Flexor Retinaculum (Hand) Earth's Lab
The flexor retinaculum of the hand attaches to the hamate bone's hamulus, which is a curved process that lies on the bottom of the hamate bone. It connects to the middle of the pisiform, which is a small wrist bone that is shaped like a pea. In addition, it connects laterally to the scaphoid and across the middle of the trapezium.
The Wrist and Hand TeachMe Orthopedics
Flexor Retinaculum Thick connective tissue which forms the roof of the carpal tunnel. Turns the carpal arch into the carpal tunnel by bridging the space between the medial and lateral parts of the arch. Spans between the hook of hamate and pisiform (medially) to the scaphoid and trapezium (laterally).

15 The Forearm Fascia and Retinacula Musculoskeletal Key
The flexor retinaculum of the hand is a fibrous band that is quite durable and extends over the carpus. The carpus is a group of bones located in the wrist between the ulna, the radius and.
STRUCTURES UNDER EXTENSOR RETINACULUM OF HAND MEDizzy
The roof of the carpal tunnel is formed by the flexor retinaculum (also known as transverse carpal ligament), a thick connective tissue ligament. This ligament bridges the space between the medial and lateral ends of the carpal arch, converting the arch into a tunnel. Contents Tendons of flexor digitorum profundus muscle

Pin em Musculoskeletal System
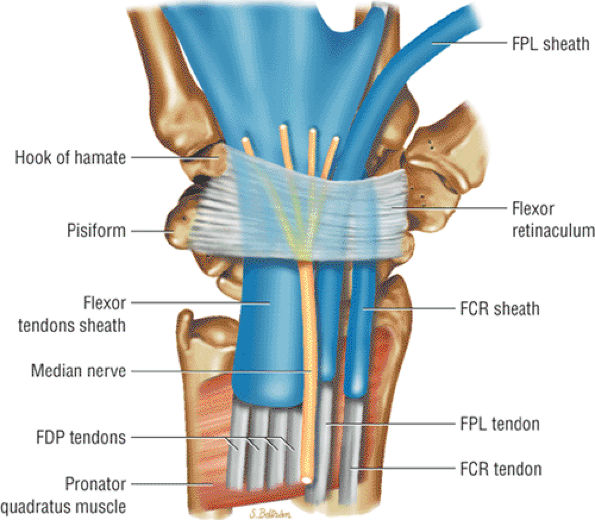
The flexor retinaculum forms the roof of the carpal tunnel, through which the median nerve and the long finger flexors tendons of finger and thumb run. The tendons run in three palmar synovial tendon sheaths.

View of the wrist showing the flexor retinaculum at the wrist and the
Anatomy of the flexor retinaculum For an accurate definition of the anatomic limits of the carpal tunnel, 26 cadaver upper extremities were studied by gross (lo), histologic (3), and radiographic (13) methods.. Fig. 2. A, Sagittal section of left wrist and hand, with orthochromatic film used for contrast enhancement. B, Drawing of.
The flexor retinaculum of Hand Gross anatomy , Attachments and Relations YouTube
Flexor Tendon Injuries are traumatic injuries to the flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus tendons that can be caused by laceration or trauma. Diagnosis is made clinically by observing the resting posture of the hand to assess the digital cascade and the absence of the tenodesis effect.

Flexor & Extensor Retinaculum Musculoskeletal System Limbs (Anatomy)
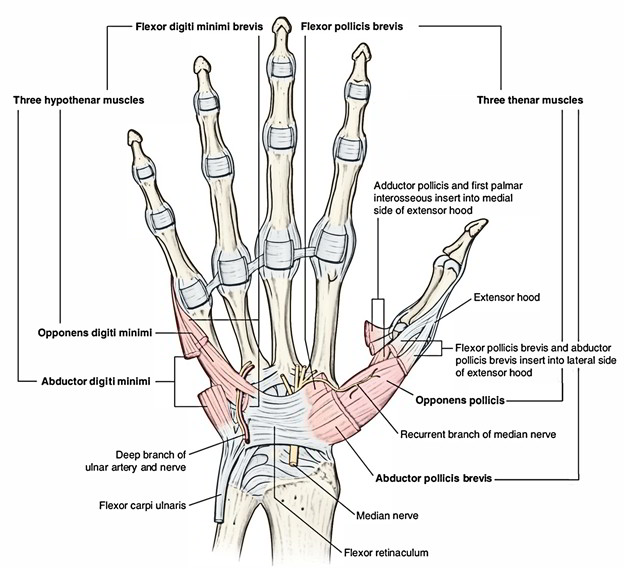
Key Facts about thenar muscles; Abductor pollicis brevis: Origin - tubercles of the scaphoid and trapezium; flexor retinaculum Insertion - base of the proximal phalanx 1 (via radial sesamoid bone) Innervation - Recurrent branch of median nerve (C8, T1) Function - thumb abduction (moving away from the hand) at carpometacarpal joint 1: Flexor pollicis brevis: Origin - flexor retinaculum.

