
Derivative of Tan Differentiation & Formula Video & Lesson Transcript
All derivatives of circular trigonometric functions can be found from those of sin ( x) and cos ( x) by means of the quotient rule applied to functions such as tan ( x) = sin ( x )/cos ( x ). Knowing these derivatives, the derivatives of the inverse trigonometric functions are found using implicit differentiation .

Derivative of Tangent x Formula, Rules, Examples
The differentiation of t a n − 1 x with respect to x is 1 1 + x 2. i.e. d d x t a n − 1 x = 1 1 + x 2. Proof using chain rule : Let y = t a n − 1 x. Then, t a n ( t a n − 1 x) = x tan y = x Differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get d d x (tan y) = d d x (x) d d x (tan y) = 1 By chain rule, s e c 2 y d y d x = 1 d y d x = 1 s e c 2 y
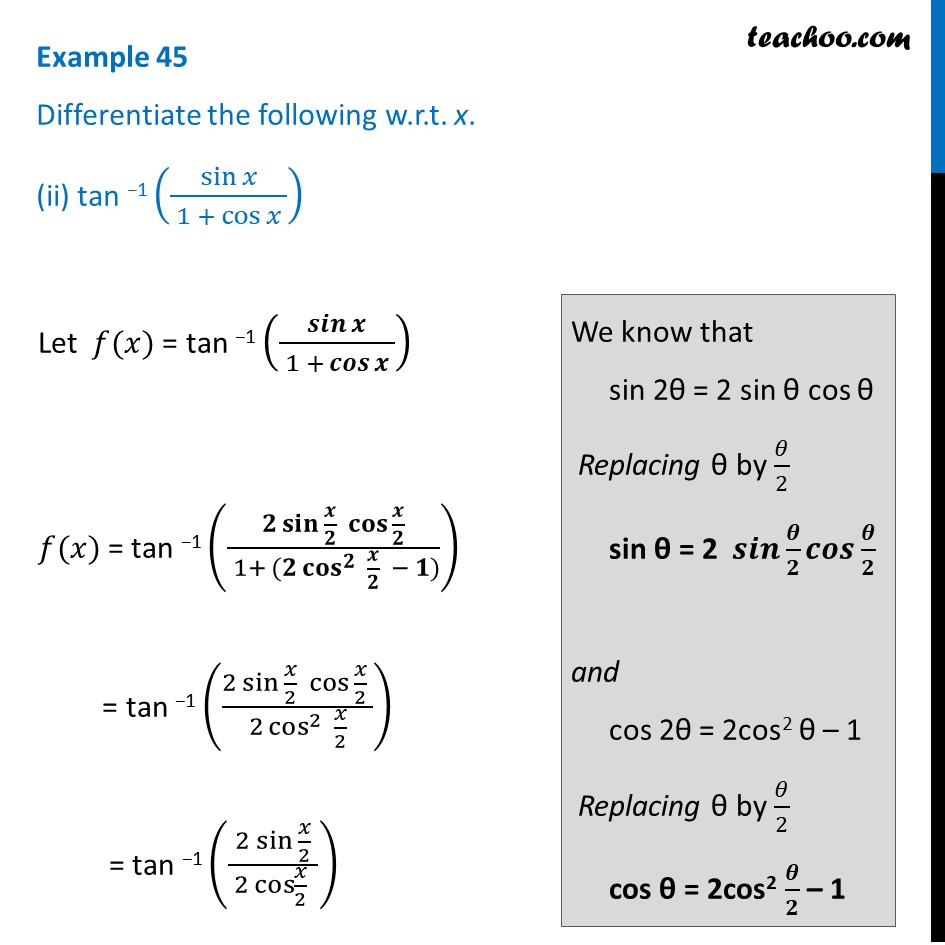
Example 45 (ii) Differentiate tan^1 (sin x/ (1 + cos x)) Teachoo
Differentiation of tan inverse x is the process of evaluating the derivative of tan inverse x with respect to x which is given by 1/ (1 + x 2 ). The derivative of tan inverse x can be calculated using different methods such as the first principle of derivatives and using implicit differentiation.

