
Using Stoichiometry in Conversions Scientific Tutor
Multiply wt% ELEMENT by numerical value below for equivalent expressed as OXIDE. Element. Oxide. Factor. Silver. Ag 2 O. 1.0741. Aluminium.

The Stoichiometric Chart YouTube
Stoichiometry is simply the math behind chemistry. Given enough information, one can use stoichiometry to calculate masses, moles, and percents within a chemical equation.. Once we know the moles of solute we can look at the periodic table and figure out the conversion from moles to grams. Molality = moles solute kg solvent: Now we simply.
Stoichiometry CHEMISTRY HELP
Stoichiometry. We shall set up Stoichiometric Tables using A as our basis of calculation in the following reaction. We will use the stoichiometric tables to express the concentration as a function of conversion. We will combine C i = f(X) with the appropriate rate law to obtain -r A = f(X). Topics. Batch System Stoichiometric Table
J² + H = Element 119 Kariodisonium Stoichiometry Calculations
Apply a stoichiometric conversion factor to convert between the molar quantities of two substances that participate in a chemical reaction.. Recall that, when using a calculator, each conversion factor should be entered in parentheses, or the "=" key should be used after each division. In this case, 7.53 × (1 mol O 2 ÷ 2).

Pin on Chemistry woes
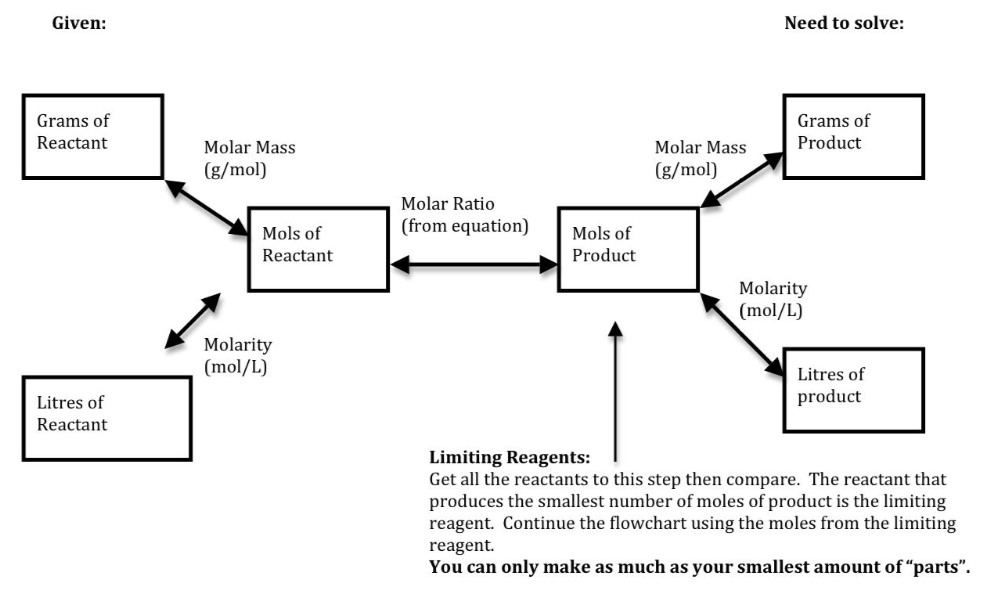
Stoichiometry Flowchart & Chemical Conversions According to Wikipedia stoichiometry is the calculation of quantitative (measurable) relationships of the reactants and products in chemical reactions. For example, if I start with 10 gallons of gasoline, how many liters of oxygen gas would be required to burn the 10 gallons of gasoline?