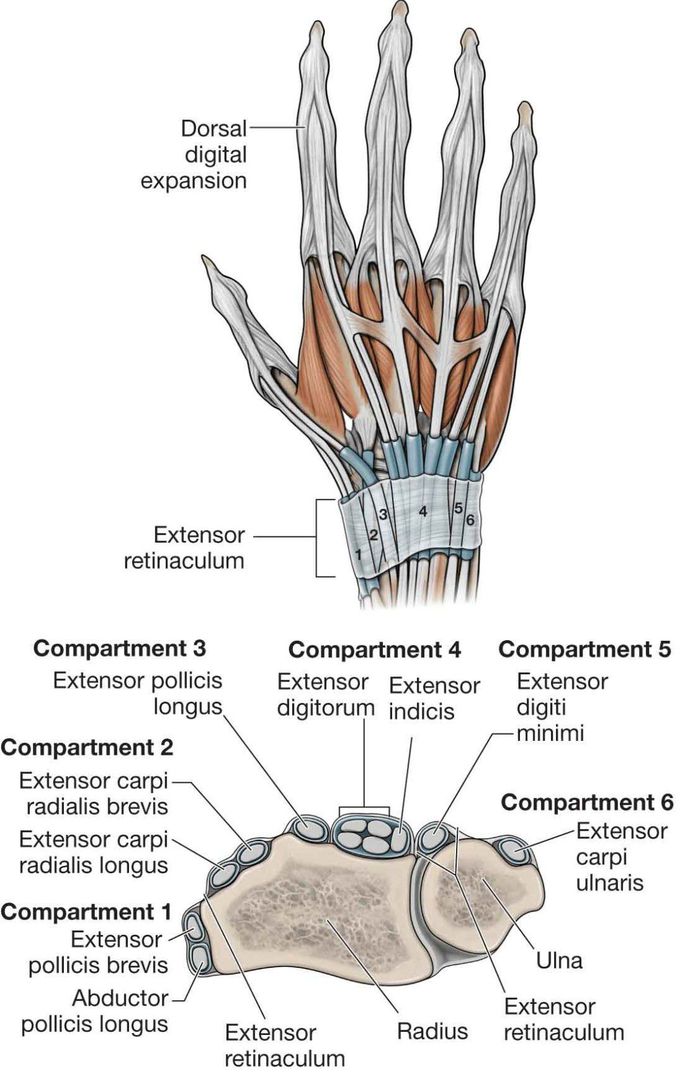
Schematic diagram of extensor compartments of wrist. Extensor retin.... Download Scientific
Causes Most commonly, a flexor tendon injury results from lacerations (cuts). A laceration to the forearm, hand or wrist can result in injury to the flexor tendons. When a flexor tendon injury happens there can be inability to bend the fingers, thumb or wrist.

