
2 Hierarchy of evidence. Source Modified from New Evidence Pyramid. 5 Download Scientific Diagram
Levels of evidence. The above "evidence pyramid" shows a hierarchy of the quality of evidence presented in research articles, with the highest quality at the top moving down to the lowest quality at the bottom. Systematic reviews: involve a comprehensive plan and search strategy to identify, appraise, and synthesis all relevant (and high.

Levels of Evidence Speech Language Pathology LibGuides at Idaho State University
The pyramid of evidence: systematic reviews, meta analyses, RCTs. SR, Systematic reviews; MA, meta-analyses. Evidence pyramid: beyond traditional hierarchy. The evidence pyramid with its origin in evidence-based medicine gives the highest importance to the RCT study design as the best method to generate reliable and unbiased evidence. The.
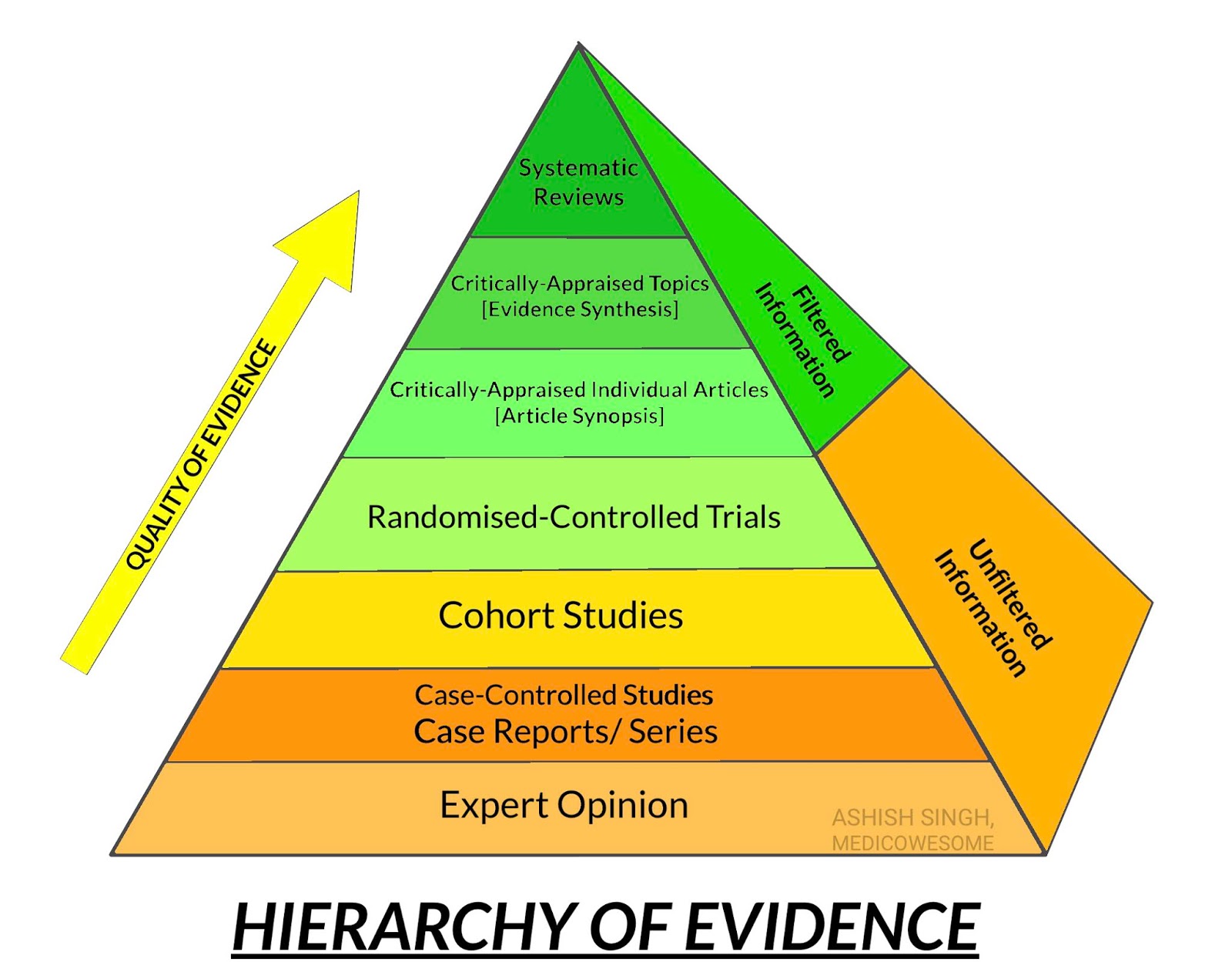
Medicowesome Hierarchy Of Evidence
Levels of Evidence. The evidence pyramid is often used to illustrate the development of evidence. At the base of the pyramid is animal research and laboratory studies - this is where ideas are first developed. As you progress up the pyramid the amount of information available decreases in volume, but increases in relevance to the clinical.

