
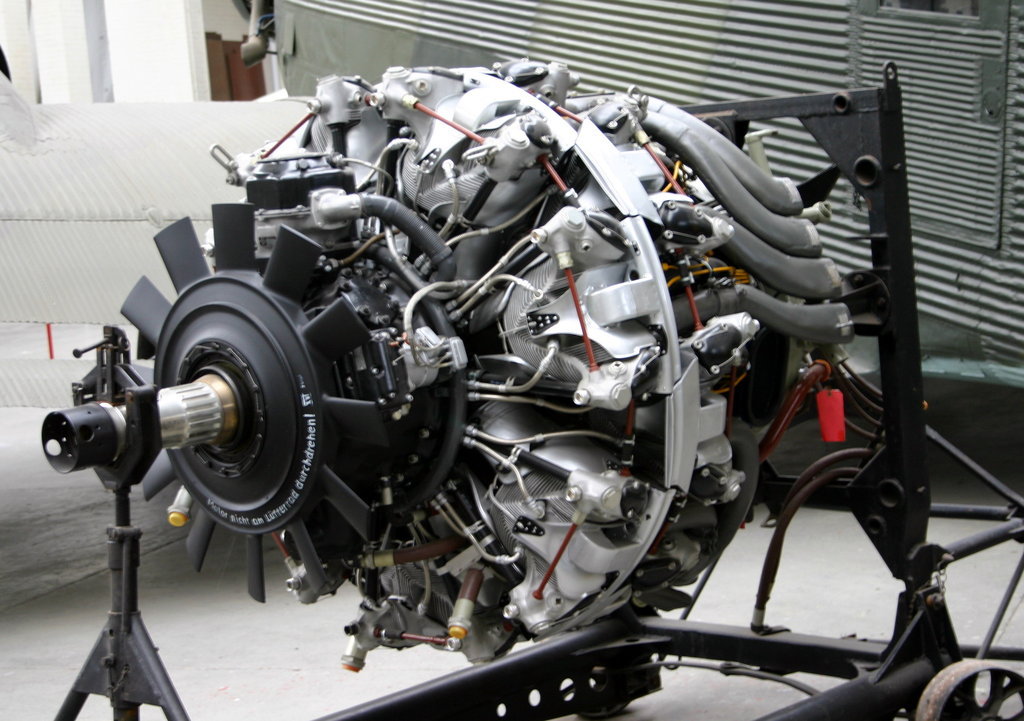
Museum of the History of Aircraft Engine Building. Aircraft Engines on Stands. Turbine Engines
The history of aviation extends for more than two thousand years, from the earliest forms of aviation such as kites and attempts at tower jumping to supersonic and hypersonic flight by powered, heavier-than-air jets . Kite flying in China dates back to several hundred years BC and slowly spread around the world.