Wrist Joint AnatomyBones, Movements, Ligaments, Tendons Abduction, Flexion
Last updated: October 29, 2023 Revisions: 55 format_list_bulleted Contents add The muscles that act on the hand can be divided into two groups: Extrinsic muscles - located in the anterior and posterior compartments of the forearm. They control crude movements and produce a forceful grip. Intrinsic muscles - located within the hand itself.
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/retinaculum-flexorum/UfDcRtsSwVXr5QZEpzZZSQ_MtMxTgGEQj_Retinaculum_flexorum_1.png)
Flexor retinaculum (Retinaculum flexorum) Kenhub
NLM NIH HHS USA.gov The flexor retinaculum is a fibrous connective tissue band that forms the anterior roof of the carpal tunnel (see Image. Flexor Retinaculum of the Wrist). Many experts consider the flexor retinaculum synonymous with the transverse carpal and annular ligaments.
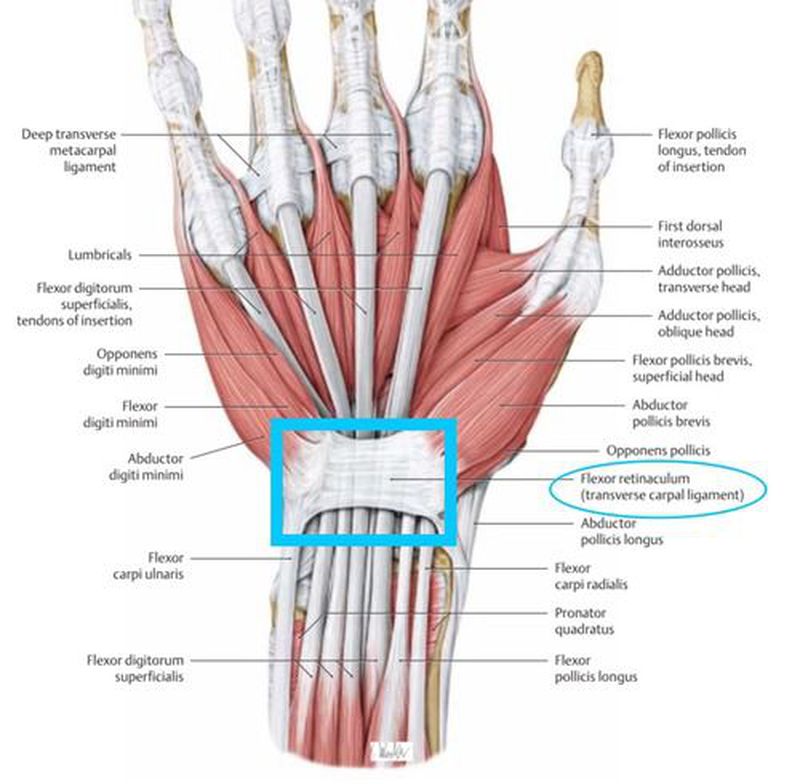
Flexor Retinaculum MEDizzy
Flexor retinaculum of the hand (flexor retinaculum; transverse carpal ligament) Fibrous thickening of the palmar deep fascia located at the proximal part of the palm; Medial: pisiform and hook of hamate; Lateral: scaphoid and trapezium
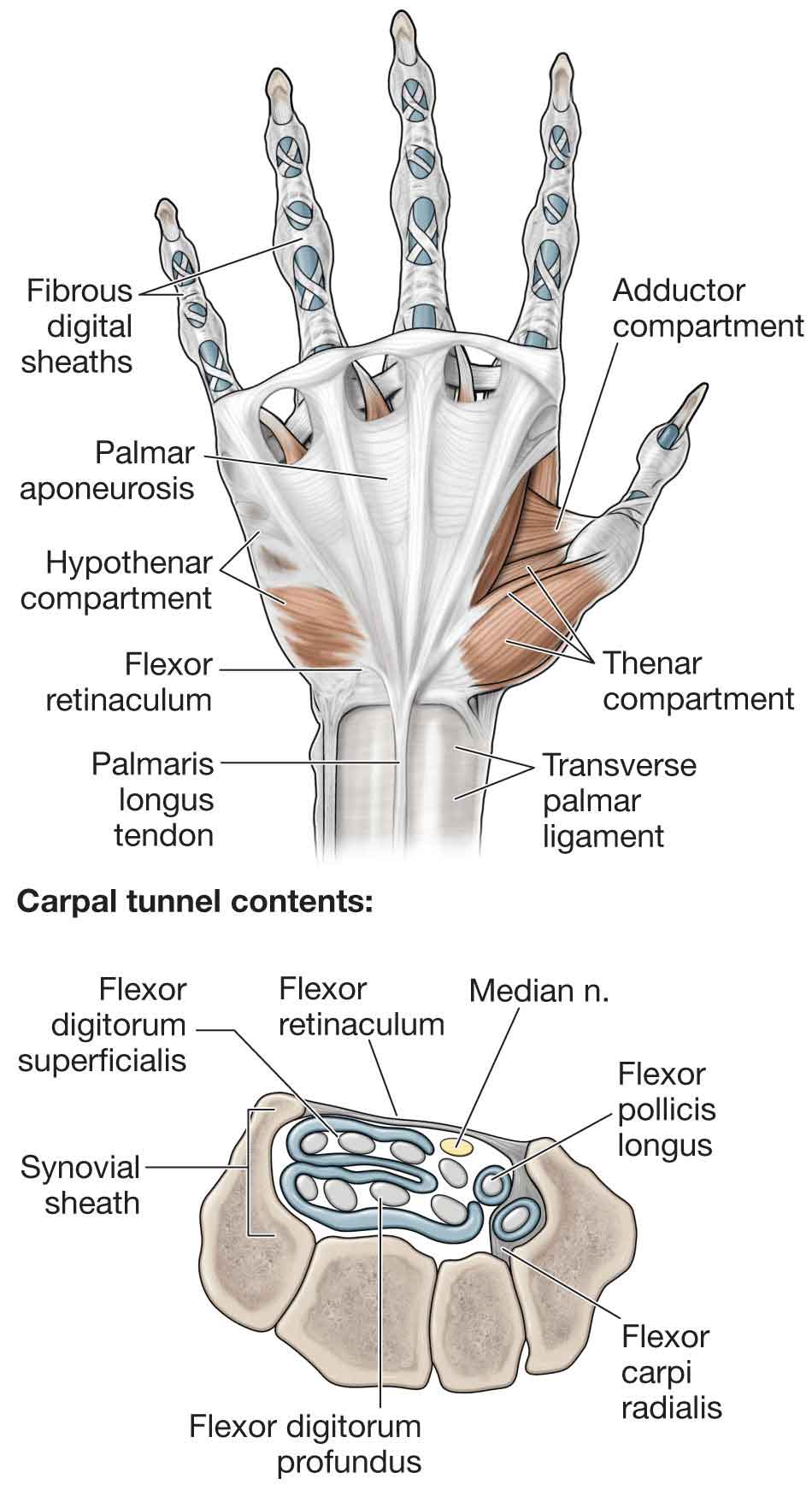
The Forearm, Wrist, and Hand Musculoskeletal Key
Flexor retinaculum of hand Flexor retinaculum is a strong fibrous band which bridges the anterior concavity of the carpal bones thus converts it into a tunnel, the carpal tunnel [1]. Attachments Medially, To the pisiform bone To the hook of the hamate Laterally, To the tubercle of the scaphoid To the crest of the trapezium [1]