Stoichiometry Flow Chart YouTube
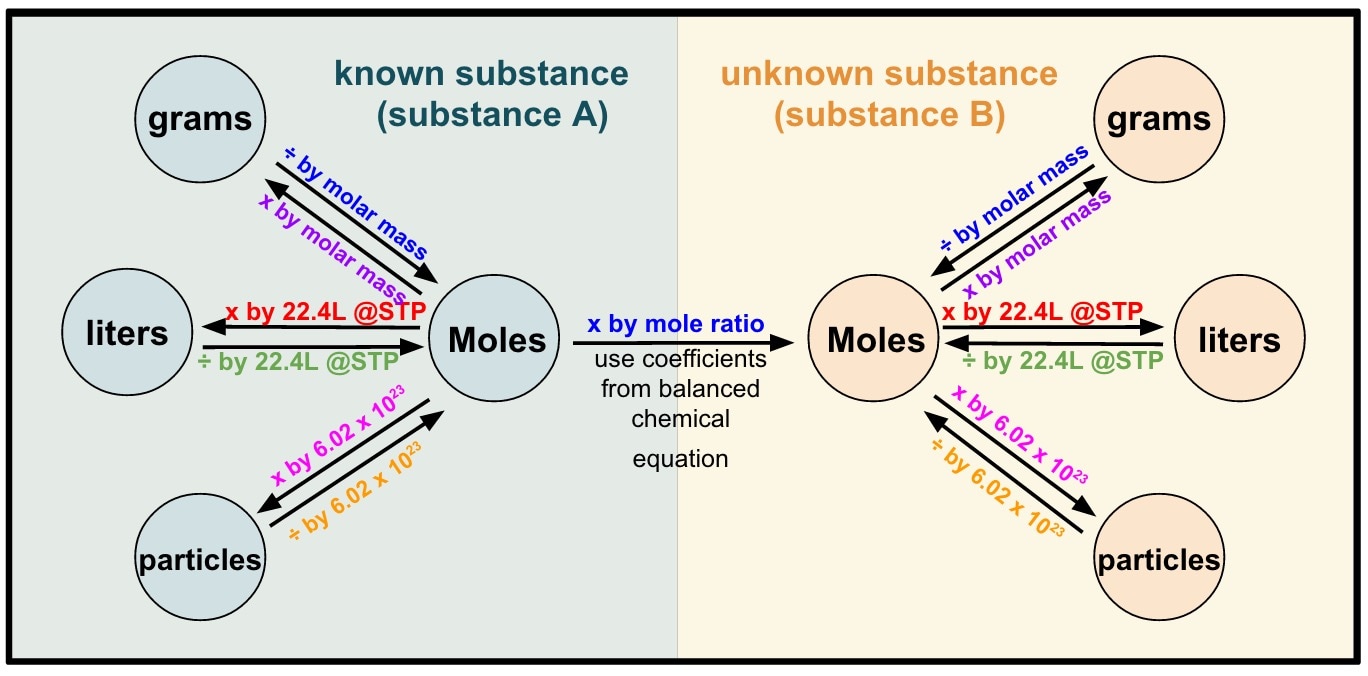
These quantitative relationships are known as the reaction's stoichiometry, a term derived from the Greek words stoicheion (meaning "element") and. This will simply require use of the moles-to-numbers conversion factor, Avogadro's number. The balanced equation shows that carbon dioxide is produced from propane in a 3:1 ratio:.
Stoichiometry Review Mr. Siemianowski Eisenhower High School
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): A Flowchart for Stoichiometric Calculations Involving Pure Substances. The molar masses of the reactants and the products are used as conversion factors so that you can calculate the mass of product from the mass of reactant and vice versa. Flowchart of steps in stoichiometric calculations.
stoichiometry flowchart introduction YouTube
Stoichiometry Tutorials: Dimensional Analysis / Stoichiometric Conversions (from a complete OLI stoichiometry course) Dimensional analysis allows us to change the units used to express a value. For instance, it allows us to convert between volume expressed in liters and volume expressed in gallons.

Extended Reaction Stoichiometry Road Map — Examples Expii
Stoichiometry is the field of chemistry that is concerned with the relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions. For any balanced chemical reaction, whole numbers (coefficients) are used to show the quantities (generally in moles ) of both the reactants and products. For example, when oxygen and hydrogen react to produce.