Vought F4U Corsair Warplane Technical Specs, History and Pictures Aircrafts and Planes
(December 2010) Precursors Jet engines can be dated back to the invention of the aeolipile around 150 BC. This device used steam power directed through two nozzles so as to cause a sphere to spin rapidly on its axis. [1]
J79 Aircraft Jet Engine Side 1 of 1 The Portal to Texas History
Important landmarks and events along the way to the invention of the airplane include an understanding of the dynamic reaction of lifting surfaces (or wings), building absolutely reliable engines that produced sufficient power to propel an airframe, and solving the problem of flight control in three dimensions.
Bmw aircraft engines history
jet engine, any of a class of internal-combustion engines that propel aircraft by means of the rearward discharge of a jet of fluid, usually hot exhaust gases generated by burning fuel with air drawn in from the atmosphere.. General characteristics. The prime mover of virtually all jet engines is a gas turbine.Variously called the core, gas producer, gasifier, or gas generator, the gas turbine.
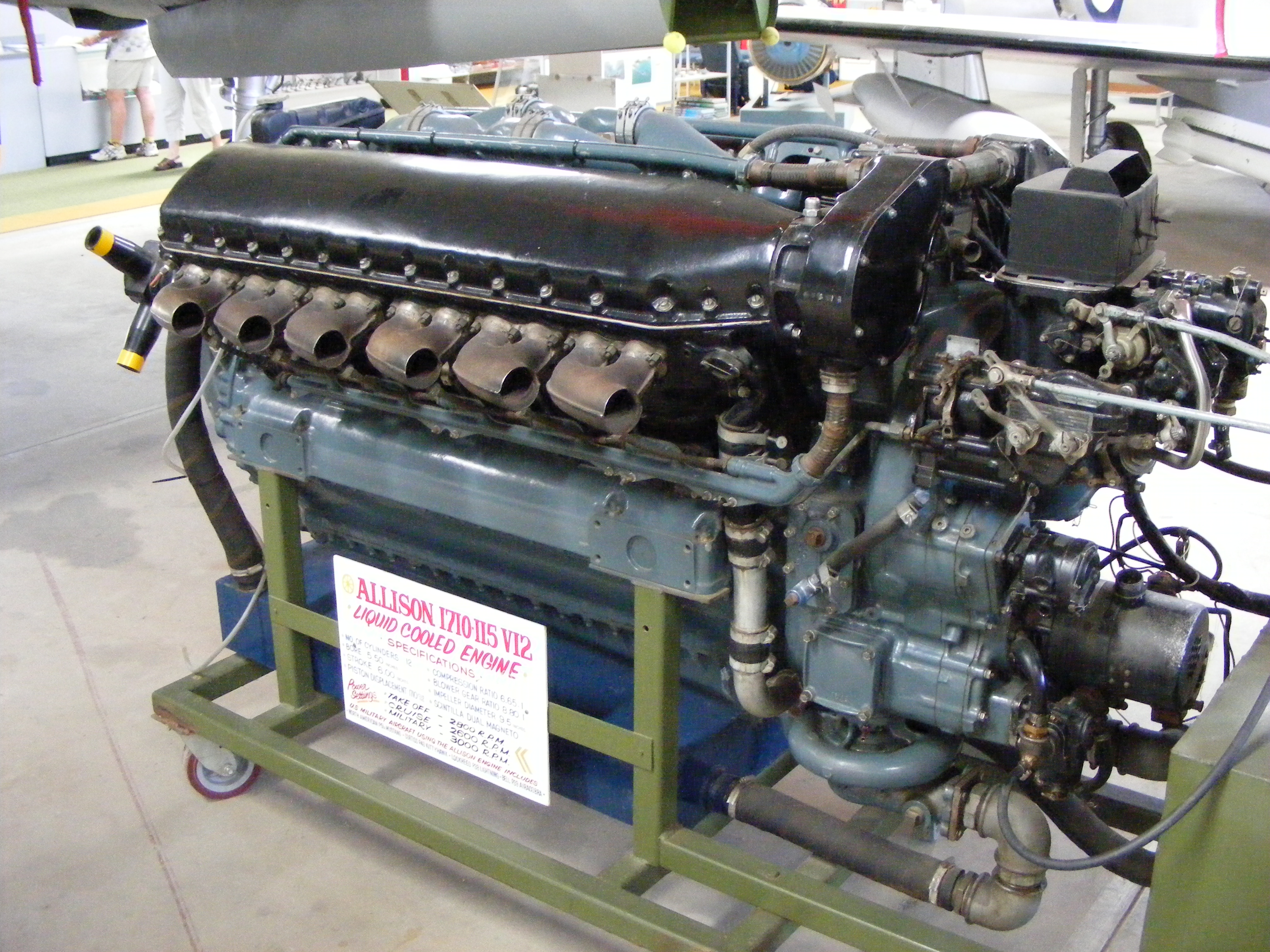

FileAllison 1710115 V12 Aircraft engine.jpg Wikipedia
When the United States entered World War I in 1917, the U.S. government searched for a company to develop the first airplane engine "booster" for the fledgling U.S. aviation industry. This booster, or turbosupercharger, installed on a piston engine, used the engine's exhaust gases to drive an air compressor to boost power at higher altitude.

A SHORT HISTORY OF EARLY ENGINES THE FIRST JET ENGINE Jetset Airmotive, Inc.
Due to the unreliability of early jet engine designs, in 1943 the U.S. Navy asked Ryan Aircraft to create a fighter aircraft that utilized both the traditional piston engine and a turbojet. The result was the Ryan XFR-1 Fireball—the Navy's first aircraft to include jet propulsion. A Wright R-1820 piston engine in the nose powered the.

Museum of the History of Aircraft Engine Building. Aircraft Engines on Stands. Turbine Engines
The long history of Rolls-Royce begins over 100 years ago - coincidentally, only months after the Wright Brothers' iconic 120 ft bound had launched mankind's forays into the skies.. Nevertheless, development of aircraft engines continued on a shoestring budget throughout the 1920s, inspired by great men whose names now adorn plaques in.