The EvidenceBased Medicine Pyramid! Students 4 Best Evidence
A pyramid has expressed the idea of hierarchy of medical evidence for so long, that not all evidence is the same. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses have been placed at the top of this pyramid for several good reasons. However, there are several counterarguments to this placement. We suggest another way of looking at the evidence-based.
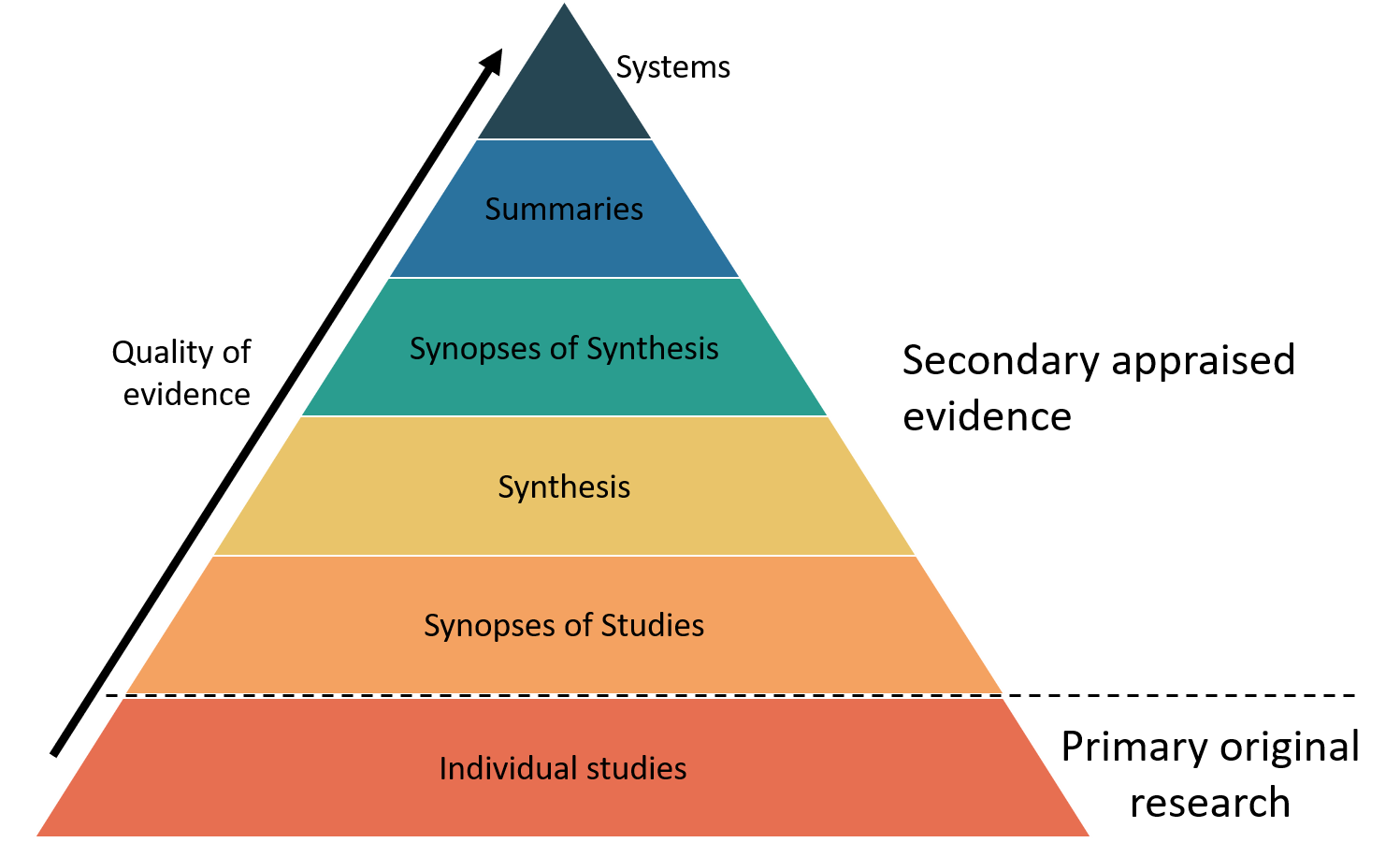
Levels of Evidence Nursing Research LibGuides at Bushnell University
The Joanna Briggs Institute specializes in promoting and supporting evidence-based healthcare by providing access to resources for professionals in nursing, midwifery, medicine, and allied health. With over 64 collaborating centers and groups, servicing over 90 countries, the Institute is a recognised global leader in evidence-based healthcare.