Derivada Tan X Estudiar
The differentiation of the tan inverse function can be written in terms of any variable. Here are some of the examples to learn how to express the formula for the derivative of inverse tangent function in calculus. ( 1) d d y ( tan − 1 ( y)) = 1 1 + y 2 ( 2) d d l ( tan − 1 ( l)) = 1 1 + l 2 ( 3) d d z ( tan − 1 ( z)) = 1 1 + z 2 Proof

Question 1 Find derivative of tan (2x + 3) Chapter 5 Class 12
tan^-1(x) Natural Language; Math Input; Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random. Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music…

Derivative of Tangent x Formula, Rules, Examples
Example 3.5.2: Finding the Derivative of a Function Containing cos x. Find the derivative of g(x) = cosx 4x2. Solution. By applying the quotient rule, we have. g′ (x) = ( − sinx)4x2 − 8x(cosx) (4x2)2. Simplifying, we obtain. g′ (x) = − 4x2sinx − 8xcosx 16x4 = − xsinx − 2cosx 4x3.
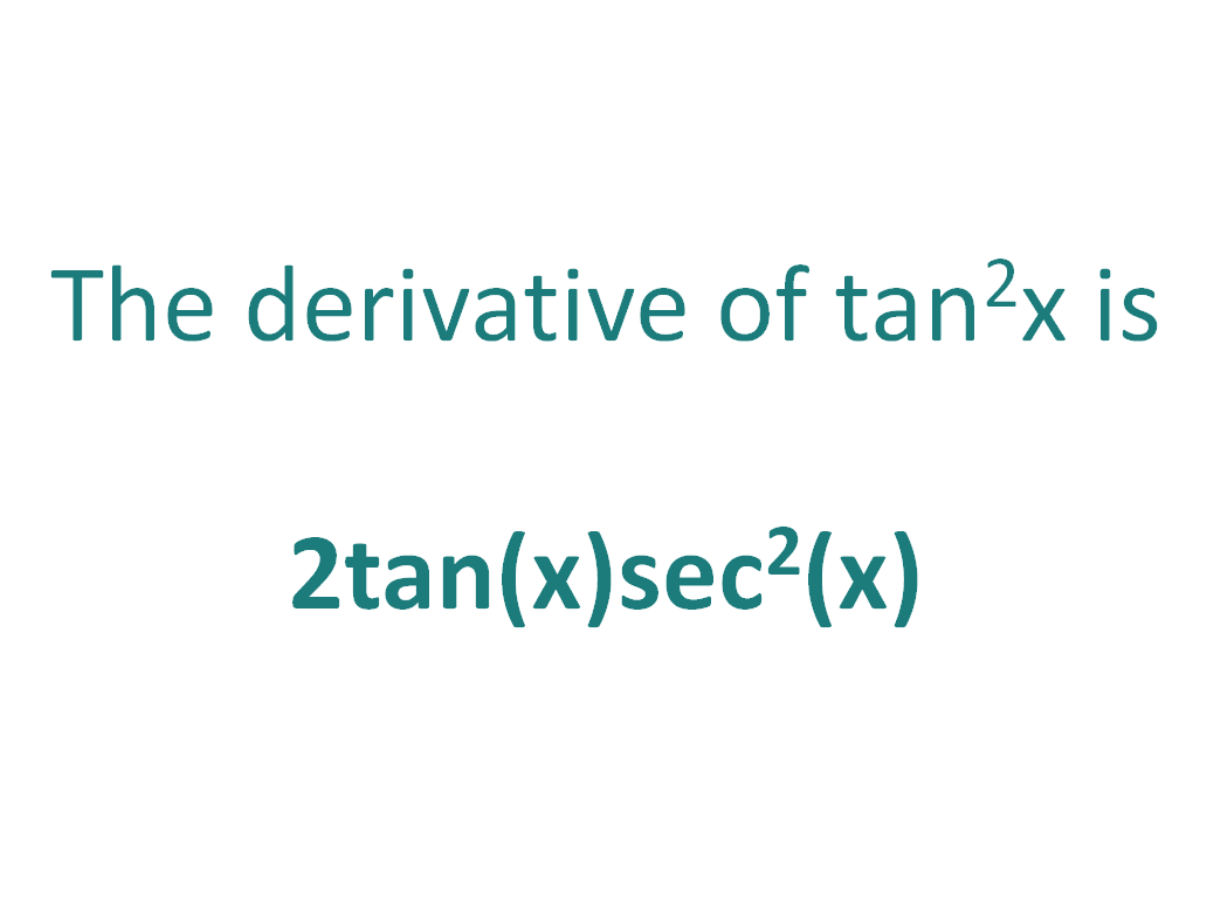
The Derivative of tan^2x DerivativeIt
[Math Processing Error] Answer link I'm assuming you are thinking of this as being a function of two independent variables x and y: z=tan^ {-1} (y/x). The answers are \frac {\partial z} {\partial x}=-\frac {y} {x^ {2}+y^ {2}} and \frac {\partial z} {\partial y}=\frac {x} {x^2+y^2}.