Museum Of The History Of Aircraft Engine Building. Aircraft Engines On Stands. Turbine Engines
The J-79 jet engine, exponentially more powerful than the radial engine, made for faster fighters that could carry bomb loads greater than World War II bombers. The F-4 was a multi-role aircraft.

Museum Of The History Of Aircraft Engine Building. Aircraft Engines On Stands. Turbine Engines
As early as 1808, Englishman Sir George Cayley designed and experimented with a calorific engine which burned gunpowder as the fuel (Berliner, pp. 12-15). The gaseous products of combustion drove a piston within a cylinder that converted the reciprocating piston's motion to mechanical work, possibly rowing Cayley's "aerial oar".

Aircraft Engines History Engineering Channel
A cutaway drawing of the 1903 Wright Flyer engine. The earliest aero engines were stationary—either radial in style or in line. The Antoinette series was the most commonly used. These were succeeded by the popular rotary engine.
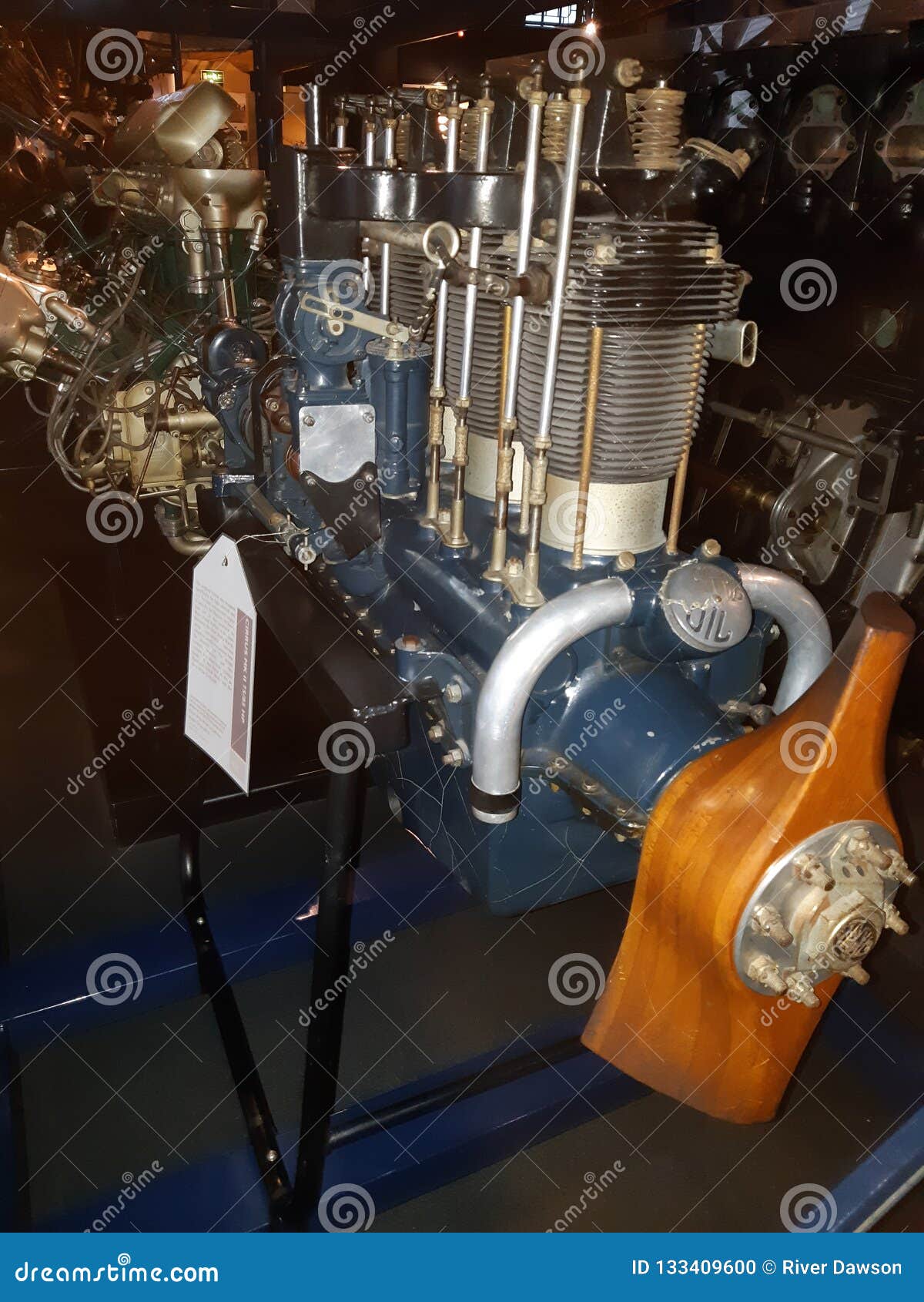
History of Flight Aircraft Engines Editorial Image Image of museum, engines 133409600
geaviation.com The General Electric GE90 is a series of high-bypass turbofan aircraft engines built by GE Aviation for the Boeing 777, with thrust ratings ranging from 74,000 to 115,000 lbf (330 to 510 kN). According to the Guinness Book of Records, the engine holds the record for the highest thrust at 127,900 lbf (569 kN).