Hierarchy of evidence (Polit and Beck, 2014). RCT randomised... Download Scientific Diagram
The proposed new evidence-based medicine pyramid. (A) The traditional pyramid. (B) Revising the pyramid: (1) lines separating the study designs become wavy (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation), (2) systematic reviews are 'chopped off' the pyramid. (C) The revised pyramid: systematic reviews are a lens through.
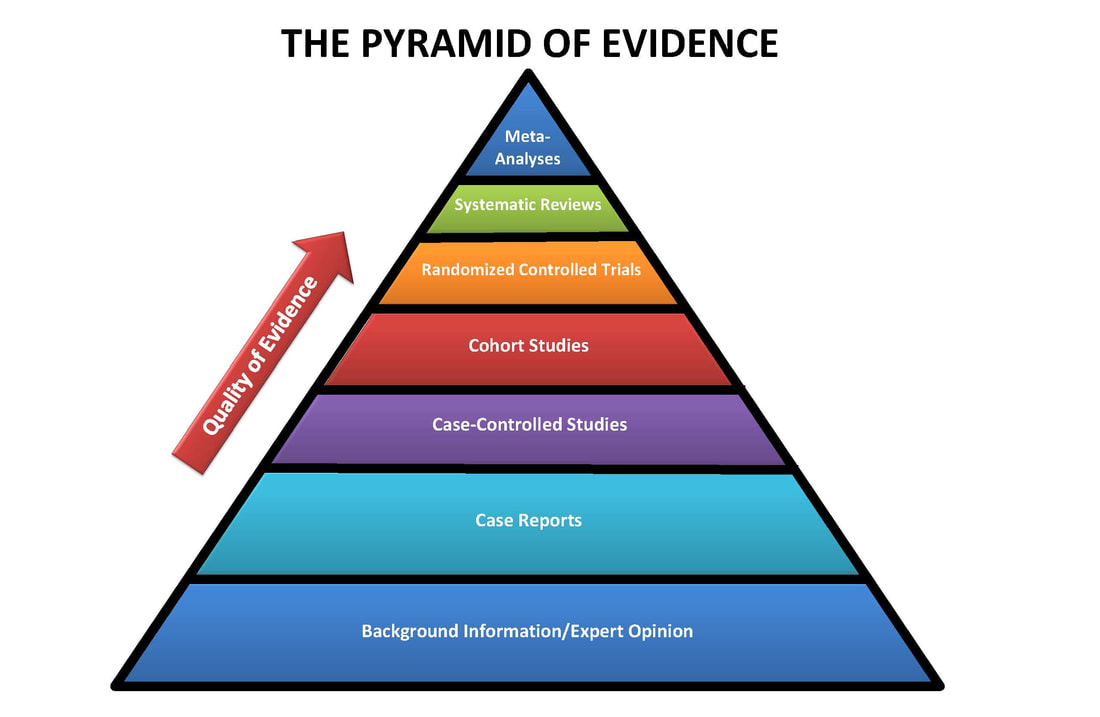
Evidence Ellis Medical Library
Filtered Resources. Filtered resources appraise the quality of studies and often make recommendations for practice.. Systematic Reviews / Meta-Analyses. Authors of a systematic review ask a specific clinical question, perform a comprehensive literature search, eliminate the poorly done studies and attempt to make practice recommendations based on the well-done studies.

