
Radiology Schools, Radiology Student, Radiology Technician, Radiology
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. The hand series consists of posteroanterior, oblique, and lateral projections. Although additional radiographs can be taken for specific indications. The series primarily examines the radiocarpal and distal radioulnar joints, the carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges.

Normal Hand X Ray Colorvir Xray photo of normal right hand Stock
Review the wrist. A hand radiograph contains a PA and oblique view of the distal radius and ulna and the carpus. check the wrist as you would for a wrist radiograph ( an approach) distal radius. carpal alignment. carpometacarpal articulation. bone cortex.

Hand Radiographic Anatomy wikiRadiography Radiology student
X-ray cervical spine: lateral. X-ray cervical spine: AP. X-ray cervical spine: open-mouth peg. X-ray thoracic spine: frontal and lateral. X-ray lumbar spine: oblique. X-ray sacrum: frontal. CT cervical spine: bone window axial. CT cervical spine: bone window sagittal. CT cervical spine: bone window coronal.

Paediatric Hand Radiology student, Pediatrics, Medical knowledge
A hand X-ray (radiograph) is a test that creates a picture of the inside of your hand. The picture shows the inner structure ( anatomy) of your hand in black and white. Calcium in your bones absorbs more radiation, so your bones appear white on the X-ray. Soft tissues, such as muscle, fat and organs, absorb less radiation, so they appear.

Wrist Radiographic Anatomy wikiRadiography Medical radiography
Description. Hand X-Ray Anatomy and Interpretation Checklist 1. Soft tissues - Look carefully at the soft tissue over all the bones for any swelling or foreign body. The swelling should prompt a careful search of the underlying bone or joint.⠀ 2. Bones - All the bones of the hand should be examined carefully and systematically.

Xray Hand
Shaft of third metacarpal. Neck of fifth metacarpal. Head of forth metacarpal. Metacarpophalangeal joint. Proximal phalanx. Middle phalanx. Distal phalanx. Sesamoid bones (flexor pollicis brevis, adductor pollicis). Terminal tuft.
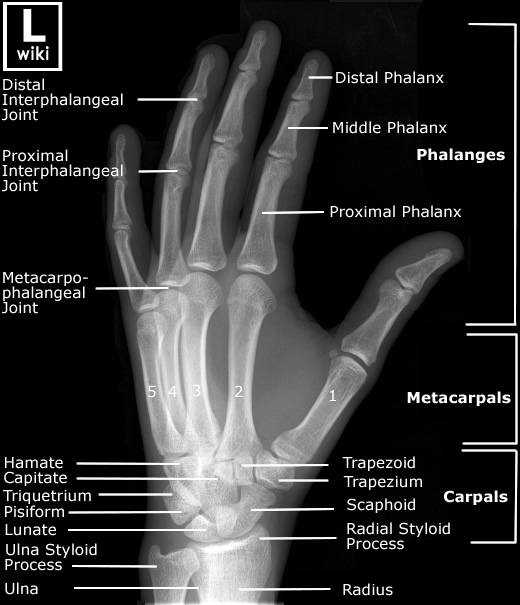
Hand Radiographic Anatomy wikiRadiography
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like metacarpophalangeal joint, Hamate, Capitate and more.

Medical Education on (With images) Radiology student, Radiology
Download scientific diagram | Skeletal anatomy [4] and an X-ray image of a hand [5]. from publication: Applying Deep Learning in Medical Images: The Case of Bone Age Estimation | Objectives A.

Read on to find out more about my review areas on a hand XRay
Access my FREE Online Membership today → https://www.thenotedanatomist.com___Unlock my Premium Tutoring Memberships → https://www.thenotedanatomist.com/premi.

Read on to find out more about my review areas on a hand XRay
A physician may perform a hand x-ray, MRI or ultrasound to rule out, assess, evaluate and diagnose the problem. A hand x-ray is often used to determine type of injury, extent of injury, and helps to determine treatment of the injury. Hand x-rays can detect broken bones and arthritis of the hand.

Sports medicine stats Metacarpal fractures and other fractures of the
The radiocarpal joint has a 4-15° volar tilt and the hand is usually held in slight flexion and ulnar deviation. The radial styloid is distal to the ulnar styloid. Radial inclination to the ulna is assessed on the PA view and should be 20-25°. Figure 2.1 (a) Normal AP view with line drawing; (b) normal AP view; (c) AP view of right wrist.

Pin by Blake on Random things Radiology student, Radiology schools
Skeletal age assessment (SAA) is a clinical procedure which is used in determining the SA of children and adolescents. Bone development is influenced by a number of factors, including nutrition, hormonal secretions, and genetics. There are several factors to be borne in mind when using methods of assessing skeletal maturity.
HAND X RAY PA HAND RadTechOnDuty
Fundamentals of the Wrist and Hand: wrist complex: 20°extension and 10°ulnar deviation MCP joint: 45°flexion PIP joint: 30°flexion DIP joint: slight flexion In a rested position, the palm of the hand is concave. The thumb is located 90°to the fingers and is of particular importance to the dexterity of the hand. Functional position of the wrist and hand has been determined to be:

[Figure, Wrist xray with labeled osseous anatomy] StatPearls NCBI
extends from the radiocarpal joint to the tips of fingers. similar series. wrist series. distal radius and ulna, carpals and proximal metacarpals. scaphoid series. wrist series plus two additional scaphoid views. thumb series. just for looking at the thumb. both hands.

Xray Of Hand Bones
Indications. The oblique hand view is requested for diagnosing a variety of clinical indications such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, suspected fracture or dislocation and localizing foreign bodies. It is also particularly useful in providing more information regarding the degree and location of any suspected fracture or dislocation.

Hand Radiographic Anatomy wikiRadiography Diagnostic imaging
License Image The following bones are visible in this hand x ray: distal phalanges middle phalanges proximal phalanges metacarpal bones carpal bones radius ulna sesamoid bone The carpal bones are: trapezium trapezoid capitate hamate scaphoid lunate triquetral pisiform See Also:Hand BonesHand Bones