Differentiation of tan inverse x is ? Brainly.in
Free derivative calculator - differentiate functions with all the steps. Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph
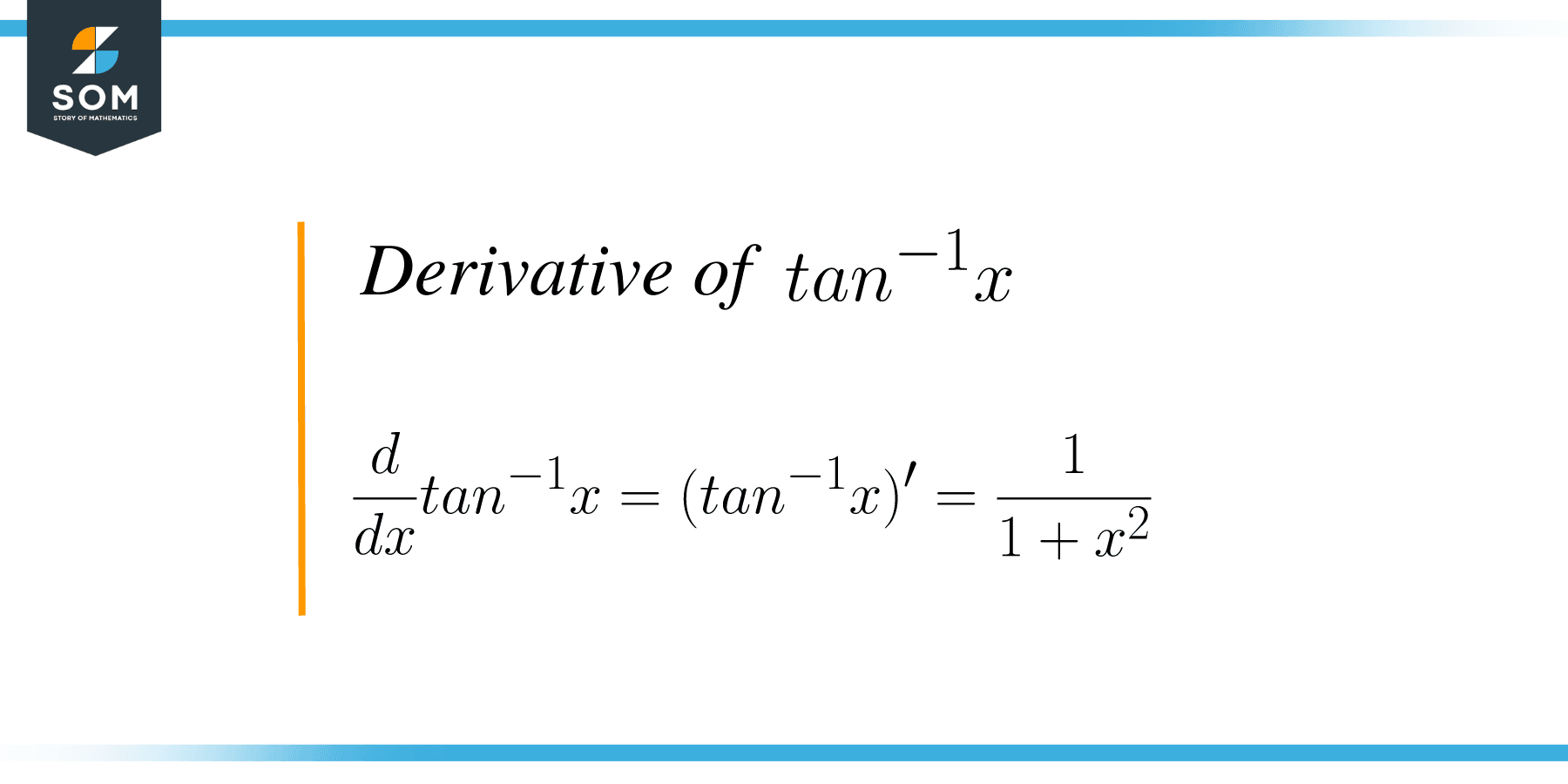
Derivative of Tan^1 x Detailed Explanation and Examples The Story of Mathematics A History
How Wolfram|Alpha calculates derivatives. Wolfram|Alpha calls Wolfram Languages's D function, which uses a table of identities much larger than one would find in a standard calculus textbook. It uses well-known rules such as the linearity of the derivative, product rule, power rule, chain rule and so on. Additionally, D uses lesser-known rules.

Differentiation of (tanx)^2 YouTube
