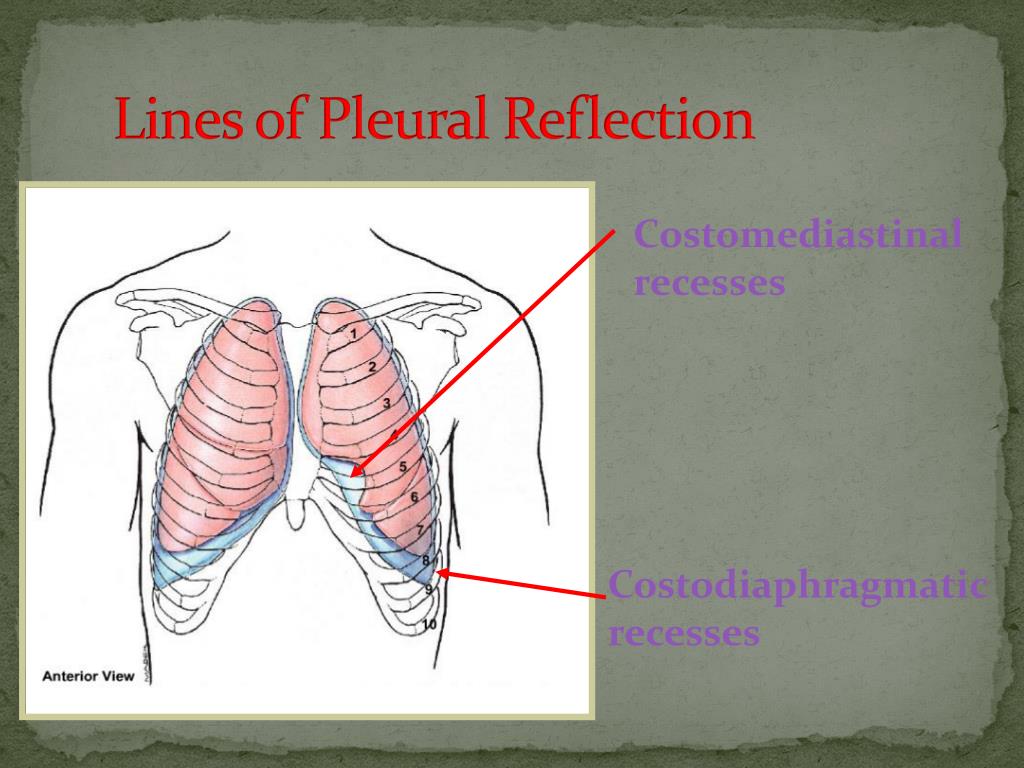
The lines of pleural reflection outline where parietal pleura abruptly changes direction as it passes from one wall of the pleural cavity to another. Right and left parietal pleura reflect in an asymmetric manner due to the presence of the heart.

Pleura Diagram Quizlet
Figure 1. A Layers of the thoracic wall. B Anterolateral view of the pleurae with the ribs partially removed and the parietal pleura removed on the right lung. C Anterolateral view of the surfaces of the parietal pleura, with the ribs partially removed and the left lung removed completely. Figure 2.
hanson's anatomy — Pleural reflections
It is a sharp and thin border that overlays the pericardium that reaches the area where the parietal pleura reflects at the junction of the costal cartilages and the mediastinum (i.e. the costomediastinal line of pleural reflection). While this border is almost vertical on the right-hand side, on the left, it has a variable course.
PPT Pleura and Lungs PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1931660
Pleura: Anatomy. The pleura is a serous membrane that lines the walls of the thoracic cavity and the surface of the lungs. This structure of mesodermal origin covers both lungs, the mediastinum, the thoracic surface of the diaphragm, and the inner part of the thoracic cage. The pleura is divided into a visceral pleura and parietal pleura.
5 The Pleura Radiology Key
Reflections of the Pleura (pleural recesses, ligament and fascia):Commencing at the sternum, the pleura passes lateralward, lines the inner surfaces of the costal cartilages, ribs, and Intercostales, and at the back part of the thorax passes over the sympathetic trunk and its branches, and is reflected upon the sides of the bodies of the vertebr.
Lecture 3 lungs & pleura
The visceral and the mediastinal parietal pleurae are connected at the root of the lung ("hilum") through a smooth fold known as pleural reflections, and a bell sleeve -like extension of visceral pleura hanging under to the hilum is known as the pulmonary ligament .

Anatomy of the pleura Osmosis
The lines of pleural reflection are formed by the parietal pleura as it changes direction (reflects) from one wall of the pleural cavity to another. The sternal lines of reflection are where the costal parietal pleura becomes continuous with the mediastinal pleura.
PPT THORACIC CAVITY PowerPoint Presentation ID479328
Knowledge of the anatomy of the lines of pleural reflection, triangular ligaments, and pleural recesses is important to thoracic surgeons because their anatomic areas are used daily for radiographic interpretation as well as for the performance of procedures such as chest tube insertion, thoracentesis, and pericardiocentesis. Their knowledge is.