Hierarchy of evidence (28) Download Scientific Diagram
The concept of the "hierarchy of evidence" refers to a tabular representation (sometimes presented as a pyramid) of the relative strengths of various investigational methodologies in providing the evidence that is used in evidence-based medicine and evidence-based behavioral medicine. Byar (cited by Piantadosi 2005) listed different types.
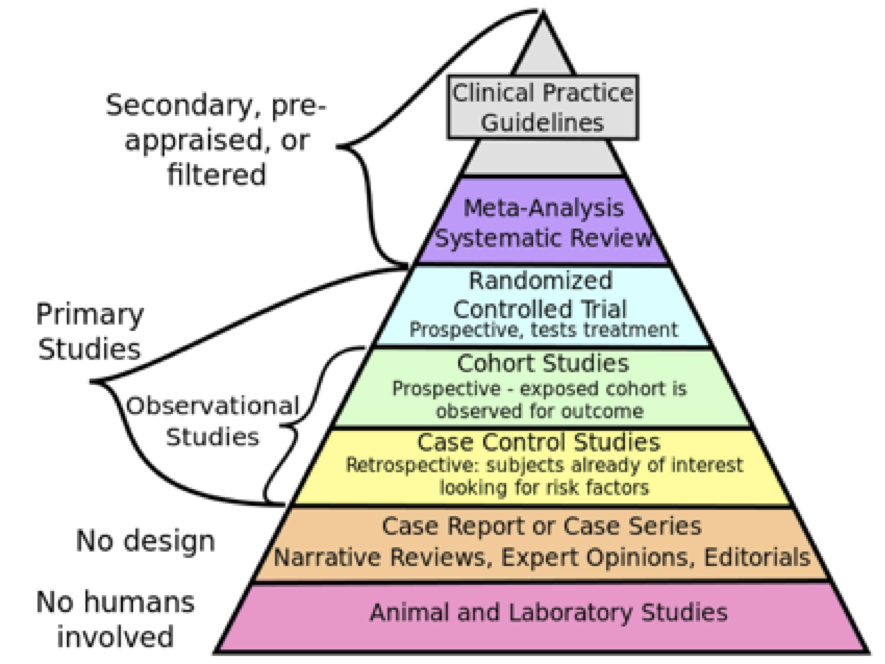
The Hierarchy of Evidence Applied Statistics in Healthcare Research
The Evidence-Based Medicine Pyramid is simply a diagram that was created to help us understand how to weigh different levels of evidence in order to make health-related decisions. It helps us put the results of each study design into perspective, based on the relative strengths and weaknesses of each design. Allow me to be your guide as we tour.

The evidentiary pyramid in evidencebased medicine. Source "Research... Download Scientific
fi. on its own as a surrogate for risk of bias. Certain meth-odological limitations of a study, imprecision, inconsist-ency and indirectness, were factors independent from study design and can affect the quality of evidence derived from any study design. For example, a meta-analysis of RCTs evaluating intensive glycaemic control in non.