1 It boils down to: what do you mean by $\tan^ {-1} (x)$. I think most people think of it as the inverse tangent function, i.e. $\arctan (x)$, but some think of it as $\frac {1} {\tan (x)}$. The derivative of the former is $\frac {1} {1+x^2}$, and the derivative of $\tan (x)$ is $\sec^2 (x)$.

Find derivative dy/dx of x = tan y. Implicit Differentiation YouTube
Differentiate algebraic and trigonometric equations, rate of change, stationary points, nature, curve sketching, and equation of tangent in Higher Maths.
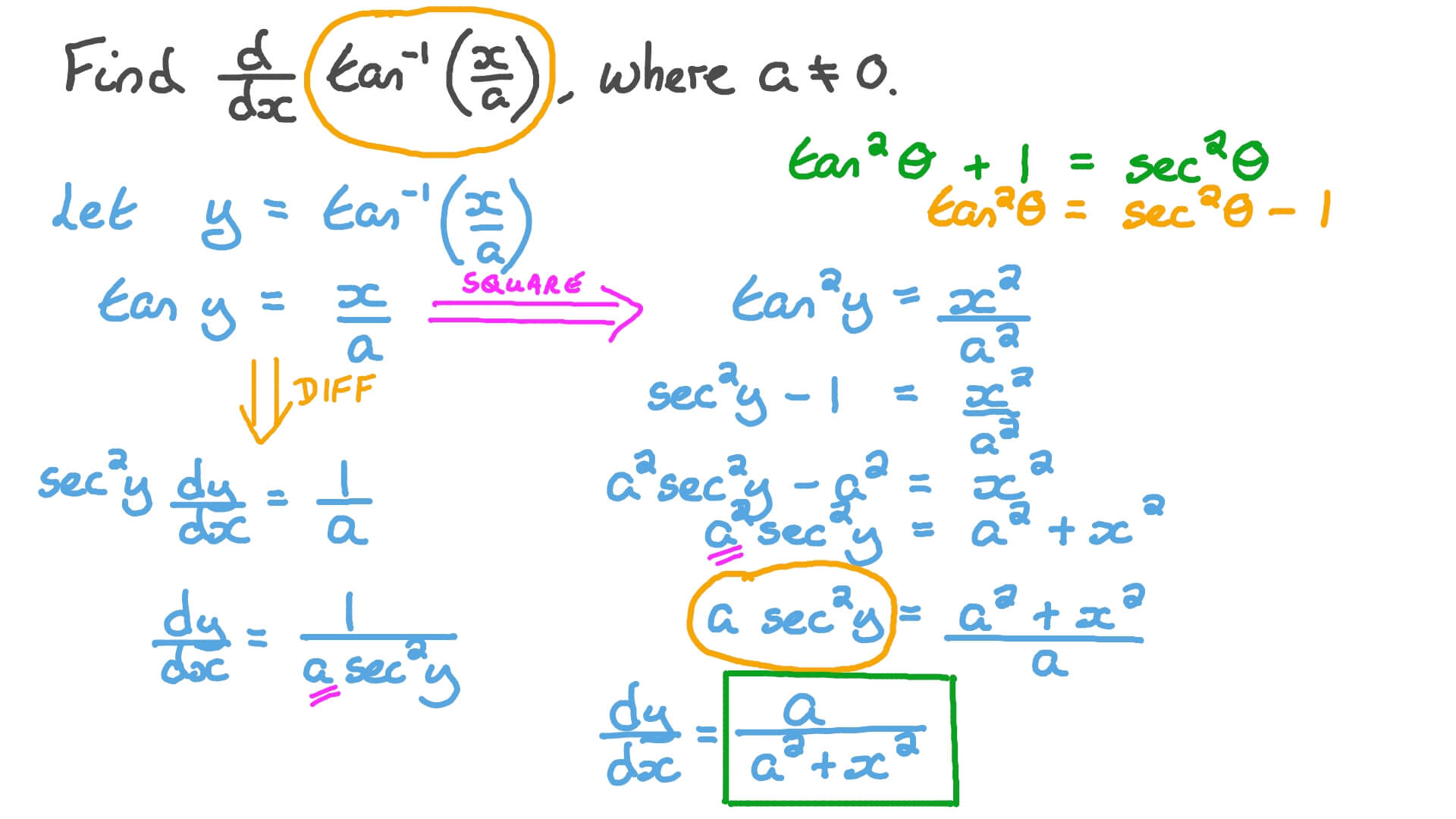
Question Video The Derivative of an Inverse Tangent Function Nagwa
1 Answer Jim H Aug 4, 2015 Use the derivative of tan−1 and the chain rule. Explanation: The derivative of tan−1x is 1 1 +x2 (for "why", see note below) So, applying the chain rule, we get: d dx (tan−1u) = 1 1 +u2 ⋅ du dx In this question u = 2x, so we get: d dx (tan−12x) = 1 1 +(2x)2 ⋅ d dx (2x) = 2 1 + 4x2 Note If y = tan−1x, then tany = x