Flexor Retinaculum of Hand Anatomy l Surface marking l Structures Passing l Superficial l Deep
In the fingers, the flexor tendons run through osseo-fibrous tunnels formed by the annular and cruciform pulleys and covered by the flexor retinaculum. In a "trigger-finger", mechanical overuse causes thickening of the annular pulley, narrowing of the osseofibrous tunnel, and stenosing tenosynovitis of the adjacent flexor tendons (Fig. 18).
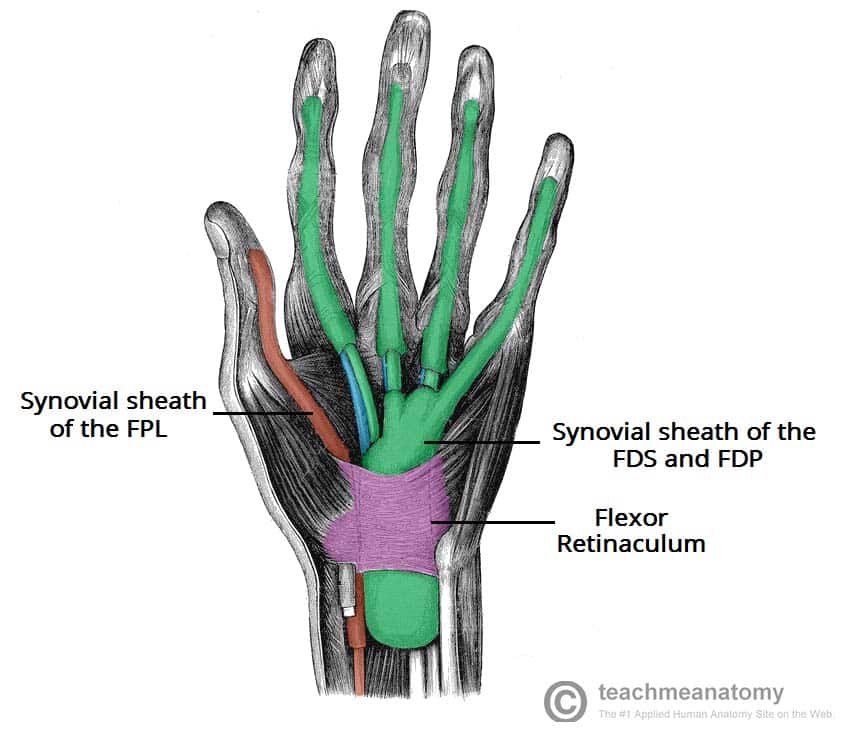
The Carpal Tunnel Borders Contents TeachMeAnatomy
The flexor retinaculum is a strong fibrous band that covers the carpal bones of the palmar side of the hand. The distal border of the flexor retinaculum is concave inferiorly and is attached to the tubercle of the trapezium and to the hook of the hamate.

Science quotes, Human body anatomy, Quran
The flexor retinaculum is a strong, transverse, fibrous band that confines the flexor tendons of the five fingers, together with their synovial sheaths and the median nerve, to the arch of the carpus, which it converts into the carpal tunnel (figs. 11-2, 11-3 and 11-4 ).