Study design Evidencebased practice in health LibGuides at La Trobe University
The proposed new evidence-based medicine pyramid. (A) The traditional pyramid. (B) Revising the pyramid: (1) lines separating the study designs become wavy (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation), (2) systematic reviews are 'chopped off' the pyramid. (C) The revised pyramid: systematic reviews are a lens through.
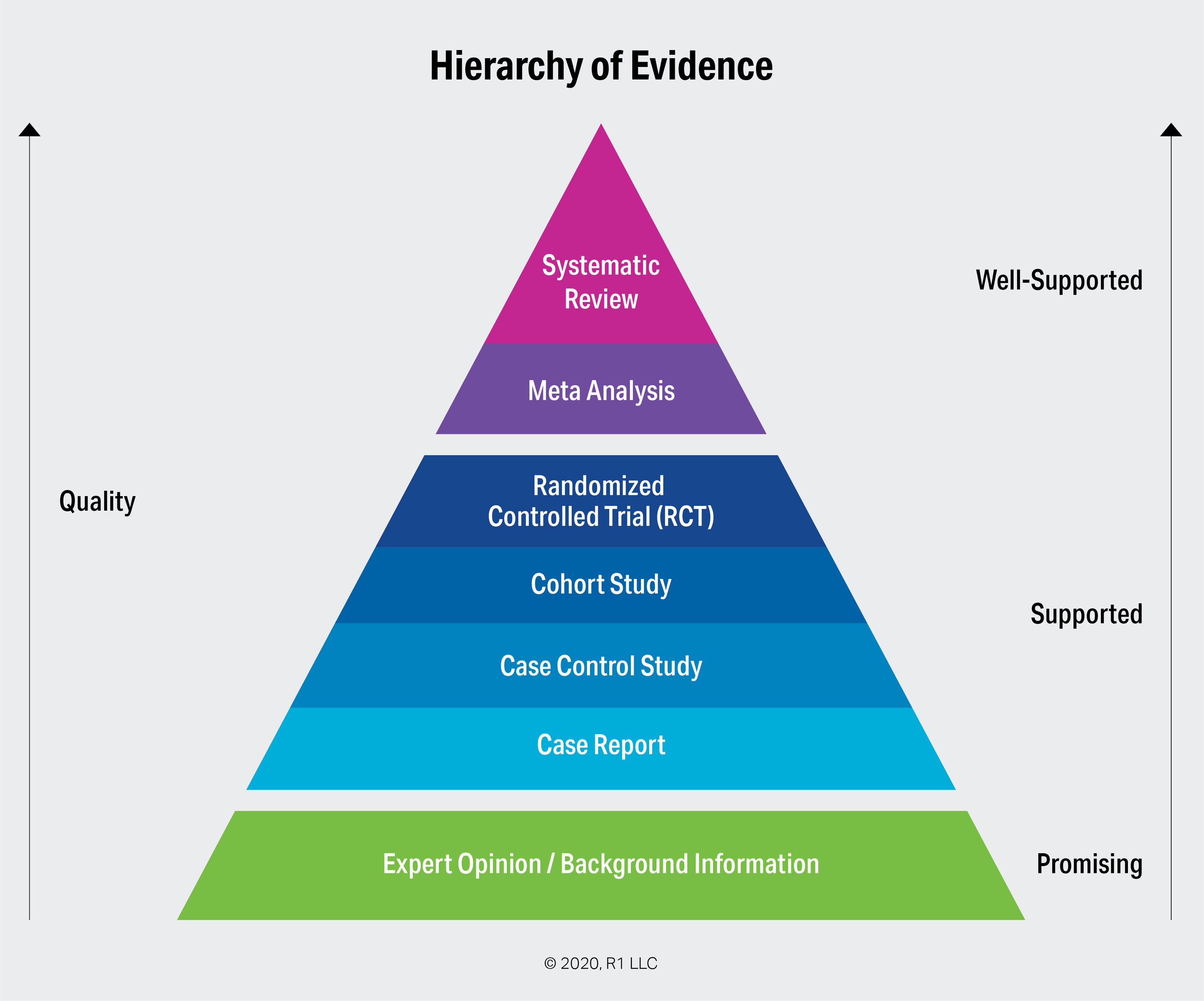
Upon What Evidence Are 'EvidenceBased' Practices Based? — R1 Learning
Studies are assigned levels of evidence based on their methodology. The evidence pyramid is an easy way to visualize this hierarchy of evidence.