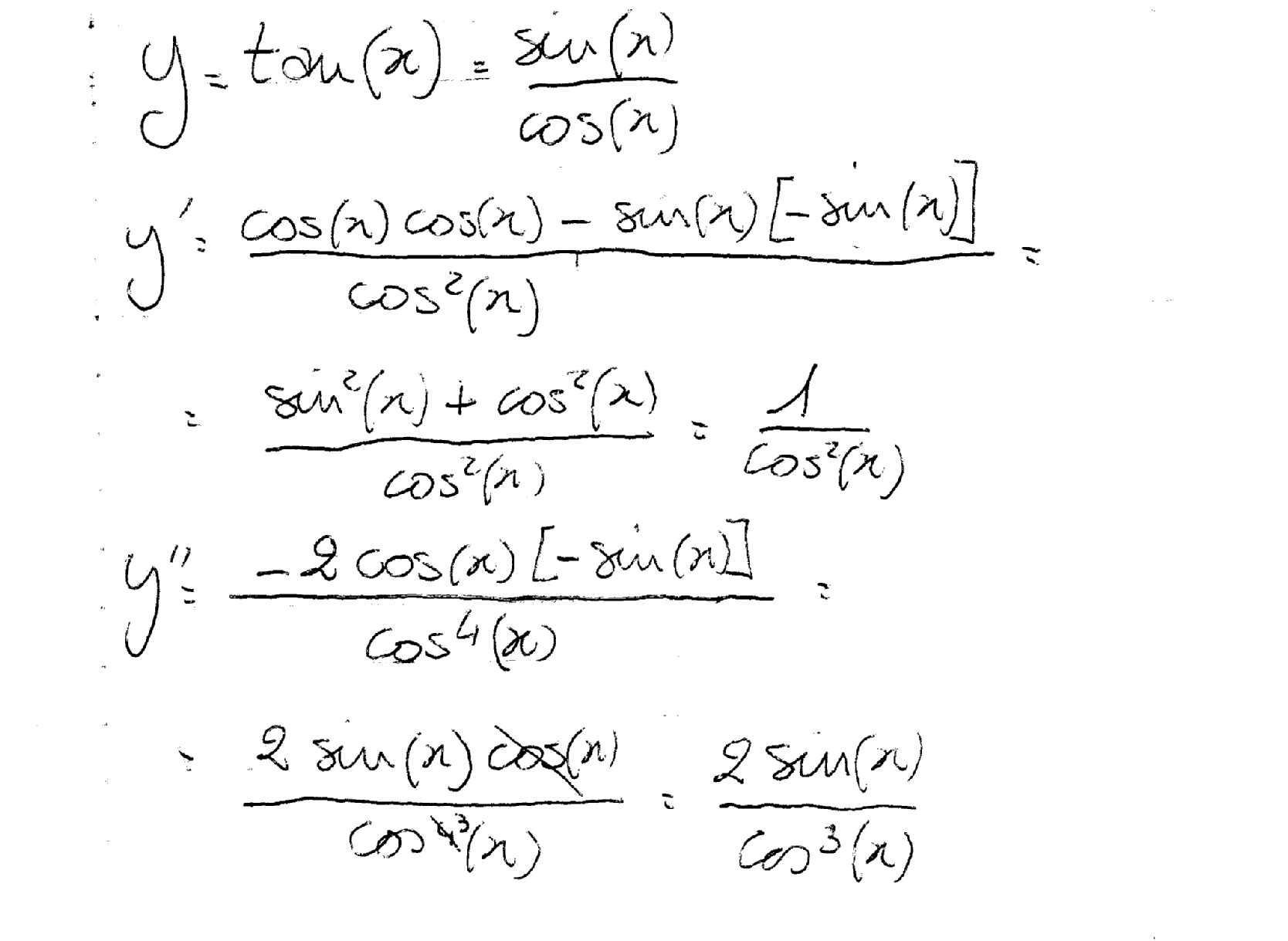
Derivative of Tangent Definition, equation, formula and more
1 Answer Truong-Son N. Jul 1, 2015 I seem to recall my professor forgetting how to deriving this. This is what I showed him: y = arctanx tany = x sec2y dy dx = 1 dy dx = 1 sec2y Since tany = x 1 and √12 +x2 = √1 +x2, sec2y = ( √1 + x2 1)2 = 1 + x2 ⇒ dy dx = 1 1 + x2 I think he originally intended to do this: dy dx = 1 sec2y sec2y = 1 + tan2y

Differentiation of tan^2(x) and (x^3+x)^4 YouTube
Explanation: u = tan−1( y x) This problem needs a slight prerequisite of chain rule, and quotient rule. du dx = 1 1 + (y x)2 y − xdy dx x2 = x2 y − xdy dx x2 + y2 Thus, d dx (tan−1( y x)) = x2 y − x dy dx x2 +y2 Answer link Ultrilliam Jul 6, 2018 It really depends upon what you are doing, and which independent variables matter to you.

Differentiation of inverse tan YouTube
Symbolab is the best derivative calculator, solving first derivatives, second derivatives, higher order derivatives, derivative at a point, partial derivatives, implicit derivatives, derivatives using definition, and more. Is velocity the first or second derivative? Velocity is the first derivative of the position function.

Q1 Differentiate tan^(1)(1/x) Differentiate Tan inverse 1 by x YouTube
Here is a list of the derivatives that you need to know: d (sin x) = cos x dx. d (cos x) = -sin x dx. d (sec x) = sec x tan x dx. d (cosec x) = -cosec x cot x dx. d (tan x) = sec²x dx. d (cot x) = -cosec²x dx. One condition upon these results is that x must be measured in radians. Applying the Chain Rule