Ms J's Chemistry Class 10/01/2017 11/01/2017
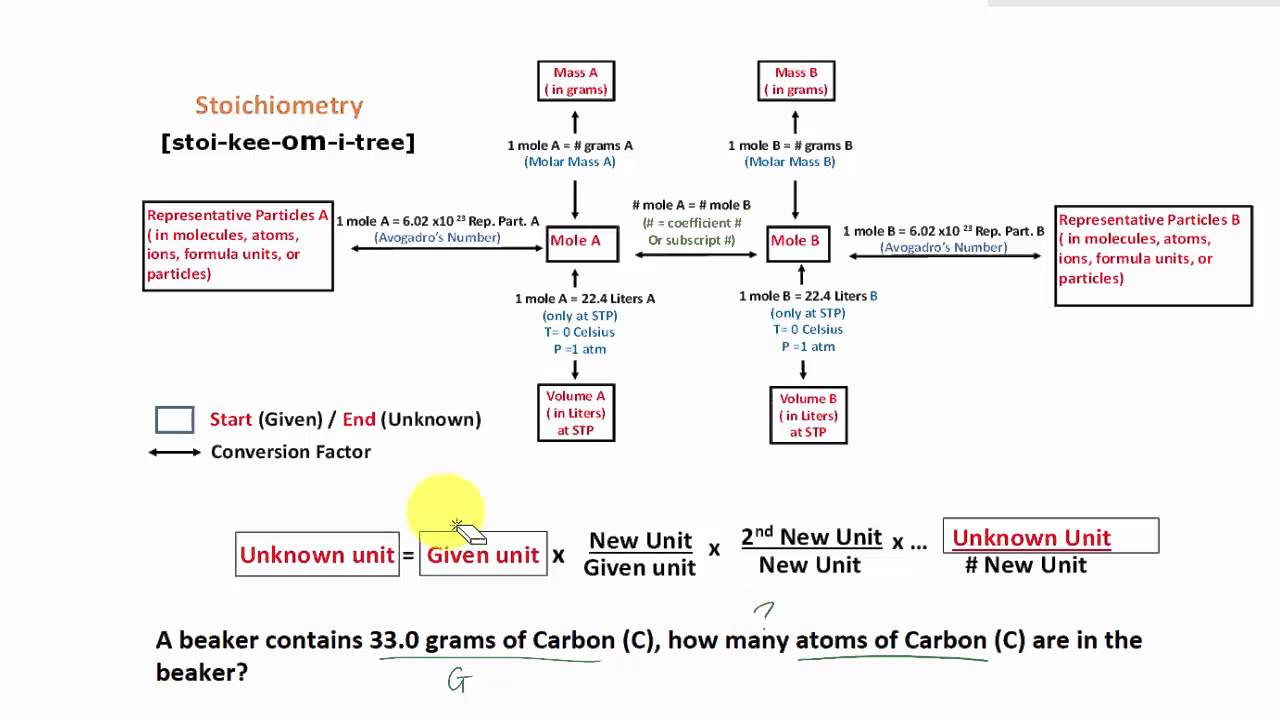
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry Conversions Conversions Procedure Step 1: Determine where you are starting and finishing Step 2: Start calculation by writing down what you know Step 3: Use dimensional analysis Set up problem so you can cancel out units Tools Available Avogadro's Constant 6.022×10 6 7 - 𝑜 Periodic Table (M)
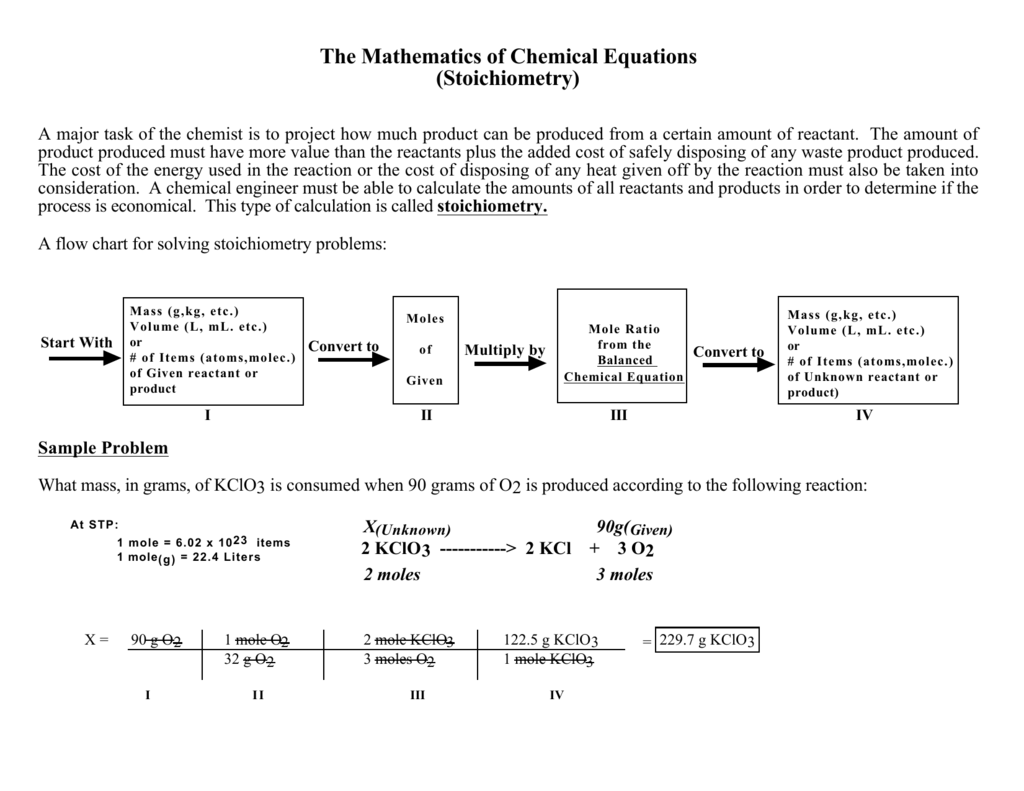
Stoichiometry Flow Chart
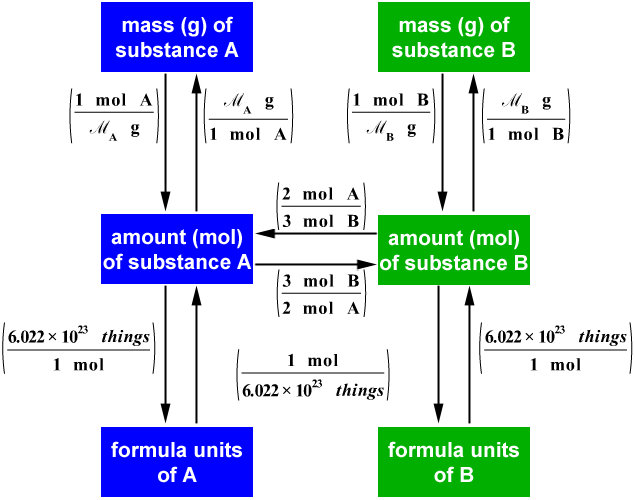
1 mol Fe 2 O 3: 2 mol Al Using this ratio, we could calculate how many moles of Al are needed to fully react with a certain amount of Fe 2 O 3 , or vice versa. In general, mole ratios can be used to convert between amounts of any two substances involved in a chemical reaction.

Stoichiometry Conversions Chart chegos.pl
The balanced equation must now be used to convert moles of Fe (s) to moles of H 2 (g). Remember that the balanced equation's coefficients state the stoichiometric factor or mole ratio of reactants and products. 3.74 x 10 -5 mol Fe (s) ( 1mol H 2 (g)/ 1mol Fe (s)) = 3.74 x 10 -5 mol H 2 (g) Step 5: Check units.
.PNG)
Stoichiometry, Gas Stoichiometry Presentation Chemistry
Updated December 21, 2023. The Stoichiometric Conversion Calculator is a valuable tool used in chemistry to determine the percentage of the desired product formed in a chemical reaction. It aids in understanding the efficiency of a reaction by calculating the conversion percentage based on actual and theoretical stoichiometric values.