Acquire the Evidence EBM Resource Center Library Research Guides at New York Medical College
One way to organize the different types of evidence involved in evidence-based practice research is the levels of evidence pyramid. The pyramid includes a variety of evidence types and levels. Filtered resources: pre-evaluated in some way. systematic reviews. critically-appraised topics. critically-appraised individual articles.

Evidencebased medicine pyramid. The levels of evidence are... Download Scientific Diagram
Quick Guide. The pyramid shows the different publication types for evidence based practice. The higher up in the pyramid you go the better the quality of the research. The box below the pyramid defines the different types of resources.
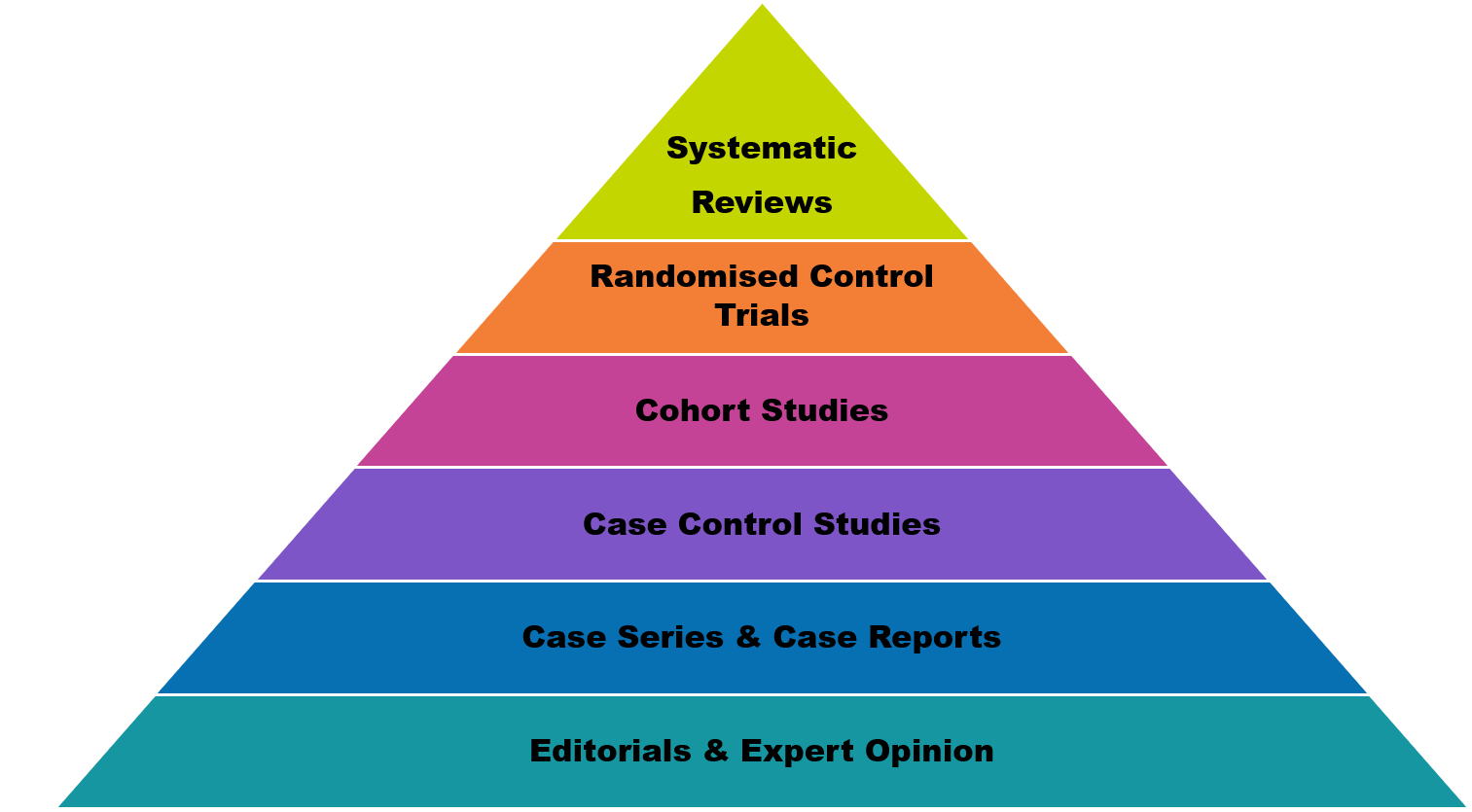
Introduction Evidence Based Practice Library Guides at CQUniversity