Museum of the History of Aircraft Engine Building. Aircraft Engines on Stands. Turbine Engines
The X-planes were operated by the NACA and later by NASA in conjunction with the U.S. Air Force. The Bell X-1 rocket-powered experimental aircraft was the first piloted aircraft to fly faster than Mach 1 in level flight. With the introduction of the turbojet engine, new aircraft were designed to fly faster and higher.

Museum of the History of Aircraft Engine Building. Aircraft Engines on Stands. Turbine Engines
The Ernst Heinkel Aircraft Company adapted their ideas and flew the second aircraft engine of this development in an HE-178 aircraft on Aug. 27, 1939 in what would be the first true jet-propelled.

Museum Of The History Of Aircraft Engine Building. Aircraft Engines On Stands. Turbine Engines
The 100th Anniversary of flight has us looking back at some evolutionary and revolutionary aircraft engines.
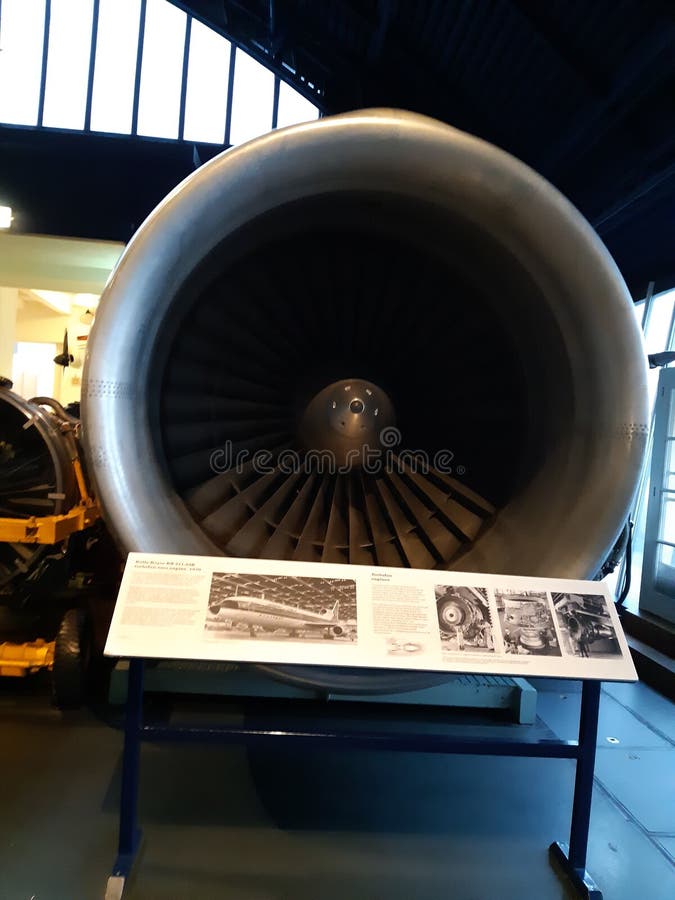

History of Flight Aircraft Engines Editorial Image Image of london, science 133409605
The first was the adoption of the turbofan engine. The turbofan gains economy by having much of its thrust pass around the engine core rather than through it. The second stage was marked by the introduction of the wide-bodied, 400-seat Boeing 747 in 1969. This large, swift, and long-ranged aircraft created a transportation revolution.

Pin by Robert Chase on Wright engines Pratt & Whitney Aircraft engine, Radial engine, Aircraft
An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Aircraft using power components are referred to as powered flight . [1] Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines , although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years many small UAVs have used electric.