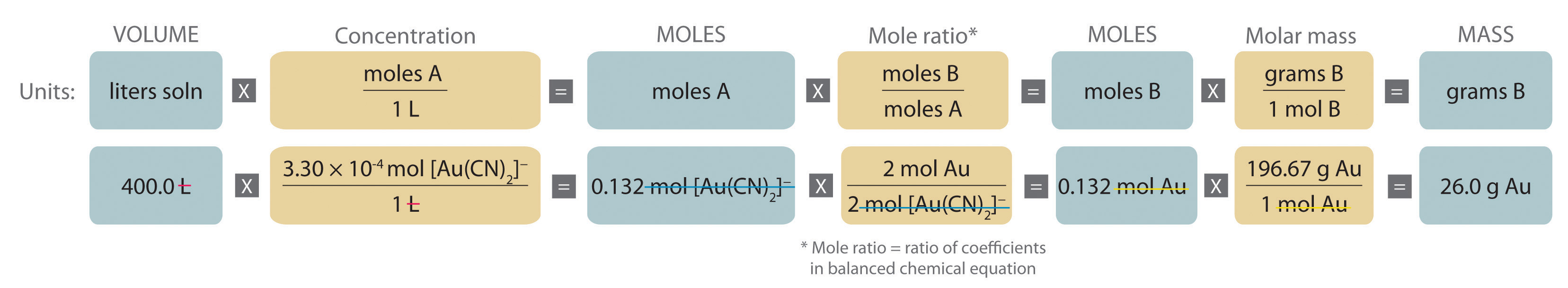
Stoichiometry of Reactions in Solution
3Ag(s) + Al(NO 3) 3(aq) → 3AgNO 3 + Al(s) Solution. Here, we first must convert the mass of Ag to moles before using the balanced chemical equation and then the definition of molarity as a conversion factor: 3.66 gAg × 1 molAg 107.97 gAg × 1 molAl(NO3)3 3 molAg ×1Lsolution0.0995. The strikeouts show how the units cancel.
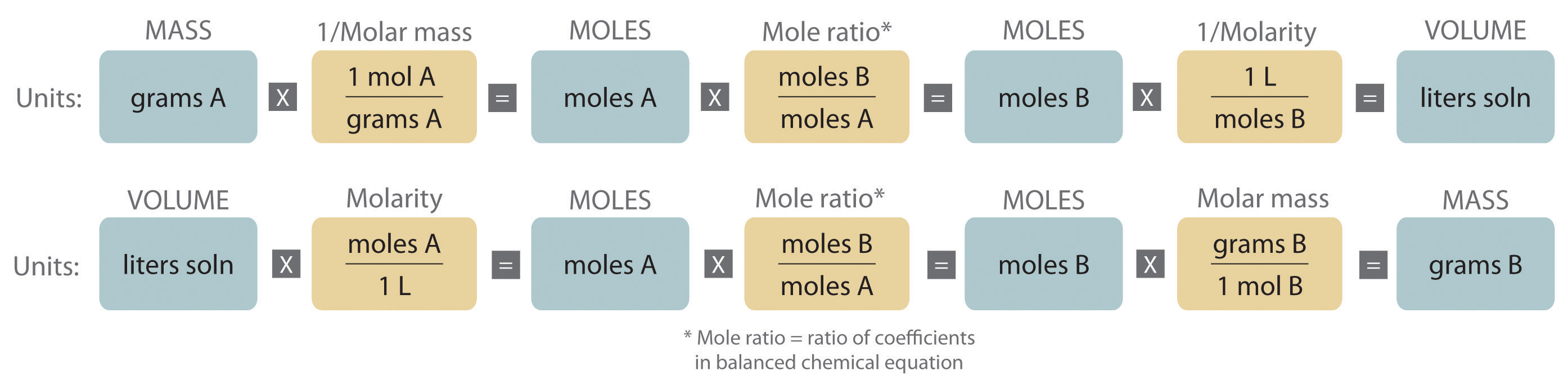
Stoichiometry of Reactions in Solution
This stoichiometry calculator lets you calculate the relative amounts of reactants and products involved in a chemical reaction.

Stoichiometry Chemistry Activities
To perform a stoichiometric calculation, enter an equation of a chemical reaction and press the Start button. The reactants and products, along with their coefficients will appear above. Enter any known value. The remaining values will automatically be calculated.