The evidence-based medical literature is usually represented graphically as being arranged in a pyramid shape, the idea being that it is spread over several levels, with the higher ones, towards the top of the pyramid, being equated with higher standards and thus, implicitly, better quality evidence. In actual fact, this pyramid-shaped.
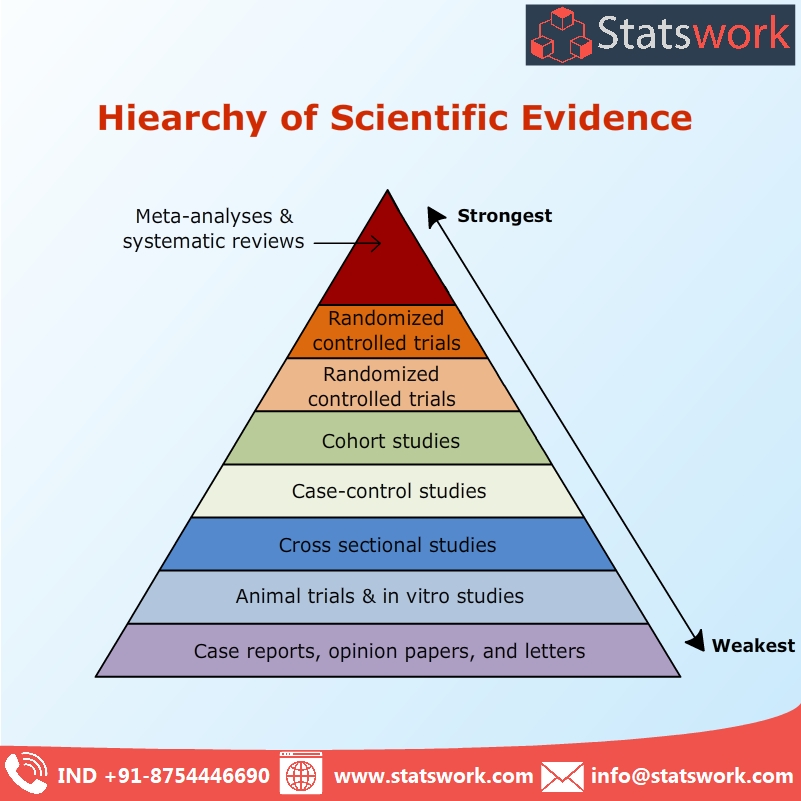
hierarchy scientific evidence statswork
A hierarchy of evidence, comprising levels of evidence (LOEs), that is, evidence levels (ELs), is a heuristic used to rank the relative strength of results obtained from experimental research, especially medical research.There is broad agreement on the relative strength of large-scale, epidemiological studies.More than 80 different hierarchies have been proposed for assessing medical evidence.